Wnt-C59PORCN inhibitor,highly potent and selective CAS# 1243243-89-1 |
- IWR-1-endo
Catalog No.:BCC5102
CAS No.:1127442-82-3
- LGK-974
Catalog No.:BCC5103
CAS No.:1243244-14-5
- XAV-939
Catalog No.:BCC1120
CAS No.:284028-89-3
- WIKI4
Catalog No.:BCC2455
CAS No.:838818-26-1
- ICG 001
Catalog No.:BCC3632
CAS No.:847591-62-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1243243-89-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 57519544 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H21N3O | M.Wt | 379.45 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | C59 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 73.3 mg/mL (193.17 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
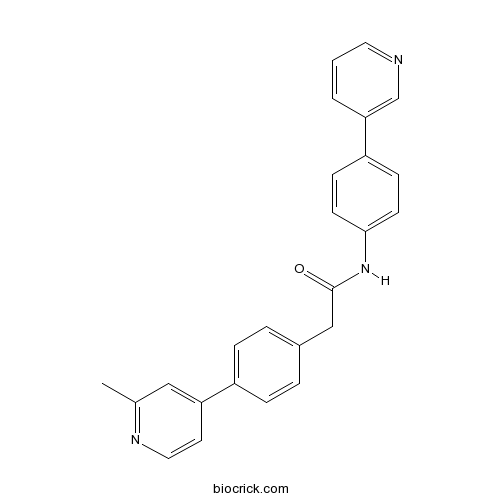
| Chemical Name | 2-[4-(2-methylpyridin-4-yl)phenyl]-N-(4-pyridin-3-ylphenyl)acetamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=NC=CC(=C1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)CC(=O)NC3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=CN=CC=C4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KHZOJCQBHJUJFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H21N3O/c1-18-15-22(12-14-27-18)20-6-4-19(5-7-20)16-25(29)28-24-10-8-21(9-11-24)23-3-2-13-26-17-23/h2-15,17H,16H2,1H3,(H,28,29) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Highly potent inhibitor of Porcupine (PORCN), a membrane-bound O-acyltransferase (MBOAT) (IC50 = 74 pM). Shown to inhibit Wnt signaling pathways. Blocks progression of mammary tumors in MMTV-WNT1 transgenic mice and downregulates Wnt/β-catenin target genes. Induces cardiomyocyte differentiation from human iPSCs following culture with CHIR 99021. Cell permeable and orally bioavailable. |

Wnt-C59 Dilution Calculator

Wnt-C59 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6354 mL | 13.177 mL | 26.3539 mL | 52.7079 mL | 65.8848 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5271 mL | 2.6354 mL | 5.2708 mL | 10.5416 mL | 13.177 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2635 mL | 1.3177 mL | 2.6354 mL | 5.2708 mL | 6.5885 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0527 mL | 0.2635 mL | 0.5271 mL | 1.0542 mL | 1.3177 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0264 mL | 0.1318 mL | 0.2635 mL | 0.5271 mL | 0.6588 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Wnt-C59 is a selective inhibitor of Wnt signaling with IC50 value of 74 pM [1].
Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways made of proteins and play an important role in passing signals from outside of a cell through cell surface receptors to the inside of the cell [1, 2].
Wnt-C59 is a potent Wnt inhibitor and has a different selectivity with the reported Wnt inhibitor crizotinib. When tested with HT1080 and Hela cells, Wnt-C59 showed inhibition on activation of a multimerized TCF-binding site driving luciferase mediated by Wnt3A by completely abrogating Wnt secretion [1]. In 5 human CC cell lines CC-LP-1, SUN-1079, WITT-1, SNU-1196, and CC-SW-1, Wnt-C59 treatment decreased cell viability, reduced cell proliferation and increased cell apoptosis by inhibiting Wnt signaling [2].
In C57/BL6 mice model transplanted with fragments from 2 independent primary MMTV-WNT1 tumors, oral administration of Wnt-C59 (10 mg/kg/d) for 17 days significantly arrested tumor growth and decreased tumor weights after sacrificing mice [1]. When tested with CD1 nude mice model with CC cell lines (CC-LP-1 and CC-SW-1) subcutaneous xenograft into the flanks, administration ofWnt-C59 inhibited cell growth and increased cell apoptosis compared with control group [2].
References:
[1]. Proffitt, K.D., et al., Pharmacological inhibition of the Wnt acyltransferase PORCN prevents growth of WNT-driven mammary cancer. Cancer Res, 2013. 73(2): p. 502-7.
[2]. Boulter, L., et al., WNT signaling drives cholangiocarcinoma growth and can be pharmacologically inhibited. J Clin Invest, 2015. 125(3): p. 1269-85.
- RN486
Catalog No.:BCC3921
CAS No.:1242156-23-5
- 12-Ursene-3,16,22-triol
Catalog No.:BCN6126
CAS No.:1242085-06-8
- Laxiracemosin H
Catalog No.:BCN6910
CAS No.:1241871-28-2
- 6-O-Vanilloylajugol
Catalog No.:BCN6125
CAS No.:124168-04-3
- (R)-DRF053 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7726
CAS No.:1241675-76-2
- Alcesefoliside
Catalog No.:BCN2933
CAS No.:124151-38-8
- Scutebarbatine O
Catalog No.:BCN8377
CAS No.:960302-88-9
- 2-Hydroxytetracosanoic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1599
CAS No.:124111-47-3
- 1-Caffeoylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5911
CAS No.:1241-87-8
- (-)-Hydroxydihydrobovolide
Catalog No.:BCN7890
CAS No.:124097-54-7
- 16-Epikoumidine
Catalog No.:BCN3915
CAS No.:124096-81-7
- Etomoxir
Catalog No.:BCC1564
CAS No.:124083-20-1
- LGK-974
Catalog No.:BCC5103
CAS No.:1243244-14-5
- Paucinervin A
Catalog No.:BCN7308
CAS No.:1243249-16-2
- Lenalidomide hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1697
CAS No.:1243329-97-6
- 9-(1H-Benzotriazol-1-ylmethyl)-9H-carbazole
Catalog No.:BCC8792
CAS No.:124337-34-4
- MG 149
Catalog No.:BCC5149
CAS No.:1243583-85-8
- Cannabidiolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6127
CAS No.:1244-58-2
- CGS 21680 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4316
CAS No.:124431-80-7
- VU 0364739 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7875
CAS No.:1244640-48-9
- 16R-sitsirikine
Catalog No.:BCN3492
CAS No.:1245-00-7
- 2,2'-Bicinchoninic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8487
CAS No.:1245-13-2
- Retusin
Catalog No.:BCN7794
CAS No.:1245-15-4
- 16-Oxoalisol A
Catalog No.:BCN3460
CAS No.:124515-98-6
Wnt-C59 arrests stemness and suppresses growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in mice by inhibiting the Wnt pathway in the tumor microenvironment.[Pubmed:25980501]
Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 10;6(16):14428-39.
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is responsible for the generation of cancer stem cells (CSCs) in many human tumors, including nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Recent studies demonstrate that Wnt or PORCN inhibitor, Wnt-C59, inhibits tumor growth in MMTV-WNT1 transgenic mice. The effect of Wnt-C59 in human tumors is not clear. In this study, the NPC cell lines investigated manifest heterogeneous responses to Wnt-C59 treatment. Wnt-C59 decreased tumor growth of SUNE1 cells in mice immediately following the administration of Wnt-C59. Mice injected with HNE1 cells did not develop visible tumors after the treatment of Wnt-C59, while control mice developed 100% tumors. Wnt-C59 inhibited stemness properties of NPC cells in a dosage-dependent manner by arresting sphere formation in both HNE1 and SUNE1 cells. Thus, Wnt-C59 has the potential to eradicate CSCs in human tumors. Active beta-catenin and Axin2 proteins were strongly expressed in stromal cells surrounding growing tumors, confirming the importance of Wnt signaling activities in the microenvironment being driving forces for cell growth. These novel findings confirm the ability of Wnt-C59 to suppress Wnt-driven undifferentiated cell growth in NPC. Both anti-Wnt signaling and anti-CSC approaches are feasible strategies in cancer therapy.
WNT-C59, a Small-Molecule WNT Inhibitor, Efficiently Induces Anterior Cortex That Includes Cortical Motor Neurons From Human Pluripotent Stem Cells.[Pubmed:26941358]
Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Apr;5(4):552-60.
UNLABELLED: The recapitulation of human neural development in a controlled, defined manner from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) has considerable potential for studies of human neural development, circuit formation and function, and the construction of in vitro models of neurological diseases. The inhibition of Wnt signaling, often by the recombinant protein DKK1, is important for the induction of cortical neurons. Here, we report a novel differentiation method using a small-molecule WNT inhibitor, Wnt-C59 (C59), to efficiently induce human anterior cortex. We compared two types of small molecules, C59 and XAV939 (XAV), as substitutes for DKK1 to induce cortical neurons from PSCs in serum-free embryoid body-like aggregate culture. DKK1 and XAV inhibited only the canonical pathway of Wnt signaling, whereas C59 inhibited both the canonical and noncanonical pathways. C59 efficiently induced CTIP2+/COUP-TF1- cells, which are characteristic of the cells found in the anterior cortex. In addition, when grafted into the cortex of adult mice, the C59-induced cells showed abundant axonal fiber extension toward the spinal cord. These results raise the possibility of C59 contributing to cell replacement therapy for motor neuron diseases or insults. SIGNIFICANCE: For a cell therapy against damaged corticospinal tract caused by neurodegenerative diseases or insults, cortical motor neurons are needed. Currently, their induction from pluripotent stem cells is considered very promising; however, an efficient protocol to induce motor neurons is not available. For efficient induction of anterior cortex, where motor neurons are located, various WNT inhibitors were investigated. It was found that one of them could induce anterior cortical cells efficiently. In addition, when grafted into the cortex of adult mice, the induced cells showed more abundant axonal fiber extension toward spinal cord. These results raise the possibility that this inhibitor contributes to a cell-replacement therapy for motor neuron diseases or insults.
Chemically defined generation of human cardiomyocytes.[Pubmed:24930130]
Nat Methods. 2014 Aug;11(8):855-60.
Existing methods for human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) cardiac differentiation are efficient but require complex, undefined medium constituents that hinder further elucidation of the molecular mechanisms of cardiomyogenesis. Using hiPSCs derived under chemically defined conditions on synthetic matrices, we systematically developed an optimized cardiac differentiation strategy, using a chemically defined medium consisting of just three components: the basal medium RPMI 1640, L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate and rice-derived recombinant human albumin. Along with small molecule-based induction of differentiation, this protocol produced contractile sheets of up to 95% TNNT2(+) cardiomyocytes at a yield of up to 100 cardiomyocytes for every input pluripotent cell and was effective in 11 hiPSC lines tested. This chemically defined platform for cardiac specification of hiPSCs will allow the elucidation of cardiomyocyte macromolecular and metabolic requirements and will provide a minimal system for the study of maturation and subtype specification.
Pharmacological inhibition of the Wnt acyltransferase PORCN prevents growth of WNT-driven mammary cancer.[Pubmed:23188502]
Cancer Res. 2013 Jan 15;73(2):502-7.
Porcupine (PORCN) is a membrane bound O-acyltransferase that is required for Wnt palmitoylation, secretion, and biologic activity. All evaluable human Wnts require PORCN for their activity, suggesting that inhibition of PORCN could be an effective treatment for cancers dependent on excess Wnt activity. In this study, we evaluated the PORCN inhibitor Wnt-C59 (C59), to determine its activity and toxicity in cultured cells and mice. C59 inhibits PORCN activity in vitro at nanomolar concentrations, as assessed by inhibition of Wnt palmitoylation, Wnt interaction with the carrier protein Wntless/WLS, Wnt secretion, and Wnt activation of beta-catenin reporter activity. In mice, C59 displayed good bioavailability, as once daily oral administration was sufficient to maintain blood concentrations well above the IC(50). C59 blocked progression of mammary tumors in MMTV-WNT1 transgenic mice while downregulating Wnt/beta-catenin target genes. Surprisingly, mice exhibit no apparent toxicity, such that at a therapeutically effective dose there were no pathologic changes in the gut or other tissues. These results offer preclinical proof-of-concept that inhibiting mammalian Wnts can be achieved by targeting PORCN with small-molecule inhibitors such as C59, and that this is a safe and feasible strategy in vivo.
WNT10B/beta-catenin signalling induces HMGA2 and proliferation in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer.[Pubmed:23307470]
EMBO Mol Med. 2013 Feb;5(2):264-79.
Wnt/beta-catenin signalling has been suggested to be active in basal-like breast cancer. However, in highly aggressive metastatic triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) the role of beta-catenin and the underlying mechanism(s) for the aggressiveness of TNBC remain unknown. We illustrate that WNT10B induces transcriptionally active beta-catenin in human TNBC and predicts survival-outcome of patients with both TNBC and basal-like tumours. We provide evidence that transgenic murine Wnt10b-driven tumours are devoid of ERalpha, PR and HER2 expression and can model human TNBC. Importantly, HMGA2 is specifically expressed during early stages of embryonic mammogenesis and absent when WNT10B expression is lost, suggesting a developmentally conserved mode of action. Mechanistically, ChIP analysis uncovered that WNT10B activates canonical beta-catenin signalling leading to up-regulation of HMGA2. Treatment of mouse and human triple-negative tumour cells with two Wnt/beta-catenin pathway modulators or siRNA to HMGA2 decreases HMGA2 levels and proliferation. We demonstrate that WNT10B has epistatic activity on HMGA2, which is necessary and sufficient for proliferation of TNBC cells. Furthermore, HMGA2 expression predicts relapse-free-survival and metastasis in TNBC patients.
Adult interfollicular tumour-initiating cells are reprogrammed into an embryonic hair follicle progenitor-like fate during basal cell carcinoma initiation.[Pubmed:23178882]
Nat Cell Biol. 2012 Dec;14(12):1282-94.
Basal cell carcinoma, the most frequent human skin cancer, arises from activating hedgehog (HH) pathway mutations; however, little is known about the temporal changes that occur in tumour-initiating cells from the first oncogenic hit to the development of invasive cancer. Using an inducible mouse model enabling the expression of a constitutively active Smoothened mutant (SmoM2) in the adult epidermis, we carried out transcriptional profiling of SmoM2-expressing cells at different times during cancer initiation. We found that tumour-initiating cells are massively reprogrammed into a fate resembling that of embryonic hair follicle progenitors (EHFPs). Wnt/ beta-catenin signalling was very rapidly activated following SmoM2 expression in adult epidermis and coincided with the expression of EHFP markers. Deletion of beta-catenin in adult SmoM2-expressing cells prevents EHFP reprogramming and tumour initiation. Finally, human basal cell carcinomas also express genes of the Wnt signalling and EHFP signatures.


