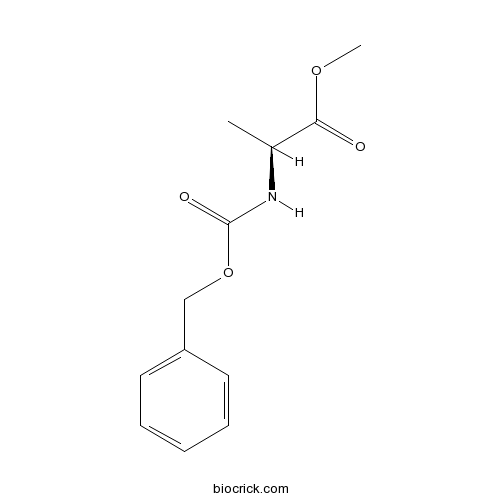
Z-Ala-OMeCAS# 28819-05-8 |
- Fulvestrant
Catalog No.:BCC1081
CAS No.:129453-61-8
- Bazedoxifene
Catalog No.:BCC1411
CAS No.:198481-32-2
- Bazedoxifene acetate
Catalog No.:BCC1412
CAS No.:198481-33-3
- (E)-2-Decenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC1292
CAS No.:334-49-6
- Toremifene
Catalog No.:BCC2010
CAS No.:89778-26-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 28819-05-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6993447 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H15NO4 | M.Wt | 237.25 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in water or 1% acetic acid | ||
| Chemical Name | methyl (2S)-2-(phenylmethoxycarbonylamino)propanoate | ||
| SMILES | CC(C(=O)OC)NC(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OMDVFTVXPVXANK-VIFPVBQESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H15NO4/c1-9(11(14)16-2)13-12(15)17-8-10-6-4-3-5-7-10/h3-7,9H,8H2,1-2H3,(H,13,15)/t9-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Z-Ala-OMe Dilution Calculator

Z-Ala-OMe Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.215 mL | 21.0748 mL | 42.1496 mL | 84.2993 mL | 105.3741 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.843 mL | 4.215 mL | 8.4299 mL | 16.8599 mL | 21.0748 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4215 mL | 2.1075 mL | 4.215 mL | 8.4299 mL | 10.5374 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0843 mL | 0.4215 mL | 0.843 mL | 1.686 mL | 2.1075 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0421 mL | 0.2107 mL | 0.4215 mL | 0.843 mL | 1.0537 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Z-Ala-OMe
- SB408124
Catalog No.:BCC4972
CAS No.:288150-92-5
- Cixiophiopogon A
Catalog No.:BCN2778
CAS No.:288143-27-1
- Fraxinellone
Catalog No.:BCN1272
CAS No.:28808-62-0
- 4,7-Bis(5-bromo-2-thienyl)-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole
Catalog No.:BCC8668
CAS No.:288071-87-4
- Heraclenin
Catalog No.:BCN5187
CAS No.:2880-49-1
- Tetrazole
Catalog No.:BCC2847
CAS No.:288-94-8
- Peptone, bacteriological
Catalog No.:BCC1210
CAS No.:288-88-0
- H-Cys(Acm)-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2903
CAS No.:28798-28-9
- Nordihydrocapsaicin
Catalog No.:BCN2387
CAS No.:28789-35-7
- 4,5,6,7-Tetrahydrothieno [3,2,c]pyridine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8664
CAS No.:28783-41-7
- Rosuvastatin
Catalog No.:BCC4139
CAS No.:287714-41-4
- Apigenin 5-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN5185
CAS No.:28757-27-9
- IBMX
Catalog No.:BCC7502
CAS No.:28822-58-4
- 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylglycol
Catalog No.:BCN5188
CAS No.:28822-73-3
- Phlorigidoside B
Catalog No.:BCN5189
CAS No.:288248-46-4
- Y-320
Catalog No.:BCC5202
CAS No.:288250-47-5
- Denudanolide A
Catalog No.:BCN6522
CAS No.:288259-72-3
- alpha-Asarone
Catalog No.:BCN3837
CAS No.:2883-98-9
- Lithospermic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5369
CAS No.:28831-65-4
- (-)-dicentrine
Catalog No.:BCC8167
CAS No.:28832-07-7
- Cediranib (AZD217)
Catalog No.:BCC1121
CAS No.:288383-20-0
- H-Asp(OBzl)-OBzl.TosOH
Catalog No.:BCC2886
CAS No.:2886-33 -1
- S-(-)-Carbidopa
Catalog No.:BCN8453
CAS No.:28860-95-9
- Z-D-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2758
CAS No.:28862-80-8
Papain-catalysed synthesis of dipeptides: a novel approach using free amino acids as nucleophiles.[Pubmed:1366382]
Enzyme Microb Technol. 1990 Jan;12(1):56-60.
For the first time, papain-catalysed synthesis of peptide bonds was successfully carried out using free amino acids as nucleophiles. In kinetically controlled experiments employing pH-Stat-mode, the ester substrates Z-Ala-OMe and Z-Gly-OMe were coupled with alanine, glutamine, and Cys(Acm)-OH, respectively. Under optimized reaction conditions (pH 9.2, high ratio nucleophile/carboxyl component, 10 mumol substrate mg-1 papain), the peptide yields ranged from 17% to 79%, depending on the structure of the amino and/or carboxyl component. The peptides formed were not hydrolysed under the chosen reaction conditions. With Z-Gly-OMe as the ester substrate, formation of the dipeptide was both rapid and high yielding. Papain-catalysed formation of peptide bonds applying free amino acids as nucleophiles might serve as an economic and easily manageable approach for the synthesis of short-chain peptides to be used in clinical nutrition.
Kinetically controlled synthesis of dipeptides using ficin as biocatalyst.[Pubmed:1760130]
Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1991 Oct;14(2):183-91.
The application of the sulfhydryl protease ficin as biocatalyst is proposed as a novel method for enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of dipeptides. The negligible peptidase but considerable esterase activity at alkaline pH facilitated the kinetically controlled formation of peptide bonds by coupling the ester substrates Z-Ala-OMe and Z-Gly-OMe with L-alanine, D-alanine, L-glutamine, D-glutamine and L-Cys(acetamidomethyl) respectively. The reaction is accomplished without the occurrence of secondary peptide hydrolysis. Under optimum reaction conditions (pH 9.2, high ratio nucleophile/carboxyl component, 4.8% ethanol, 40 degrees C), the peptide yields ranged from 5 to 91%, depending on the structure of the amino and/or carboxyl component. No racemization was observed in the enzymatic reaction. Application of short-chain peptides has been advocated recently in clinical nutrition. Ficin-catalyzed peptide synthesis might be an attractive biotechnological approach for the synthesis of suitable dipeptides in this respect.
Kinetically controlled enzymatic synthesis of dipeptide precursor of L-alanyl-L-glutamine.[Pubmed:22172107]
Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2011 Nov-Dec;58(6):449-55.
An important nutritional dipeptide precursor, benzoyloxycarbonyl protected L-alanyl-L-glutamine (Z-Ala-Gln), was successfully prepared through a kinetically controlled enzymatic peptide synthesis method. A commercially available and low-cost protease (papain) was used as biocatalyst with Z-Ala-OMe and Gln as acyl donor and nucleophile, respectively. The dipeptide yield was 35.5% under the optimized reaction conditions: 35 degrees C, pH 9.5, and the ratio of acyl donor/nucleophile is 1:10. Based on the reaction mechanism and experimental data, the kinetic model was established, which was in accordance with the Michaelis-Menten equation, and the apparent Michaelis constant K(m)(app) and the apparent maximum reaction rate r(max)(app) were calculated as 1.71 mol/L and 6.09 mmol/(L Min), respectively.


