Tubuloside ACAS# 112516-05-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 112516-05-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 21637830 | Appearance | Powder |
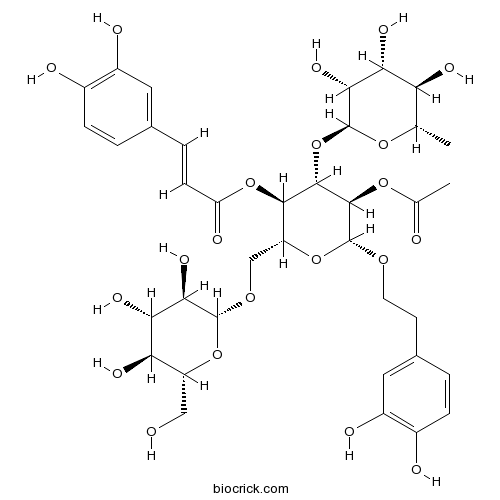
| Formula | C37H48O21 | M.Wt | 828.76 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol; insoluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | [(2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)-5-acetyloxy-6-[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]-2-[[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]-4-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-3-yl] (E)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2C(C(OC(C2OC(=O)C)OCCC3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O)COC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O)OC(=O)C=CC5=CC(=C(C=C5)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KZLDMAIXPXOZCX-BBQAUMBQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C37H48O21/c1-15-26(45)28(47)31(50)36(53-15)58-33-32(57-25(44)8-5-17-3-6-19(40)21(42)11-17)24(14-52-35-30(49)29(48)27(46)23(13-38)55-35)56-37(34(33)54-16(2)39)51-10-9-18-4-7-20(41)22(43)12-18/h3-8,11-12,15,23-24,26-38,40-43,45-50H,9-10,13-14H2,1-2H3/b8-5+/t15-,23+,24+,26-,27+,28+,29-,30+,31+,32+,33-,34+,35+,36-,37+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Tubuloside A has anti-inflammatory, antioxidative and hepatoprotective activities. Tubuloside A shows stronger free radical scavenging activities than alpha-tocopherol on 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical and xanthine/xanthine oxidase (XOD) generated superoxide anion radical (O2-.). |
| Targets | NADPH-oxidase | NOS | NO | TNF-α |
| In vitro | Studies on the Tissue Culture of Cistanche Plants: I. Callus Induction and Shoot Differentiation from the Seed of Cistanche tubulosa Wight[Reference: WebLink]Plant Biotechnology 12(1), 46-54, 1995-04-01Cistanche tubulosa Wight. is an important herbal medicine including such phenylethanoide glycosides as echinacoside (E), Tubuloside A (TA), acteoside (A) and 2′-acetylacteoside (2′AA), and is a holoparasitic plant distributed in a wide range from the North African to Chinese in and and semi arid regions. Inhibition of nitric oxide by phenylethanoids in activated macrophages.[Pubmed: 10913595]Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Jul 14;400(1):137-44.Nitric oxide (NO) is one of the pro-inflammatory molecules. Some phenylethanoids have been previously shown to possess anti-inflammatory effects. |
| Cell Research | Acylated phenylethanoid oligoglycosides with hepatoprotective activity from the desert plant Cistanche tubulosa.[Pubmed: 20159656 ]Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Mar 1;18(5):1882-90.The methanolic extract from fresh stems of Cistanche tubulosa (Orobanchaceae) was found to show hepatoprotective effects against D-galactosamine (D-GalN)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced liver injury in mice. |
| Structure Identification | Biol Pharm Bull. 1996 Dec;19(12):1580-5.Antioxidative effects of phenylethanoids from Cistanche deserticola.[Pubmed: 8996643]
|

Tubuloside A Dilution Calculator

Tubuloside A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2066 mL | 6.0331 mL | 12.0662 mL | 24.1324 mL | 30.1655 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2413 mL | 1.2066 mL | 2.4132 mL | 4.8265 mL | 6.0331 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1207 mL | 0.6033 mL | 1.2066 mL | 2.4132 mL | 3.0166 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0241 mL | 0.1207 mL | 0.2413 mL | 0.4826 mL | 0.6033 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0121 mL | 0.0603 mL | 0.1207 mL | 0.2413 mL | 0.3017 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Neolinine
Catalog No.:BCN6564
CAS No.:112515-37-4
- Isoabsouline
Catalog No.:BCN1955
CAS No.:112513-34-5
- Absouline
Catalog No.:BCN1954
CAS No.:112513-33-4
- Picrasidine S
Catalog No.:BCN6006
CAS No.:112503-87-4
- Aristolactam FI
Catalog No.:BCN6005
CAS No.:112501-42-5
- 6-Aldehydo-isoophiopogonone A
Catalog No.:BCN6629
CAS No.:112500-90-0
- 5-Aminoisoquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8736
CAS No.:1125-60-6
- 4,4-Pentamethylenepiperidine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6059
CAS No.:1125-01-5
- H-Glu(OcHex)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2929
CAS No.:112471-82-6
- U-54494A hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6668
CAS No.:112465-94-8
- 3-Phenyl-1-(pyrrol-1-yl)propan-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN4005
CAS No.:112448-69-8
- AZ3146
Catalog No.:BCC3731
CAS No.:1124329-14-1
- Citrusinol
Catalog No.:BCN8083
CAS No.:112516-43-5
- CI994 (Tacedinaline)
Catalog No.:BCC2159
CAS No.:112522-64-2
- ent-16alpha,17-Dihydroxyatisan-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN6607
CAS No.:112523-91-8
- Pioglitazone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2278
CAS No.:112529-15-4
- 4-O-Methylepisappanol
Catalog No.:BCN3674
CAS No.:112529-37-0
- Mps1-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC5590
CAS No.:1125593-20-5
- A 804598
Catalog No.:BCC6198
CAS No.:1125758-85-1
- SKLB610
Catalog No.:BCC3647
CAS No.:1125780-41-7
- 4-Allylpyrocatechol
Catalog No.:BCN6009
CAS No.:1126-61-0
- Iso-mogroside V
Catalog No.:BCN3047
CAS No.:1126032-65-2
- Dicyclanil
Catalog No.:BCC8938
CAS No.:112636-83-6
- U-73122
Catalog No.:BCC5199
CAS No.:112648-68-7
Acylated phenylethanoid oligoglycosides with hepatoprotective activity from the desert plant Cistanche tubulosa.[Pubmed:20159656]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Mar 1;18(5):1882-90.
The methanolic extract from fresh stems of Cistanche tubulosa (Orobanchaceae) was found to show hepatoprotective effects against D-galactosamine (D-GalN)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced liver injury in mice. From the extract, three new phenylethanoid oligoglycosides, kankanosides H(1) (1), H(2) (2), and I (3), were isolated together with 16 phenylethanoid glycosides (4-19) and two acylated oligosugars (20, 21). The structures of 1-3 were determined on the basis of spectroscopic properties as well as of chemical evidence. Among the isolates, echinacoside (4, IC(50)=10.2 microM), acteoside (5, 4.6 microM), isoacteoside (6, 5.3 microM), 2'-acetylacteoside (8, 4.8 microM), and Tubuloside A (10, 8.6 microM) inhibited D-GalN-induced death of hepatocytes. These five isolates, 4 (31.1 microM), 5 (17.8 microM), 6 (22.7 microM), 8 (25.7 microM), and 10 (23.2 microM), and cistantubuloside B(1) (11, 21.4 microM) also reduced TNF-alpha-induced cytotoxicity in L929 cells. Moreover, principal constituents (4-6) exhibited in vivo hepatoprotective effects at doses of 25-100mg/kg, po.
Inhibition of nitric oxide by phenylethanoids in activated macrophages.[Pubmed:10913595]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Jul 14;400(1):137-44.
Nitric oxide (NO) is one of the pro-inflammatory molecules. Some phenylethanoids have been previously shown to possess anti-inflammatory effects. Seven phenylethanoids from the stems of Cistanche deserticola, viz. isoacteoside, tubuloside B, acteoside, 2'-O-acetylacteoside, echinacoside, cistanoside A and Tubuloside A, were tested for their effect on NO radical generation by activated murine macrophages. At the concentration of 100-200 microM, all the phenylethanoids reduced (6.3-62.3%) nitrite accumulation in lipopolysaccharide (0.1 microgram/ml)-stimulated J774.1 cells. At 200 microM, they inhibited by 32.2-72.4% nitrite accumulation induced by lipopolysaccharide (0.1 microgram/ml)/interferon-gamma (100 U/ml) in mouse peritoneal exudate macrophages. However, these compounds did not affect the expression of inducible nitric oxide (iNOS) mRNA, the iNOS protein level, or the iNOS activity in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated J774.1 cells. Instead, they showed a clear scavenging effect (6.9-43.9%) at the low concentrations of 2-10 microM of about 12 microM nitrite generated from an NO donor, 1-propanamine-3-hydroxy-2-nitroso-1-propylhydrazino (PAPA NONOate). These results indicate that the phenylethanoids have NO radical-scavenging activity, which possibly contributes to their anti-inflammatory effects.
Antioxidative effects of phenylethanoids from Cistanche deserticola.[Pubmed:8996643]
Biol Pharm Bull. 1996 Dec;19(12):1580-5.
The acetone-H2O (9:1) extract from the stem of Cistanche deserticola showed a strong free radical scavenging activity. Nine major phenylethanoid compounds were isolated from this extract. They were identified by NMR as acteoside, isoacteoside, 2'-acetylacteoside, tubuloside B, echinacoside, Tubuloside A, syringalide A 3'-alpha-rhamnopyranoside, cistanoside A and cistanoside F. All of these compounds showed stronger free radical scavenging activities than alpha-tocopherol on 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical and xanthine/xanthine oxidase (XOD) generated superoxide anion radical (O2-.). Among the nine compounds, isoacteoside and tubuloside B, whose caffeoyl moiety is at 6'-position of the glucose, showed an inhibitory effect on XOD. We further studied the effects of these phenylethanoids on the lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes induced by enzymatic and non-enzymatic methods. As expected, each of them exhibited significant inhibition on both ascorbic acid/Fe2+ and ADP/NADPH/Fe3+ induced lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes, which were more potent than alpha-tocopherol of caffeic acid. The antioxidative effect was found to be potentiated by an increase in the number of phenolic hydroxyl groups in the molecule.


