Vinyl CinnamateCAS# 3098-92-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

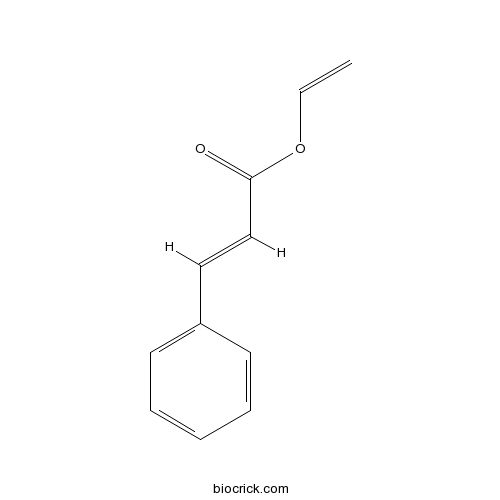
| Cas No. | 3098-92-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5371819 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C11H10O2 | M.Wt | 174.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | ethenyl (E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | C=COC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WGXGKXTZIQFQFO-CMDGGOBGSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H10O2/c1-2-13-11(12)9-8-10-6-4-3-5-7-10/h2-9H,1H2/b9-8+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Vinyl Cinnamate is a nartural product from Cinnamomum cassia Presl. |
| In vitro | Initiated chemical vapor deposition and light-responsive cross-linking of poly(vinyl cinnamate) thin films.[Pubmed: 24817405]Macromol Rapid Commun. 2014 Aug;35(15):1345-50.The first vapor-phase deposition of poly(Vinyl Cinnamate) (PVCin) is reported. Dispersibility and emulsion-stabilizing effect of cellulose nanowhiskers esterified by vinyl acetate and vinyl cinnamate.[Pubmed: 23883187]Biomacromolecules. 2013 Aug 12;14(8):2937-44. The surface of cotton cellulose nanowhiskers (CNW's) was esterified by vinyl acetate (VAc) and Vinyl Cinnamate (VCin), in the presence of potassium carbonate as catalyst. Reactions were performed under microwave activation and monitored by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. |

Vinyl Cinnamate Dilution Calculator

Vinyl Cinnamate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.7405 mL | 28.7026 mL | 57.4053 mL | 114.8106 mL | 143.5132 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1481 mL | 5.7405 mL | 11.4811 mL | 22.9621 mL | 28.7026 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5741 mL | 2.8703 mL | 5.7405 mL | 11.4811 mL | 14.3513 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1148 mL | 0.5741 mL | 1.1481 mL | 2.2962 mL | 2.8703 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0574 mL | 0.287 mL | 0.5741 mL | 1.1481 mL | 1.4351 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- GW791343 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4974
CAS No.:309712-55-8
- 1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5913
CAS No.:30964-13-7
- 2-Amino-9H-fluoren-9-one
Catalog No.:BCC8545
CAS No.:3096-57-9
- Perillartine
Catalog No.:BCN8305
CAS No.:30950-27-7
- Doxifluridine
Catalog No.:BCC4903
CAS No.:3094-09-5
- Inauhzin
Catalog No.:BCC5146
CAS No.:309271-94-1
- Boc-Asp-OBzl
Catalog No.:BCC3363
CAS No.:30925-18-9
- Boc-N-Me-Phg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3350
CAS No.:30925-11-2
- 3β-Acetoxy-5α-androstan-17β-ol
Catalog No.:BCC8644
CAS No.:3090-70-8
- 8-Epixanthatin
Catalog No.:BCN7782
CAS No.:30890-35-8
- Kauran-18-Olc Acid,16,1719-Tnhydroxy-,(4A)
Catalog No.:BCC9235
CAS No.:308821-59-2
- Aloesin
Catalog No.:BCN8437
CAS No.:30861-27-9
- Dauricinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8162
CAS No.:30984-80-6
- SX 011
Catalog No.:BCC7731
CAS No.:309913-42-6
- Boc-Aib-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3148
CAS No.:30992-29-1
- KL 001
Catalog No.:BCC6262
CAS No.:309928-48-1
- 3-(Boc-Amino)piperidine
Catalog No.:BCC8590
CAS No.:309956-78-3
- 7-O-Methylmangiferin
Catalog No.:BCN2804
CAS No.:31002-12-7
- 1-O-(3,4-Dimethoxybenzoyl)-beta-D-glucopyranose
Catalog No.:BCN3759
CAS No.:31002-27-4
- 7-Ethoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN2708
CAS No.:31005-02-4
- Magnolin
Catalog No.:BCN5224
CAS No.:31008-18-1
- Fargesin
Catalog No.:BCN5022
CAS No.:31008-19-2
- Dihydrosphingosine
Catalog No.:BCC6778
CAS No.:3102-56-5
- Ceramide
Catalog No.:BCC2458
CAS No.:3102-57-6
Initiated chemical vapor deposition and light-responsive cross-linking of poly(vinyl cinnamate) thin films.[Pubmed:24817405]
Macromol Rapid Commun. 2014 Aug;35(15):1345-50.
The first vapor-phase deposition of poly(Vinyl Cinnamate) (PVCin) is reported. Initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) is used to synthesize PVCin thin films with an average thickness of 100 nm. Free radical polymerization and cyclization reactions compete during the deposition process, with approximately 45% of the repeat units undergoing cyclization. Exposure to UV light (lambda = 254 nm) induces dimerization (cross-linking) of the PVCin, which is quantified using spectroscopic techniques. Approximately 90% of the free cinnamate moieties are dimerized at a UV dose of 300 mJ cm(-2) . PVCin is also incorporated into a copolymer with N-isopropylacrylamide, which exhibits a characteristic change in hydrophilicity with temperature. The copolymer is selectively cross-linked through a mask, and reversible swelling of patterns with 30 mum resolution is demonstrated by submerging the film in water.
Dispersibility and emulsion-stabilizing effect of cellulose nanowhiskers esterified by vinyl acetate and vinyl cinnamate.[Pubmed:23883187]
Biomacromolecules. 2013 Aug 12;14(8):2937-44.
The surface of cotton cellulose nanowhiskers (CNW's) was esterified by vinyl acetate (VAc) and Vinyl Cinnamate (VCin), in the presence of potassium carbonate as catalyst. Reactions were performed under microwave activation and monitored by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. The supramolecular structure of CNW's before and after modification was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). Distinctively from the acetylation treatment, an increase in particles dimensions was noted after esterification with VCin, which was assigned to pi-pi stacking interactions that may exist between cinnamoyl moieties. The dispersibility and emulsion stabilizing effect of acylated CNW's was examined in ethyl acetate, toluene, and cyclohexane, three organic solvents of medium to low polarity. The acylated nanoparticles could never be dispersed in toluene nor cyclohexane, but they formed stable dispersions in ethyl acetate while remaining dispersible in water. Stable ethyl acetate-in-water, toluene-in-water, and cyclohexane-in-water emulsions were successfully prepared with CNW's grafted with acetyl moieties, whereas the VCin-treated particles could stabilize only the cyclohexane-in-water emulsions. The impact of esterification treatment on emulsion stability and droplets size was particularly discussed.


