Artemisia sphaerocephala
Artemisia sphaerocephala
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Artemisia sphaerocephala
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5560
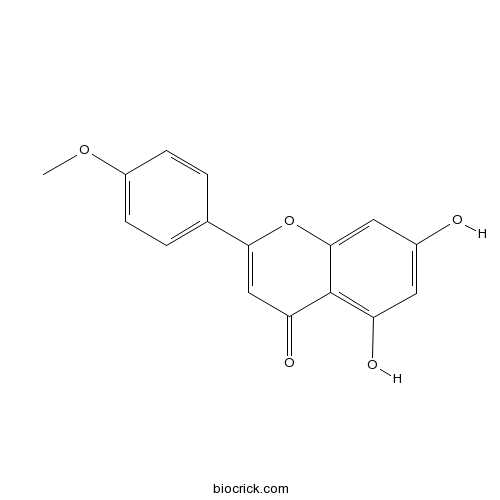
Acacetin480-44-4
Instructions
-
BCN5657
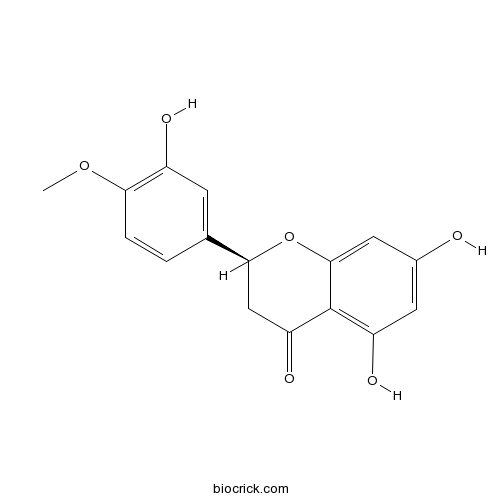
Hesperetin520-33-2
Instructions
Selection and validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in Artemisia sphaerocephala based on transcriptome sequence data.[Pubmed: 29505835]
Artemisia sphaerocephala, a dicotyledonous perennial semi-shrub belonging to the Artemisia genus of the Compositae family, is widely distributed in northwestern China. This shrub is one of the most important pioneer plants which is capable of protecting rangelands from wind erosion. It therefore plays a vital role in maintaining desert ecosystem stability. In addition, to its use as a forage grass, it has excellent prospective applications as a source of plant oil and as a plant-based fuel. The use of internal genes is the basis for accurately assessing Real time quantitative PCR. In this study, based on transcriptome data of A. sphaerocephala, we analyzed 21 candidate internal genes to determine the optimal internal genes in this shrub. The stabilities of candidate genes were evaluated in 16 samples of A. sphaerocephala. Finally, UBC9 and TIP41-like were determined as the optimal reference genes in A. sphaerocephala by Delta Ct and three various programs. There were GeNorm, NormFinder and BestKeeper.
Synthesis and structural features of phosphorylated Artemisia sphaerocephala polysaccharide.[Pubmed: 29253962]
None
Sulfation can enhance antitumor activities of Artemisia sphaerocephala polysaccharide in vitro and vivo.[Pubmed: 28893683]
None
Chemical characterization of a novel polysaccharide ASKP-1 from Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch seed and its macrophage activation via MAPK, PI3k/Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways in RAW264.7 cells.[Pubmed: 28251195]
None
Microwave-assisted synthesis, structure and anti-tumor activity of selenized Artemisia sphaerocephala polysaccharide.[Pubmed: 27810352]
None
Synthesis of selenium-containing Artemisia sphaerocephala polysaccharides: Solution conformation and anti-tumor activities in vitro.[Pubmed: 27516251]
It has been reported in our previous work that selenized Artemisia sphaerocephala polysaccharides (SeASPs) with the Se content range of 168-1703μg/g were synthesized by using Na2SeO3/HNO3/BaCl2 system. In the present work, the solution property of SeASP was studied by using size exclusion chromatography combined with multi angle laser light scattering (SEC-MALLS). A decrease in df values indicated that SeASPs with different conformational features that were highly dependent on MW. SeASPs exhibited a more rigid conformation (df value of 1.29-1.52) in low molecular weight range (MW of 1.026-1.426×10(4)g/mol) and compact spherical conformation in high molecular weight range (MW of 2.268-4.363×10(4)g/mol). It could be due to the degradation of polysaccharide chains in HNO3, which was supported in monosaccharide composition analysis. Congo red (CR) spectrophotometric method and atomic force microscopy (AFM) results also confirmed the conformational transition and the evidence on the shape of the rigid chains. In vitro anti-tumor assays, SeASP2 displayed greater anti-proliferative effects against three tumor cell lines (hepatocellular carcinoma HepG-2 cells, lung adenocarcinom A549 cells and cervical squamous carcinoma Hela cells) in a dose-dependent manner. This suggested that selenylation could significantly enhance the anti-tumor activities of polysaccharide derivatives in vitro.
Optimization for ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides with chemical composition and antioxidant activity from the Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch seeds.[Pubmed: 27316764]
Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch seeds polysaccharides have been reported to have a variety of important biological activities. However, effective extraction of Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch seeds polysaccharides is still an unsolved issue. In this study, the orthogonal rotatable central composite design was employed to optimize ultrasound-assisted extraction conditions of Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch seeds polysaccharides. Based on a single-factor analysis method, ultrasonic power, extraction time, solid-liquid ratio and extraction temperature were shown to significantly affect the yield of polysaccharides extracted from the A. sphaerocephala Krasch seeds. The optimal conditions for extraction of Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch seeds polysaccharides were determined as following: ultrasonic power 243W, extraction time 125min, solid-liquid ratio 64:1 and extraction temperature 64°C, where the experimental yield was 14.78%, which was well matched with the predicted value of 14.81%. Furthermore, ASKP was identified as a typical heteropolysaccharide with d-galacturonic acid (38.8%) d-galactose (20.2%) and d-xylose (15.5%) being the main constitutive monosaccharides. Moreover, Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch seeds polysaccharides exhibited high total reducing power and considerable scavenging activities on DPPH, hydroxyl and superoxide radicals, in a concentration-dependent manner in vitro.
[Difference of anti-fracture mechanical characteristics between lateral-root branches and adjacent upper straight roots of four plant species in vigorous growth period].[Pubmed: 27228590]
Taking four plant species, Caragana korshinskii, Salix psammophila, Hippophae rhamnides and Artemisia sphaerocephala, which were 3-4 years old and in vigorous growth period, as test materials, the anti-fracture forces of lateral-root branches and adjacent upper straight roots were measured with the self-made fixture and the instrument of TY 8000. The lateral-root branches were vital and the diameters were 1-4 mm. The results showed that the anti-fracture force and anti-fracture strength of lateral-root branches were lesser than those of the adjacent upper straight roots even though the average diameter of lateral-root branches was greater. The ratios of anti-fracture strength of lateral-root branches to the adjacent upper straight roots were 71.5% for C. korshinskii, 62.9% for S. psammophila, 45.4% for H. rhamnides and 35.4% for A. sphaerocephala. For the four plants, the anti-fracture force positively correlated with the diameter in a power function, while the anti-fracture strength negatively correlated with diameter in a power function. The anti-fracture strengths of lateral-root branches and adjacent upper straight roots for the four species followed the sequence of C. korshinskii (33.66 and 47.06 MPa) > S. psammophila (17.31 and 27.54 MPa) > H. rhamnides (3.97 and 8.75 MPa) > A. sphaerphala (2.18 and 6.15 MPa).


