SB 265610CXCR2 antagonist, potent CAS# 211096-49-0 |
- Skepinone-L
Catalog No.:BCC1953
CAS No.:1221485-83-1
- SB202190 (FHPI)
Catalog No.:BCC1093
CAS No.:152121-30-7
- SD-06
Catalog No.:BCC1937
CAS No.:271576-80-8
- BIRB 796 (Doramapimod)
Catalog No.:BCC2535
CAS No.:285983-48-4
- LY2228820
Catalog No.:BCC2528
CAS No.:862507-23-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

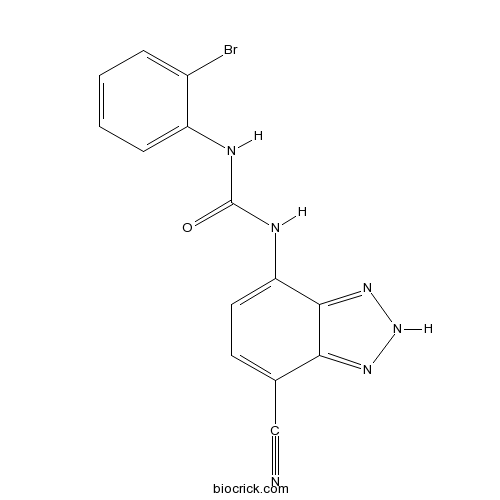
| Cas No. | 211096-49-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9841667 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H9BrN6O | M.Wt | 357.16 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 10 mM in ethanol | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-(2-bromophenyl)-3-(7-cyano-2H-benzotriazol-4-yl)urea | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C(=C1)NC(=O)NC2=CC=C(C3=NNN=C23)C#N)Br | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SEDUMQWZEOMXSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H9BrN6O/c15-9-3-1-2-4-10(9)17-14(22)18-11-6-5-8(7-16)12-13(11)20-21-19-12/h1-6H,(H2,17,18,22)(H,19,20,21) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent CXCR2 antagonist that inhibits CINC-1-mediated but not C5a-mediated Ca2+ mobilization (IC50 values are 3.4 and 6800 nM respectively). Inhibits CINC-induced chemotaxis and attenuates neutrophil accumulation in inflammatory lung injury in vivo. |

SB 265610 Dilution Calculator

SB 265610 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7999 mL | 13.9993 mL | 27.9987 mL | 55.9973 mL | 69.9966 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.56 mL | 2.7999 mL | 5.5997 mL | 11.1995 mL | 13.9993 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.28 mL | 1.3999 mL | 2.7999 mL | 5.5997 mL | 6.9997 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.056 mL | 0.28 mL | 0.56 mL | 1.1199 mL | 1.3999 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.028 mL | 0.14 mL | 0.28 mL | 0.56 mL | 0.7 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SB 265610 is a potent CXCR2 antagonist that inhibits CINC-1-mediated Ca2+ mobilization with IC50 value of 3.4nM [1] [2].
CXCR2 is an integral membrane protein that specifically binds and responds to cytokines of the CXC chemokine family.
In isolated rat neutrophils stimulated with rat CINC-1, SB 265610 inhibited Ca2+ mobilization induced by CINC-1 with IC50 value of 3.4 nM in a dose-dependent way, while inhibited Ca2+ mobilization induced by C5a only with IC50 value of 6.8uM, which showed selectivity of the antagonist for CXCR2 [1]. In equilibrium saturation binding studies, SB265610 inhibited the binding of interleukin-8 without affecting the Kd. While, IL-8 couldn’t prevent binding of SB265610. SB265610 is an allosteric inverse agonist at the CXCR2 receptor [2].
In a hyperoxia rat model, newborn rats increased lung neutrophil content. Treatment with SB-265610 reduced hyperoxia-induced neutrophil accumulation in bronchoalveolar lavage and whole lung myeloperoxidase accumulation [1].
References:
[1]. Auten RL, Richardson RM, White JR, et al. Nonpeptide CXCR2 antagonist prevents neutrophil accumulation in hyperoxia-exposed newborn rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2001, 299(1): 90-95.
[2]. Bradley ME, Bond ME, Manini J, et al. SB265610 is an allosteric, inverse agonist at the human CXCR2 receptor. Br J Pharmacol, 2009, 158(1): 328-338.
- Mahanimbine
Catalog No.:BCN3174
CAS No.:21104-28-9
- BMY 7378
Catalog No.:BCC5063
CAS No.:21102-95-4
- CART (62-76) (rat, human)
Catalog No.:BCC6008
CAS No.:210978-19-1
- W-84 dibromide
Catalog No.:BCC6682
CAS No.:21093-51-6
- Org 12962 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7718
CAS No.:210821-63-9
- Sakakin
Catalog No.:BCN4916
CAS No.:21082-33-7
- CP 471474
Catalog No.:BCC2373
CAS No.:210755-45-6
- 7,8-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCC8290
CAS No.:2107-77-9
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCC8284
CAS No.:2107-76-8
- PD 168568 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7702
CAS No.:210688-56-5
- 6alpha-Hydroxylycopodine
Catalog No.:BCN7403
CAS No.:21061-92-7
- 1,11b-Dihydro-11b-hydroxymaackiain
Catalog No.:BCN3914
CAS No.:210537-05-6
- Marsformoxide B
Catalog No.:BCN6687
CAS No.:2111-46-8
- Sobetirome
Catalog No.:BCC1957
CAS No.:211110-63-3
- Rubranol
Catalog No.:BCN4917
CAS No.:211126-61-3
- 9,17-Octadecadiene-12,14-diyne-1,11,16-triol
Catalog No.:BCN1497
CAS No.:211238-60-7
- m-Chlorophenylbiguanide hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6650
CAS No.:2113-05-5
- R18
Catalog No.:BCC2383
CAS No.:211364-78-2
- Astrocasine
Catalog No.:BCN2150
CAS No.:2114-92-3
- Dendrobine
Catalog No.:BCN5923
CAS No.:2115-91-5
- Dalcetrapib (JTT-705, RO4607381)
Catalog No.:BCC2328
CAS No.:211513-37-0
- WHI-P154
Catalog No.:BCC2202
CAS No.:211555-04-3
- WHI-P97
Catalog No.:BCC2056
CAS No.:211555-05-4
- WHI-P180
Catalog No.:BCC3928
CAS No.:211555-08-7
The effect of Sb-surfactant on GaInP CuPtB type ordering: assessment through dark field TEM and aberration corrected HAADF imaging.[Pubmed:28367549]
Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017 Apr 12;19(15):9806-9810.
We report on the effect of Sb on the microstructure of GaInP layers grown by metal organic vapor phase epitaxy (MOVPE). These layers exhibit a CuPtB single variant ordering due to the intentional misorientation of the substrate (Ge(001) substrates with 6 degrees misorientation towards the nearest [111] axis). The use of Sb as a surfactant during the GaInP growth does not modify the type of ordering, but it is found that the order parameter (eta) decreases with increasing Sb flux. Dark field microscopy reveals a variation of the angle of the antiphase boundaries (APBs) with Sb amount. The microstructure is assessed through high angle annular dark field (HAADF) experiments and image simulation revealing Z-contrast loss in APBs due to the superposition of ordered domains.
Direct nucleation, morphology and compositional tuning of InAs1-x Sb x nanowires on InAs (111) B substrates.[Pubmed:28346221]
Nanotechnology. 2017 Apr 21;28(16):165601.
III-V ternary nanowires are interesting due to the possibility of modulating their physical and material properties by tuning their material composition. Amongst them InAs1-x Sb x nanowires are good candidates for applications such as Infrared detectors. However, this material has not been grown directly from substrates, in a large range of material compositions. Since the properties of ternaries are alterable by tuning their composition, it is beneficial to gain access to a wide range of composition tunability. Here we demonstrate direct nucleation and growth of InAs1-x Sb x nanowires from Au seed particles over a broad range of compositions (x = 0.08-0.75) for different diameters and surface densities by means of metalorganic vapor phase epitaxy. We investigate how the nucleation, morphology, solid phase Sb content, and growth rate of these nanowires depend on the particle dimensions, and on growth conditions such as the vapor phase composition, V/III ratio, and temperature. We show that the solid phase Sb content of the nanowires remains invariant towards changes of the In precursor flow. We also discuss that at relatively high In flows the growth mechanism alters from Au-seeded to what is referred to as semi In-seeded growth. This change enables growth of nanowires with a high solid phase Sb content of 0.75 that are not feasible via Au-seeded growth. Independent of the growth conditions and morphology, we report that the nanowire Sb content changes over their length, from lower Sb contents at the base, increasing to higher amounts towards the tip. We correlate the axial Sb content variations to the axial growth rate measured in situ. We also report spontaneous core-shell formation for Au-seeded nanowires, where the core is Sb-rich in comparison to the Sb-poor shell.
Differing Mechanisms of Death Induction by Fluorinated Taxane SB-T-12854 in Breast Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:28373418]
Anticancer Res. 2017 Apr;37(4):1581-1590.
BACKGROUND/AIM: Classical taxanes are routinely used in cancer therapy. In this study, mechanisms involved in death induction by the novel fluorine-containing taxane SB-T-12854 were investigated. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We employed breast cancer SK-BR-3, MCF-7 and T47D cell lines to assess activation of individual caspases, changes in the expression of proteins of the Bcl-2 family, and the release of pro-apoptotic factors from mitochondria into the cytosol after SB-T-12854 treatment. RESULTS: Caspase-2, -8, and -9 were activated in SK-BR-3 and MCF-7 cells. Only caspase-8 was activated in T47D cells. Caspase-7 and -6 were activated in all tested cells while caspase-3 was activated only in SK-BR-3 cells. Pro-apoptotic Bad protein seems to be important for cell death induction in all tested cells. Anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and pro-apoptotic Bim, Bok, Bid and Bik seem to be also associated with cell death induction in some of the tested cells. The mitochondrial apoptotic pathway was significantly activated in association with the release of cytochrome c and Smac from mitochondria, but only in SK-BR-3 cells, not in MCF-7 and T47D cells. CONCLUSION: Cell death induced by SB-T-12854, in the tested breast cancer cells, differs regarding activation of caspases, changes in levels of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins of the Bcl-2 family and activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.
Critical evaluation of strategies for single and simultaneous determinations of As, Bi, Sb and Se by hydride generation inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry.[Pubmed:28340714]
Talanta. 2017 May 15;167:217-226.
A systematic study of hydride generation (HG) of As, Bi, Sb and Se from solutions containing As(III), As(V), Bi(III), Sb(III), Sb(V), Se(IV) and Se(VI) was presented. Hydrides were generated in a gas-liquid phase separation system using a continuous flow vapor generation accessory (VGA) by mixing acidified aqueous sample, HCl and sodium borohydride reductant (NaBH4) solutions on-line. For detection, a simultaneous axially viewed inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) was applied. Effects of the HCl concentration (related to sample and additional acid solutions) and type of the pre-reducing agents used for reduction of As(V), Sb(V) and Se(VI) into As(III), Sb(III) and Se(IV) on the analytical responses of As, Bi, Sb and Se were studied and discussed. Two compromised HG reaction conditions for simultaneous measurements of As+Bi+Sb (CC1) or As+Sb+Se (CC2) were established. It was found that choice of the pre-reductant prior to formation of the hydrides is critical in obtaining the dependable results of the analysis. Accordingly, for a As(III)+As(V)+Bi(III)+Sb(III)+Sb(V) mixture and using CC1, thiourea/thiourea-ascorbic acid interfered in Bi determination and hence, total As+Sb could be measured. If L-cysteine/L-cysteine-ascorbic acid were used, measurements of total Bi+Sb was possible in these HG reaction conditions. For a As(III)+As(V)+Sb(III)+Sb(V)+Se(IV)+Se(VI) mixture and using CC2, thiourea/thiourea-ascorbic acid and L-cysteine/L-cysteine-ascorbic acid influenced HG of Se but ensured total As+Sb determination. In contrast, heating a sample solution with HCl, although did not pre-reduce As(V) and Sb(V), assured quantitative reduction of Se(VI) to Se(IV). Finally, considering all favorable pre-reducing and HG conditions, methodologies for reliable determination of total As, Bi, Sb and Se by HG-ICP-OES were proposed. Strategies for single-, two- and three-element measurements were evaluated and validated, obtaining the detection limits (DLs) below 0.1ngg(-1) and precision typically in the range of 1.4-3.9% RSD.
Impaired healing of nitrogen mustard wounds in CXCR2 null mice.[Pubmed:12753603]
Wound Repair Regen. 2003 May-Jun;11(3):213-9.
To examine the significance of chemokine activation of CXCR2 in wound healing after chemical burn, cutaneous injury was created by topical application of nitrogen mustard on CXCR2 wild type (+/+), heterozygous (+/-), and knockout (-/-) mice. Wounds were analyzed histologically for neutrophil and monocyte infiltration and for reepithelialization at postwound days 4, 7, and 10. Neutrophil recruitment to the wound site was reduced through postwound day 7 in CXCR2 -/- mice as indicated by myeloperoxidase assay and by visual quantitation. Because there is always concern that mice with targeted deletion of a specific receptor may undergo developmental adaptations to offset the loss of the receptor, we also accessed chemical wound repair in the presence of a small molecule antagonist of CXCR2. Dietary supplementation with a CXCR2 antagonist (SB-265610) during the wound repair process also markedly delayed healing parameters in CXCR2 +/+ mice, even greater than treatment with glucocorticoids. These parallel studies further establish that mice deficient in CXCR2 function exhibit delayed cutaneous wound healing that may be primarily linked to impaired neutrophil recruitment after chemical burn with nitrogen mustard. Thus, there may be a potential therapeutic benefit of treating nitrogen mustard-induced skin lesions with agonists of CXCR2 to facilitate the wound repair process.
Nonpeptide CXCR2 antagonist prevents neutrophil accumulation in hyperoxia-exposed newborn rats.[Pubmed:11561067]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Oct;299(1):90-5.
Neutrophil influx in lung injury is controlled in part by chemokines acting through the receptor, CXCR2. To avoid adverse effects of steroids typically used to modify inflammation, we evaluated the effects of competitive blockade of CXCR2 in rats on neutrophil function in vitro and on neutrophil influx in vivo in hyperoxia-induced newborn lung injury, a model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. In vitro, SB-265610 antagonizes rat cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1 (CINC-1)-induced calcium mobilization, IC50 = 3.7 nM, and rat neutrophil chemotaxis in a concentration-dependent manner, IC50 = 70 nM. In vivo, newborn rats exposed to 95% O2 for 8 days had increased lung neutrophil content. Injection with 1 to 3 mg/kg SB-265610 on days 3 to 5 reduced hyperoxia-induced neutrophil accumulation in bronchoalveolar lavage and whole lung myeloperoxidase accumulation at the highest doses. To determine whether these effects might be due in part to increased neutrophil apoptosis, peripheral neutrophils were cultured with and without SB-265610. Apoptosis was assessed by morphology, viability, and terminal transferase deoxyuridine triphosphatidyl nucleotide nick-end labeling. Treatment of neutrophils with CINC-1 reduced apoptosis compared with untreated neutrophils. SB-265610 reduced the antiapoptotic effect of CINC-1 to the levels of those untreated with CINC-1. A selective CXCR2 antagonist may be useful in diseases where neutrophil-mediated exacerbation is present.


