PNU-120596α7 nAChR modulator,positive allosteric CAS# 501925-31-1 |
- PF-562271
Catalog No.:BCC3674
CAS No.:717907-75-0
- TAE226 (NVP-TAE226)
Catalog No.:BCC3885
CAS No.:761437-28-9
- PF-573228
Catalog No.:BCC4496
CAS No.:869288-64-2
- PF-00562271
Catalog No.:BCC3684
CAS No.:939791-38-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 501925-31-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 311434 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H14ClN3O4 | M.Wt | 311.73 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | NSC 216666 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (160.40 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
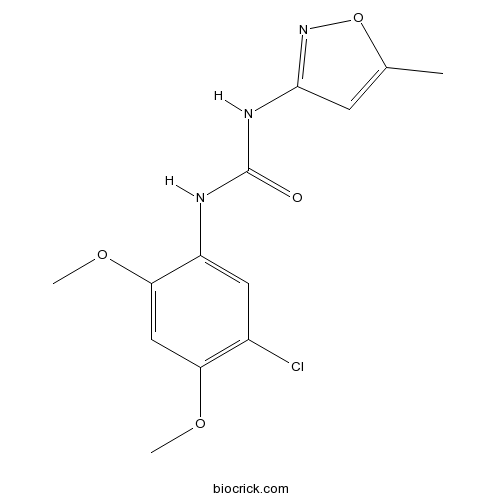
| Chemical Name | 1-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-3-yl)urea | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC(=NO1)NC(=O)NC2=CC(=C(C=C2OC)OC)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CEIIEALEIHQDBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H14ClN3O4/c1-7-4-12(17-21-7)16-13(18)15-9-5-8(14)10(19-2)6-11(9)20-3/h4-6H,1-3H3,(H2,15,16,17,18) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Positive allosteric modulator of α7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (EC50 = 216 nM), with no detectable effect on α4β2, α3β4 and α9α10 receptors. Active in vivo following systemic administration. Neuroprotective in an in vivo model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. |

PNU-120596 Dilution Calculator

PNU-120596 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2079 mL | 16.0395 mL | 32.079 mL | 64.1581 mL | 80.1976 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6416 mL | 3.2079 mL | 6.4158 mL | 12.8316 mL | 16.0395 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3208 mL | 1.604 mL | 3.2079 mL | 6.4158 mL | 8.0198 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0642 mL | 0.3208 mL | 0.6416 mL | 1.2832 mL | 1.604 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0321 mL | 0.1604 mL | 0.3208 mL | 0.6416 mL | 0.802 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
PNU-120596 is a positive allosteric modulator of α7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) [1].
PNU-120596 is a type 2 PAM. In cell-based assay, PNU-120596 significantly increases the Ca2+-mediated signal at the concentration of 3μM. It enhances the ACh-evoked Ca22+ flux with EC50 value of 216nM in SH-EP1 cells. PNU-120596 also markedly increases the agonist-evoked currents as well as the current duration in Xenopus oocytes. PNU-120596 is specific to α7nAChR over other neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. PNU-120596 also potentiates the ACh responses mediated byα7nAChRs in rat hippocampal interneurons. It is considered that PNU-120596 modulates the ACh-dependent increase via enhancing the excitatory effect of ACh on GABAergic interneurons. Furthermore, PNU-120596 is found to improve performance in rodent recognition memory model with increasing the phosphorylation of CREB [1, 2].
References:
[1] Hurst R S, Hajós M, Raggenbass M, et al. A novel positive allosteric modulator of the α7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: in vitro and in vivo characterization. The Journal of neuroscience, 2005, 25(17): 4396-4405.
[2] Bertrand D, Gopalakrishnan M. Allosteric modulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochemical pharmacology, 2007, 74(8): 1155-1163.
- NSC 74859
Catalog No.:BCC3701
CAS No.:501919-59-1
- NS 1738
Catalog No.:BCC7535
CAS No.:501684-93-1
- BI-D1870
Catalog No.:BCC5030
CAS No.:501437-28-1
- 5,6,7,4'-Tetrahydroxyflavanone 6,7-diglucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1434
CAS No.:501434-65-7
- Pilosol A
Catalog No.:BCC9121
CAS No.:501086-15-3
- 2,3-Di-O-methylthiomethyleuscaphic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5610
CAS No.:
- Phloretic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2950
CAS No.:501-97-3
- Rhododendrol
Catalog No.:BCN5609
CAS No.:501-96-2
- 2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanol
Catalog No.:BCN5608
CAS No.:501-94-0
- Hydrocinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4057
CAS No.:501-52-0
- Resveratrol
Catalog No.:BCN5607
CAS No.:501-36-0
- 8-Azabicyclo-3.2.1-octan-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1888
CAS No.:501-33-7
- SB705498
Catalog No.:BCC3854
CAS No.:501951-42-4
- Lycopene
Catalog No.:BCN5410
CAS No.:502-65-8
- Phytone
Catalog No.:BCN4628
CAS No.:502-69-2
- Cyclopentadecanone
Catalog No.:BCN3822
CAS No.:502-72-7
- HLI 373
Catalog No.:BCC2408
CAS No.:502137-98-6
- H-Trp-NH2.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3112
CAS No.:5022-65-1
- NIDA 41020
Catalog No.:BCC7810
CAS No.:502486-89-7
- SQ109
Catalog No.:BCC1962
CAS No.:502487-67-4
- Lonidamine
Catalog No.:BCC9012
CAS No.:50264-69-2
- Phloracetophenone 4'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4052
CAS No.:5027-30-5
- Oleuropeic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5611
CAS No.:5027-76-9
- Erythrocentaurin
Catalog No.:BCN7684
CAS No.:50276-98-7
The dual effect of PNU-120596 on alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channels.[Pubmed:24036349]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;718(1-3):226-34.
PNU-120596 (1-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)urea), a Type-II positive allosteric modulator of alpha(7) nicotinic acetylcholine receptors inhibits alpha(7) desensitization and robustly prolongs openings of alpha(7) channels. However, these effects may render alpha(7) channels more accessible to positively charged molecules and thus, more susceptible to voltage-dependent open-channel-block-like inhibition. To test this hypothesis, choline chloride (i.e., choline), a selective endogenous alpha(7) agonist, and bicuculline methochloride (i.e., bicuculline), a competitive alpha(7) antagonist, were used as membrane voltage-sensitive probes in whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings from hippocampal CA1 interneurons in acute brain slices in the absence and presence of PNU-120596. PNU-120596 enhanced voltage-dependent inhibition of alpha(7) responses by bicuculline and choline. In the presence of PNU-120596, alpha(7) channels favored a burst-like kinetic modality in the presence, but not absence of bicuculline and bursts of alpha(7) openings were voltage-dependent. These results suggest that PNU-120596 alters the pharmacology of alpha(7) channels by making these channels more susceptible to voltage-dependent inhibitory interactions with positively charged drugs at concentrations that do not potently inhibit alpha(7) channels without PNU-120596. This inhibition imitates alpha(7) nicotinic receptor desensitization and compromises the potentiating anti-desensitization effects of PNU-120596 on alpha(7) nicotinic receptors. This unexpected dual action of PNU-120596, and possibly other Type-II positive allosteric modulators of alpha(7) nicotinic receptors, may lead to unanticipated alpha(7) channel-drug interactions and misinterpretation of alpha(7) single-channel data.
Mode of action of the positive modulator PNU-120596 on alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.[Pubmed:24486377]
Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jun;81:42-54.
We investigated the mode of action of PNU-120596, a type II positive allosteric modulator of the rat alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expressed by GH4C1 cells, using patch-clamp and fast solution exchange. We made two important observations: first, while PNU-120596 rapidly associated to desensitized receptors, it had at least hundredfold lower affinity to resting conformation, therefore at 10 muM concentration it dissociated from resting receptors; and second, binding of PNU-120596 slowed down dissociation of choline molecules from the receptor radically. We propose that when agonist concentration is transiently elevated in the continuous presence of the modulator (as upon the neuronal release of acetylcholine in a modulator-treated animal) these two elements together cause occurrence of a cycle of events: Binding of the modulator is limited in the absence of the agonist. When the agonist is released, it binds to the receptor, and induces desensitization, thereby enabling modulator binding. Modulator binding in turn traps the agonist within its binding site for a prolonged period of time. Once the agonist finally dissociated, the modulator can also dissociate without re-binding, and the receptor assumes its original resting conformation. In kinetic simulations this "trapped agonist cycle" mechanism did not require that the orthosteric and allosteric ligands symmetrically modify each other's affinity, only the modulator must decrease agonist accessibility, and the agonist must induce a conformation that is accessible to the modulator. This mechanism effectively prolongs and amplifies the effect of the agonist.
Positive allosteric modulator of alpha7 nicotinic-acetylcholine receptors, PNU-120596 augments the effects of donepezil on learning and memory in aged rodents and non-human primates.[Pubmed:23168113]
Neuropharmacology. 2013 Apr;67:201-12.
The development of novel therapeutic agents for disorders of cognition such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) is of paramount importance given the ever-increasing elderly population, however; there is also considerable interest in any strategy that might enhance the clinical efficacy of currently available treatments. The purpose of this study was to evaluate an adjunctive treatment strategy to memory enhancement, namely combining the commonly prescribed acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI) donepezil, with a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of alpha7 nicotinic-acetylcholine receptors (alpha7-nAChRs), PNU-120596. The treatment strategy was evaluated in a (non-spatial) spontaneous novel object recognition (NOR) task in young rats; a water maze spatial learning and recall procedure in aged, cognitively-impaired rats, and a delayed match to sample (working/short term memory) task in aged rhesus monkeys. In all three experiments a similar drug response was observed, namely that donepezil administered alone improved task performance in a dose-dependent manner; that PNU-120596 administered alone was without significant effect, but that the combination of PNU-120596 with a subthreshold dose of donepezil was effective. The positive effect of the drug combination appeared to be alpha7-nAChR mediated given that it was blocked in the NOR task by the selective alpha7-nAChR antagonist methyllycaconitine (MLA). Collectively, these data indicate that PNU-120596 increases the effective dose range of donepezil in learning/memory-related tasks in young and age-impaired animal models. The results suggest that alpha7-nAChR-selective PAMs like PNU-120596 have potential as adjunctive treatments with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., donepezil) for age-related illnesses such as AD as well memory disorders not necessarily associated with advanced age.
An Unaltered Orthosteric Site and a Network of Long-Range Allosteric Interactions for PNU-120596 in alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors.[Pubmed:26211363]
Chem Biol. 2015 Aug 20;22(8):1063-73.
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are vital to neuronal signaling, are implicated in important processes such as learning and memory, and are therapeutic targets for neural diseases. The alpha7 nAChR has been implicated in Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia, and allosteric modulators have become one focus of drug development efforts. We investigate the mode of action of the alpha7-selective positive allosteric modulator, PNU-120596, and show that the higher potency of acetylcholine in the presence of PNU-120596 is not due to an altered agonist binding site. In addition, we propose several residues in the gating interface and transmembrane region that are functionally important to transduction of allosteric properties, and link PNU-120596, the acetylcholine binding region, and the receptor gate. These results suggest global protein stabilization from a communication network through several key residues that alter the gating equilibrium of the receptor while leaving the agonist binding properties unperturbed.
A positive allosteric modulator of alpha7 nAChRs augments neuroprotective effects of endogenous nicotinic agonists in cerebral ischaemia.[Pubmed:23713819]
Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;169(8):1862-78.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Activation of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) can be neuroprotective. However, endogenous choline and ACh have not been regarded as potent neuroprotective agents because physiological levels of choline/ACh do not produce neuroprotective levels of alpha7 activation. This limitation may be overcome by the use of type-II positive allosteric modulators (PAMs-II) of alpha7 nAChRs, such as 1-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)-urea (PNU-120596). This proof-of-concept study presents a novel neuroprotective paradigm that converts endogenous choline/ACh into potent neuroprotective agents in cerebral ischaemia by inhibiting alpha7 nAChR desensitization using PNU-120596. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: An electrophysiological ex vivo cell injury assay (to quantify the susceptibility of hippocampal neurons to acute injury by complete oxygen and glucose deprivation; COGD) and an in vivo middle cerebral artery occlusion model of ischaemia were used in rats. KEY RESULTS: Choline (20-200 muM) in the presence, but not absence of 1 muM PNU-120596 significantly delayed anoxic depolarization/injury of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons, but not CA1 stratum radiatum interneurons, subjected to COGD in acute hippocampal slices and these effects were blocked by 20 nM methyllycaconitine, a selective alpha7 antagonist, thus, activation of alpha7 nAChRs was required. PNU-120596 alone was ineffective ex vivo. In in vivo experiments, both pre- and post-ischaemia treatments with PNU-120596 (30 mg.kg(-1) , s.c. and 1 mg.kg(-1) , i.v., respectively) significantly reduced the cortical/subcortical infarct volume caused by transient focal cerebral ischaemia. PNU-120596 (1 mg.kg(-1) , i.v., 30 min post-ischaemia) remained neuroprotective in rats subjected to a choline-deficient diet for 14 days prior to experiments. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: PNU-120596 and possibly other PAMs-II significantly improved neuronal survival in cerebral ischaemia by augmenting neuroprotective effects of endogenous choline/ACh.
An allosteric modulator of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor possessing cognition-enhancing properties in vivo.[Pubmed:17625074]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Oct;323(1):294-307.
Augmentation of nicotinic alpha7 receptor function is considered to be a potential therapeutic strategy aimed at ameliorating cognitive and mnemonic dysfunction in relation to debilitating pathological conditions, such as Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia. In the present report, a novel positive allosteric modulator of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), 1-(5-chloro-2-hydroxy-phenyl)-3-(2-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-urea (NS1738), is described. NS1738 was unable to displace or affect radioligand binding to the agonist binding site of nicotinic receptors, and it was devoid of effect when applied alone in electrophysiological paradigms. However, when applied in the presence of acetylcholine (ACh), NS1738 produced a marked increase in the current flowing through alpha7 nAChRs, as determined in both oocyte electrophysiology and patch-clamp recordings from mammalian cells. NS1738 acted by increasing the peak amplitude of ACh-evoked currents at all concentrations; thus, it increased the maximal efficacy of ACh. Oocyte experiments indicated an increase in ACh potency as well. NS1738 had only marginal effects on the desensitization kinetics of alpha7 nAChRs, as determined from patch-clamp studies of both transfected cells and cultured hippocampal neurons. NS1738 was modestly brain-penetrant, and it was demonstrated to counteract a (-)-scopolamine-induced deficit in acquisition of a water-maze learning task in rats. Moreover, NS1738 improved performance in the rat social recognition test to the same extent as (-)-nicotine, demonstrating that NS1738 is capable of producing cognitive enhancement in vivo. These data support the notion that alpha7 nAChR allosteric modulation may constitute a novel pharmacological principle for the treatment of cognitive dysfunction.
A novel positive allosteric modulator of the alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: in vitro and in vivo characterization.[Pubmed:15858066]
J Neurosci. 2005 Apr 27;25(17):4396-405.
Several lines of evidence suggest a link between the alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) and brain disorders including schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, and traumatic brain injury. The present work describes a novel molecule, 1-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(5-methyl-isoxazol-3-yl)-urea (PNU-120596), which acts as a powerful positive allosteric modulator of the alpha7 nAChR. Discovered in a high-throughput screen, PNU-120596 increased agonist-evoked calcium flux mediated by an engineered variant of the human alpha7 nAChR. Electrophysiology studies confirmed that PNU-120596 increased peak agonist-evoked currents mediated by wild-type receptors and also demonstrated a pronounced prolongation of the evoked response in the continued presence of agonist. In contrast, PNU-120596 produced no detectable change in currents mediated by alpha4beta2, alpha3beta4, and alpha9alpha10 nAChRs. PNU-120596 increased the channel mean open time of alpha7 nAChRs but had no effect on ion selectivity and relatively little, if any, effect on unitary conductance. When applied to acute hippocampal slices, PNU-120596 increased the frequency of ACh-evoked GABAergic postsynaptic currents measured in pyramidal neurons; this effect was suppressed by TTX, suggesting that PNU-120596 modulated the function of alpha7 nAChRs located on the somatodendritic membrane of hippocampal interneurons. Accordingly, PNU-120596 greatly enhanced the ACh-evoked inward currents in these interneurons. Systemic administration of PNU-120596 to rats improved the auditory gating deficit caused by amphetamine, a model proposed to reflect a circuit level disturbance associated with schizophrenia. Together, these results suggest that PNU-120596 represents a new class of molecule that enhances alpha7 nAChR function and thus has the potential to treat psychiatric and neurological disorders.


