Bupleurum scorzonerifolium
Bupleurum scorzonerifolium
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Bupleurum scorzonerifolium
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
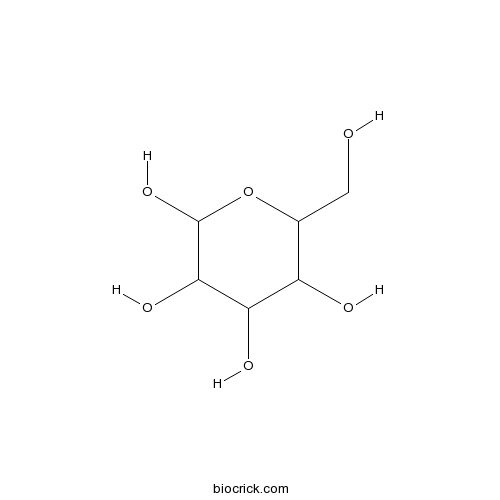
BCC8311
D-(+)-Mannose3458-28-4
Instructions
-
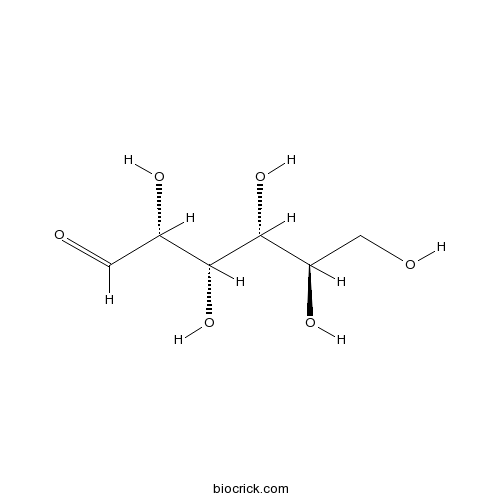
BCN1259
D-(+)-Glucose50-99-7
Instructions
-
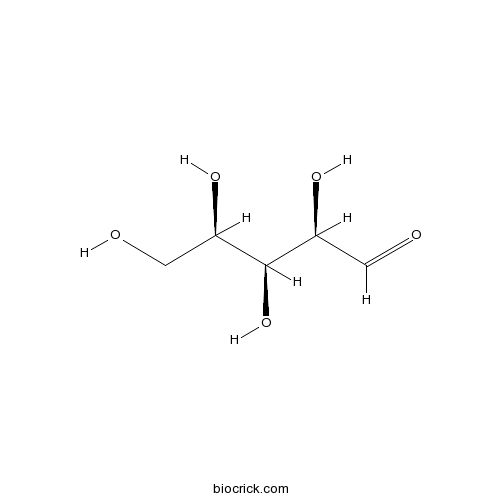
BCN1010
D-(+)-Xylose58-86-6
Instructions
-
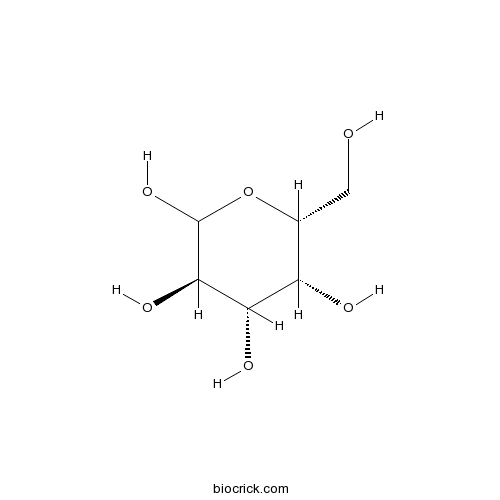
BCN8528
D-Galactose59-23-4
Instructions
Constituents of Essential Oil and Lipid Fraction from the Aerial Part of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. (Apiaceae) from Different Habitats.[Pubmed: 29925820]
None
Comparison of root transcriptomes and expressions of genes involved in main medicinal secondary metabolites from Bupleurum chinense and Bupleurum scorzonerifolium, the two Chinese official Radix bupleuri source species.[Pubmed: 25117935]
Radix bupleuri, roots of Bupleurum species, is a widely used traditional Chinese medicine. Here, we compared the root transcriptomes of both Bupleurum chinense DC. and Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. A total of 313 483 and 342 263 high quality expressed sequence tags were obtained, respectively. In addition, 17 117 (59.2%) and 19 416 (62.8%) unigenes for B. chinense and B. scorzonerifolium had homologous genes in the opposite dataset. For B. chinense, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes database (KEGG) annotation identified carbohydrate metabolism, energy metabolism and amino acid metabolism as the three highest groups in the metabolism category. For B. scorzonerifolium, the lipid metabolism group had the most unigenes. Genes that may participate in the biosynthesis of terpenoid, triterpenoid, sterol, lignan and flavonoids were identified according to their annotations. (Tri)terpenoid-related genes were predominantly found in B. chinense. The expressions of certain genes were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) in the roots of the two species. A total of 558 putative transcription factors (TFs) and 137 transcriptional regulators (TRs) among 1364 TFs and 327 TRs, and 610 TFs and 129 TRs among 1600 TFs and 323 TRs were specific for B. chinense and B. scorzonerifolium, respectively. Our transcriptome comparison reflects the different types and proportions of metabolites synthesized by the two species. The data, especially, those genes involved in the biosynthesis of particular types of metabolites, will provide the basis for further investigations of the secondary metabolite repertoire of the two Bupleurum species, as well as other species from the genus of Bupleurum.
Cell type-specific qualitative and quantitative analysis of saikosaponins in three Bupleurum species using laser microdissection and liquid chromatography-quadrupole/time of flight-mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 24863374]
Cell type-specific metabolite analysis is a promising method for understanding plant metabolite production, function, transport and storage. In the present study, laser microdissection (LMD) and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole/time of flight-mass spectrometry are combined to determine where secondary metabolites are accumulated in the roots of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd, Bupleurum chinense DC. and Bupleurum falcatum L. Four tissues, namely cork, cortex, phloem and xylem, were microdissected by laser microdissection, and their chemical profiles were analyzed. The main metabolites are saikosaponins. Different tissues contained different saikosaponins. Generally, the cork and cortex from all three species contained more types of saikosaponins and higher contents of saikosaponins a, c and d than did the phloem and xylem. Interestingly, in the roots of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium and B. falcatum, the cork contained much higher contents of saikosaponins a, c and d than did the cortex; while in the root of B. chinense, the cortex contained higher contents of saikosaponins a, c and d than the cork. Explanation and application of the results are discussed. The present findings yield valuable insights into the quality evaluation of Bupleuri Radix by morphological features.
Immunocytochemical localization of saikosaponin-d in vegetative organs of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd.[Pubmed: 28510868]
Saikosaponin-d (SSd) is an important active component of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd., a traditional Chinese medicinal herb. Thus far, the biosynthetic pathway and biosynthetic site of saikosaponins in Bupleurum are largely unknown. The cellular localization of SSd will help in understanding saikosaponin biosynthesis and regulation.


