Aquilegia oxysepala
Aquilegia oxysepala
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Aquilegia oxysepala
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
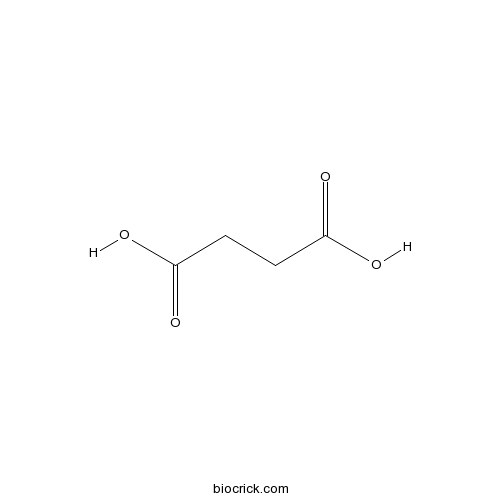
BCN5890
Succinic acid110-15-6
Instructions
-
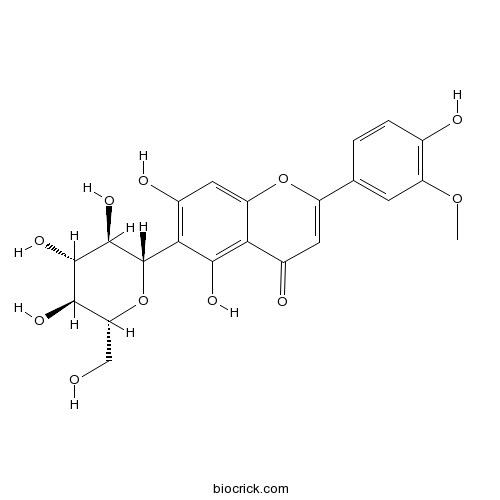
BCN7845
Isoscoparin20013-23-4
Instructions
-
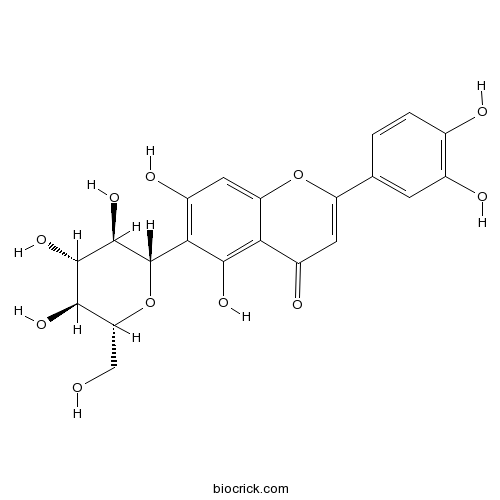
BCN4985
Luteolin-6-C-glucoside4261-42-1
Instructions
-
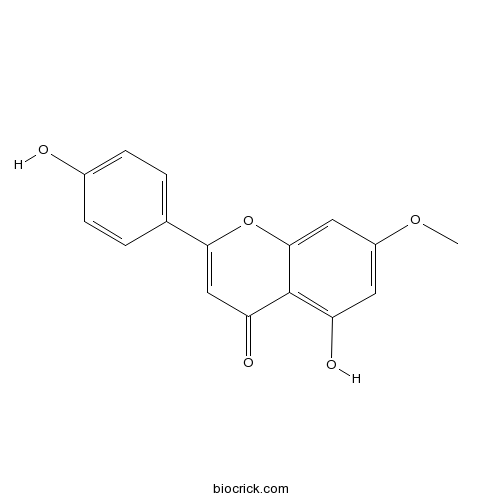
BCN5488
Genkwanin437-64-9
Instructions
Validate antibacterial mode and find main bioactive components of traditional Chinese medicine Aquilegia oxysepala.[Pubmed: 17276058]
Traditional Chinese medicines have been used for thousands of years and are still being used as one of the regular treatments for many diseases. However, their mechanisms were still unknown. In this investigation, a possible procedure combining metabonomics and principal component analysis to investigate antibacterial modes of action and find main antimicrobial component in traditional Chinese medicine, Aquilegia oxysepala, is developed. Metabolic profiles of Staphylococcus aureus treated with nine antibiotics of known modes of action and with A. oxysepala were acquired by HPLC/DAD/ESI-MS. After statistical processing by principal components analysis on metabolic profiles, two conclusions could be drawn: (1) the target of A. oxysepala may be similar to that of lincolmensin, erythromycin, chloromycetin, streptomycin, and acheomycin, whose targets are protein; (2) its bioactive component playing main antimicrobial roles on S. aureus may be maguoflorine.


