Adina rubella
Adina rubella
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Adina rubella
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5616
Oleanolic acid508-02-1
Instructions
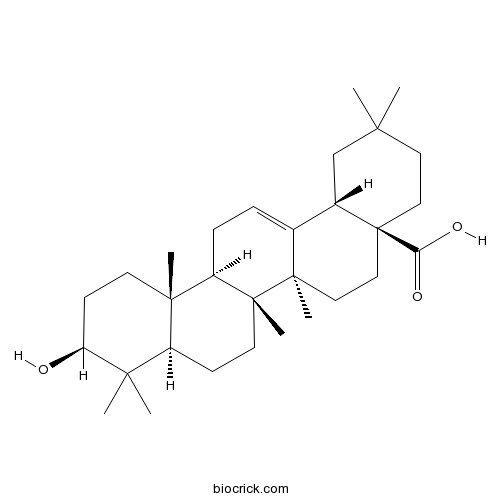
-
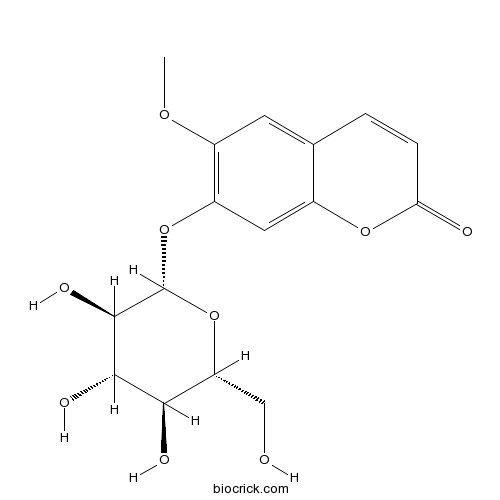
BCN5701
Scopolin531-44-2
Instructions
Inhibitory Activities of Phenolic Compounds Isolated from Adina rubella Leaves Against 5α-Reductase Associated with Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy.[Pubmed: 27399661]
Adina rubella Hance (AR), a plant native to Korea, has been used as traditional medicine for dysentery, eczema, intoxication, and external hemorrhages. Previous phytochemical studies of AR have reported several components, including terpenoids, phenolics, and alkaloids. The current study evaluated the anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory activities and 5α-reductase inhibition of isolated compounds of AR leaves to find a potential therapeutic agent for benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH). Repeated chromatographic isolation of an 80% acetone extract of AR leaves yielded seven phenolic compounds: caffeic acid (1), chlorogenic acid (2), methyl chlorogenate (3), quercetin-3-rutinoside (4), kaempferol-3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranoside (5), hyperoside (6), and grandifloroside (7). Compound 7 is a novel compound in AR. Caffeoyl derivatives 1-3 and 7 showed good anti-oxidative activities. In particular, caffeic acid (1) and grandifloroside (7) showed potent anti-inflammatory activities, and 7 also exhibited potent inhibitory activity against TNF-α and 5α-reductase. Our results show that the extract and grandifloroside (7) from leaves of AR might be developed as a source of potent anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory agents and therapeutic agent for BPH.
Complete assignments of 1H and 13C NMR spectral data for three polyhydroxylated 12-ursen-type triterpenoids from Dischidia esquirolii.[Pubmed: 18324739]
The complete assignments of all the (1)H and (13)C NMR signals of three polyhydroxylated 12-ursen-type triterpenes, 6beta,19alpha,22alpha-trihydroxyurs-12-en-3-oxo-28-oic acid (1), 3beta,6alpha,19alpha,23-tetrahydroxyurs-12-en-28- oic acid (2) and 3beta,6beta,19alpha,23-tetrahydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid (3), were carried out by means of homo- and hetero-nuclear two-dimensional NMR experiments. Compounds 1-3 were isolated from the aerial parts of Dischidia esquirolii. Of them, 1 and 2 were identified as new polyhydroxylated ursolic acid derivatives. Compound 2 is the C-6 hydroxyl epimer of 3, which was isolated first from Adina rubella, and its structure is revised in this paper.
[Studies on the chemical constituents of Adina rubella (II)].[Pubmed: 12571920]
Three constituents were isolated from Adina rubella. Their structures were identified as beta-sitosterol, quinovic acid, 3-oxo-urs-12-ene-27, 28-dioic acid.
Triterpenoid glycosides from Adina rubella.[Pubmed: 9101666]
From the roots of Adina rubella, four new quinovic acid glycosides, quinovic acid 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->4)-beta-D-fucopyranoside, quinovic acid 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->4)-beta-D-fucopyranosyl-(28-->1)-beta-D- glucopyranosyl ester, quinovic acid 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->4)-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(28-->1) -beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester and quinovic acid 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(28-->1)- beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester, were isolated. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of hydrolytic and spectral methods.
Triterpenoid glycosides from Adina rubella.[Pubmed: 7662280]
Two new triterpenoid glycosides, quinovic acid-3 beta-O-beta-D- glucopyranosyl-(1-->4)-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside and quinovic acid-3 beta-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-beta-D-fucopyranoside (named rubelloside A and B, respectively), were isolated from roots of Adina rubella. Their structures were elucidated by spectral and chemical means. Rubelloside B exhibited immunological enhancement.


