MC 976Vitamin D3 derivative CAS# 129831-99-8 |
- (24R)-MC 976
Catalog No.:BCC1289
CAS No.:112828-09-8
- (24S)-MC 976
Catalog No.:BCC1291
CAS No.:112849-14-6
- 1alpha, 25-Dihydroxy VD2-D6
Catalog No.:BCC1299
CAS No.:216244-04-1
- 1alpha, 24, 25-Trihydroxy VD2
Catalog No.:BCC1298
CAS No.:457048-34-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 129831-99-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71576663 | Appearance | Powder |
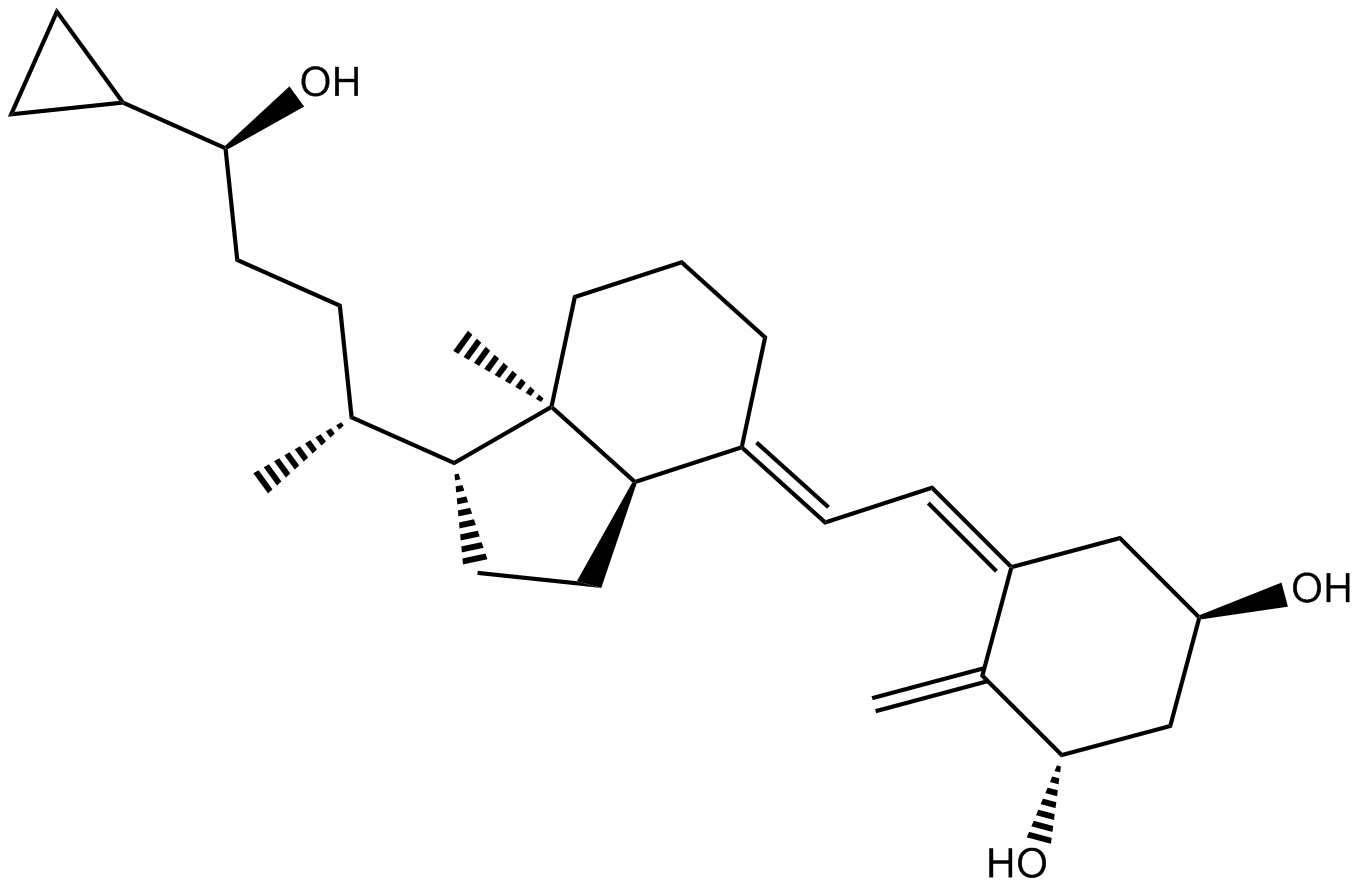
| Formula | C27H42O3 | M.Wt | 414.62 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | (1R,3S,5Z)-5-[(2E)-2-[(1R,7aR)-1-[(2R)-5-cyclopropyl-5-hydroxypentan-2-yl]-7a-methyl-2,3,3a,5,6,7-hexahydro-1H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]-4-methylidenecyclohexane-1,3-diol | ||
| SMILES | CC(CCC(C1CC1)O)C2CCC3C2(CCCC3=CC=C4CC(CC(C4=C)O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NQHWMFGCRBTMOO-KJLYFKKZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H42O3/c1-17(6-13-25(29)20-8-9-20)23-11-12-24-19(5-4-14-27(23,24)3)7-10-21-15-22(28)16-26(30)18(21)2/h7,10,17,20,22-26,28-30H,2,4-6,8-9,11-16H2,1,3H3/b19-7+,21-10-/t17-,22-,23-,24?,25?,26+,27-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | MC 976 is a derivative of Vitamin D3. |

MC 976 Dilution Calculator

MC 976 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4118 mL | 12.0592 mL | 24.1185 mL | 48.2369 mL | 60.2962 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4824 mL | 2.4118 mL | 4.8237 mL | 9.6474 mL | 12.0592 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2412 mL | 1.2059 mL | 2.4118 mL | 4.8237 mL | 6.0296 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0482 mL | 0.2412 mL | 0.4824 mL | 0.9647 mL | 1.2059 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0241 mL | 0.1206 mL | 0.2412 mL | 0.4824 mL | 0.603 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
MC 969 is an analog of the calcemic drug 1α-hydroxyvitamin D3 (1α-OH-D3) whose carbons 25, 26, and 27 in the side chain are incorporated into a cyclopropane ring. MC 976 is the in vitro metabolite of MC 969.
In vitro: Metabolite of MC 976 was generated by incubation of MC 969 in an novel in vitro human hepatocyte cell model (Hep 3B) [1].
In vivo: MC 969 and other VD3 cyclopropane ring-analogs were previously found to possess potent calcemic effects in rat in vivo [2].
Clinical trial: Currently there is no clinical data available for MC 969 and its analogues .
References:
[1] Strugnell S, Calverley MJ, Jones G. Metabolism of a cyclopropane-ring-containing analog of 1 alpha-hydroxyvitamin D3 in a hepatocyte cell model. Identification of 24-oxidized metabolites. Biochemical Pharmacology,1990; 40(2):333-341.
[2] Jones G and DeLuca HF. High-performance liquid chromatography of vitamin D and its application to endocrinology. In: Monographs on Endocrinology, Vol. 30: High-performance liquid chromatography in endocrinology (Eds. Makin HLJ and Newton R), pp. 95-139. Springer, Berlin, 1988.
- ODM-201
Catalog No.:BCC3796
CAS No.:1297538-32-9
- Anemoside B4
Catalog No.:BCN1276
CAS No.:129741-57-7
- Anemoside A3
Catalog No.:BCN2328
CAS No.:129724-84-1
- 3-Hydroxylanost-9(11)-24-dien-26-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1586
CAS No.:129724-83-0
- 2',4'-Dihydroxy-3',6'-dimethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN6158
CAS No.:129724-43-2
- Aripiprazole
Catalog No.:BCC5034
CAS No.:129722-12-9
- Dofequidar
Catalog No.:BCC4176
CAS No.:129716-58-1
- ZD 7114 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6852
CAS No.:129689-28-7
- 3,4-Dihydroxybisabola-1,10-diene
Catalog No.:BCN7326
CAS No.:129673-87-6
- 3-Hydroxybisabola-1,10-dien-9-one
Catalog No.:BCN7325
CAS No.:129673-86-5
- GR 82334
Catalog No.:BCC5802
CAS No.:129623-01-4
- Nevirapine
Catalog No.:BCC3820
CAS No.:129618-40-2
- Amicarbazone
Catalog No.:BCC5464
CAS No.:129909-90-6
- Dapoxetine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5064
CAS No.:129938-20-1
- Iloperidone hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4212
CAS No.:1299470-39-5
- Senecionine
Catalog No.:BCN2129
CAS No.:130-01-8
- 1,4-Naphthoquinone
Catalog No.:BCN8420
CAS No.:130-15-4
- Thioridazine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3869
CAS No.:130-61-0
- Protopine
Catalog No.:BCN6165
CAS No.:130-86-9
- Quinine HCl
Catalog No.:BCN2262
CAS No.:130-89-2
- Quinine
Catalog No.:BCN2341
CAS No.:130-95-0
- I-BET151 (GSK1210151A)
Catalog No.:BCC4476
CAS No.:1300031-49-5
- GSK1324726A
Catalog No.:BCC4038
CAS No.:1300031-52-0
- Dehydrocorydaline nitrate
Catalog No.:BCN2745
CAS No.:13005-09-9
Sustained Viral Suppression in HIV-infected Children on Once-daily Lopinavir/Ritonavir in Clinical Practice.[Pubmed:28475554]
Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2017 Oct;36(10):976-980.
BACKGROUND: The use of lopinavir/ritonavir once-daily (LPV/r QD) has not been approved for children. Good short-term clinical, virologic and immunologic outcomes have been observed in children on LPV/r QD. METHODS: We evaluated the long-term effectiveness of a LPV/r QD containing regimen in HIV-1-infected children in clinical practice. Selected children (0-18 years of age) with an undetectable HIV-1 RNA viral load (<50 copies/mL) for at least 6 months on a twice-daily LPV/r-containing regimen switched to LPV/r QD. The main outcome measures were the percentage of patients with an undetectable HIV-1 viral load each subsequent year after switch to LPV/r QD (on treatment and last observation carried forward), and virologic failure during follow-up (>400 copies/mL twice within 6 months). Also, the exposure to LPV on the initial once-daily dosing regimen was determined. RESULTS: Forty children (median age: 6.5 years; range: 1.0-17) were included. Median follow-up was 6.3 years (range: 1.0-10.3). During yearly follow-up, the percentage of children with an undetectable viral load varied between 82% and 100% (on treatment) and 83% and 93% (last observation carried forward). Five children (12.5%) met the criteria for failure. CD4+ and CD8+ counts remained stable at normal values. Geometric mean LPV area under the plasma concentration-time curve (linear up-log down method) over a dosing interval from time 0 to 24 hours after dosing was 169.3 mg x h/L, and last observed drug concentration was 1.35 mg/L. Adverse events were encountered in 8 patients, were mainly gastrointestinal, and in these cases, no reason to stop treatment. CONCLUSION: A once-daily LPV/r-containing regimen in HIV-1-infected children with intensive clinical and therapeutic drug monitoring is well tolerated and has good long-term clinical, virologic and immunologic outcomes.
A reference panel of 64,976 haplotypes for genotype imputation.[Pubmed:27548312]
Nat Genet. 2016 Oct;48(10):1279-83.
We describe a reference panel of 64,976 human haplotypes at 39,235,157 SNPs constructed using whole-genome sequence data from 20 studies of predominantly European ancestry. Using this resource leads to accurate genotype imputation at minor allele frequencies as low as 0.1% and a large increase in the number of SNPs tested in association studies, and it can help to discover and refine causal loci. We describe remote server resources that allow researchers to carry out imputation and phasing consistently and efficiently.
Association of Vasomotor and Other Menopausal Symptoms with Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.[Pubmed:27315068]
PLoS One. 2016 Jun 17;11(6):e0157417.
IMPORTANCE: Vasomotor symptoms (hot flushes and night sweats) and other symptoms, including depression, anxiety and panic attacks, are commonly experienced by menopausal women and have been associated with an unfavourable cardiovascular risk profile. OBJECTIVE: To investigate whether presence of menopausal symptoms is associated with the development of cardiovascular disease (CVD). METHODS: Five electronic databases (Medline, EMBASE and Web of Science) were search until February 17th, 2015 to identify relevant studies. Observational cohort studies or randomised intervention studies were eligible for inclusion if they followed participants prospectively (at least 1 year of follow-up), and reported relevant estimates on the association of any vasomotor symptoms, or other menopausal symptoms, with risk of CVD, coronary heart disease (CHD), or stroke in perimenopausal, menopausal, or postmenopausal women. Data were extracted by two independent reviewers using a pre-designed data collection form. Separate pooled relative risks (RRs) for age and non-established cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., education, ethnicity) adjusted data and for established cardiovascular risk factors and potential mediators-adjusted data (e.g., smoking, body mass index, and hypertension) were calculated. RESULTS: Out of 9,987 initially identified references, ten studies were selected, including 213,976 women with a total of 10,037 cardiovascular disease outcomes. The age and non-established cardiovascular risk factors adjusted RRs) [95% confidence intervals] for development of CHD, Stroke and CVD comparing women with and without any menopausal symptoms were 1.34 [1.13-1.58], 1.30 [0.99-1.70], 1.48 [1.21-1.80] respectively, and the corresponding RRs adjusted for cardiovascular risk factors and potential mediators were 1.18 [1.03-1.35], 1.08 [0.89-1.32], 1.29 [0.98-1.71]. However, these analyses were limited by potential unmeasured confounding and the small number of studies on this topic. CONCLUSION: Presence of vasomotor symptoms and other menopausal symptoms are generally associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, which is mainly explained by cardiovascular risk factors.
Raman Spectroscopic Characterization of Melanoma and Benign Melanocytic Lesions Suspected of Melanoma Using High-Wavenumber Raman Spectroscopy.[Pubmed:27382927]
Anal Chem. 2016 Aug 2;88(15):7683-8.
Melanoma is a pigmented type of skin cancer, which has the highest mortality of all skin cancers. Because of the low clinical diagnostic accuracy for melanoma, an objective tool is needed to assist clinical assessment of skin lesions that are suspected of (early) melanoma. The aim of this study was to identify spectral differences in the CH region of HWVN (high-wavenumber) Raman spectra between melanoma and benign melanocytic lesions clinically suspected of melanoma. We used these spectral differences to explore preliminary classification models to distinguish melanoma from benign melanocytic lesions. Data from 82 freshly excised melanocytic lesions clinically suspected of melanoma were measured using an in-house built Raman spectrometer, which has been optimized for measurements on pigmented skin lesions (excitation wavelength 976 nm and a wavelength range of the Raman signal 1340-1540 nm). Clear spectral differences were observed between melanoma and benign melanocytic lesions. These differences can be assigned mainly to the symmetric CH2 stretching vibrations of lipids. Our results show that the Raman bands between 2840 and 2930 cm(-1) have increased intensity for melanoma when compared to benign melanocytic lesions, suggesting an increase in lipid content in melanoma. These results demonstrate that spectroscopic information in the CH-stretching region of HWVN Raman spectra can discriminate melanoma from benign melanocytic lesions that are often clinically misdiagnosed as melanoma and that Raman spectroscopy has the potential to provide an objective clinical tool to improve the clinical diagnostic accuracy of skin lesions suspected of melanoma.
Patent Foramen Ovale Closure for Hypoxemia.[Pubmed:28886845]
Interv Cardiol Clin. 2017 Oct;6(4):547-554.
A patent foramen ovale (PFO) is a common anatomic finding in 20% of the normal population. Significant hypoxemia can occur in circumstances in which hemodynamic or anatomic changes predispose to increased right-to-left intra-atrial shunting. The subsequent hypoxemia produces substantial dyspnea that may affect the patient's quality of life, independent of underlying pulmonary disease. Profound hypoxemia caused by right-to-left shunt across the interatrial septum usually responds to percutaneous PFO closure. An important impediment to successful treatment is the lack of awareness of the potential role of a PFO in this condition.


