HerbacetinCAS# 527-95-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 527-95-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5280544 | Appearance | White-yellow powder |
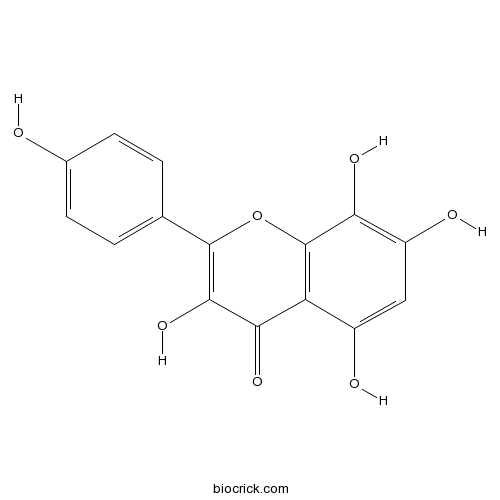
| Formula | C15H10O7 | M.Wt | 302.24 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 8-Hydroxykaempferol; Isoarticulatidin; 3,4',5,7,8-Pentahydroxyflavone | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in methan | ||
| Chemical Name | 3,5,7,8-tetrahydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C2=C(C(=O)C3=C(O2)C(=C(C=C3O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZDOTZEDNGNPOEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H10O7/c16-7-3-1-6(2-4-7)14-13(21)12(20)10-8(17)5-9(18)11(19)15(10)22-14/h1-5,16-19,21H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Herbacetin, a novel Met inhibitor with a potential utility in cancer therapeutics, suppresses the HGF-induced motility of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by inhibiting c-Met and Akt phosphorylation. Herbacetin exerts an anti-inflammatory effect through suppression of LPS-induced JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways and diminished production of proinflammatory cytokines and mediators. Herbacetin also has a strong ability to scavenge free radical and inhibit oxidative protein damage. |
| Targets | NO | TNF-α | JNK | ERK | NF-kB | NOS | p38MAPK | Akt | ROS | PARP | PI3K | Caspase |
| In vitro | Herbacetin inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase via JNK and nuclear factor-κB in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.[Pubmed: 26297979 ]Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 15;765:115-23.Herbacetin (3,4',5,7,8-pentahydroxyflavone), an active flavonol compound within flavonoid, has been shown to induce apoptosis in HepG2 cells and suppress hepatocyte growth factor-induced motility of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. However, the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of Herbacetin have not been researched. Herbacetin, a constituent of ephedrae herba, suppresses the HGF-induced motility of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by inhibiting c-Met and Akt phosphorylation.[Pubmed: 24081687]Planta Med. 2013 Nov;79(16):1525-30.Ephedrae herba suppresses hepatocyte growth factor-induced cancer cell motility by inhibiting tyrosine phosphorylation of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-Met, and the PI3K/Akt pathway. Moreover, Ephedrae herba directly inhibits the tyrosine-kinase activity of c-Met. Ephedrine-type alkaloids, which are the active component of Ephedrae herba, do not affect hepatocyte growth factor-c-Met-Akt signalling, prompting us to study other active molecules in the herb. In vitro Free Radical Scavenging and Protein Oxidation Inhibitory Effects of Herbacetin[Reference: WebLink]Food Science, 2013, 34(17):106-10.
|
| Kinase Assay | Herbacetin induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells: Involvements of ROS and PI3K/Akt pathway.[Pubmed: 23063593]Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Jan;51:426-33.Herbacetin (HER) is a natural flavonoid compound that can be extracted from Ramose Scouring Rush Herb, and its biological and pharmacological activities lack of corresponding attention. |
| Structure Identification | Phytochemistry, 1969, 8(1):177-83.Gossypetin and Herbacetin as taxonomic markers in higher plants.[Reference: WebLink]Four yellow flavonol pigments earlier reported in the Leguminosae, Ericaceae and Papaveraceae as quercetagetin glycosides have now been found to be the isomeric gossypetin derivatives. |

Herbacetin Dilution Calculator

Herbacetin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3086 mL | 16.5431 mL | 33.0863 mL | 66.1726 mL | 82.7157 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6617 mL | 3.3086 mL | 6.6173 mL | 13.2345 mL | 16.5431 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3309 mL | 1.6543 mL | 3.3086 mL | 6.6173 mL | 8.2716 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0662 mL | 0.3309 mL | 0.6617 mL | 1.3235 mL | 1.6543 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0331 mL | 0.1654 mL | 0.3309 mL | 0.6617 mL | 0.8272 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Azomycin
Catalog No.:BCC5315
CAS No.:527-73-1
- Sodium Gluconate
Catalog No.:BCC4721
CAS No.:527-07-1
- D-Penylalaninol
Catalog No.:BCC2715
CAS No.:5267-64-1
- A23187, free acid
Catalog No.:BCC6980
CAS No.:52665-69-7
- Kirenol
Catalog No.:BCN5682
CAS No.:52659-56-0
- Anisodine
Catalog No.:BCN1868
CAS No.:52646-92-1
- Siegeskaurolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6982
CAS No.:52645-97-3
- Dehydroadynerigenin digitaloside
Catalog No.:BCN4623
CAS No.:52628-62-3
- Huwentoxin IV
Catalog No.:BCC6270
CAS No.:526224-73-7
- Gnetofuran B
Catalog No.:BCN7764
CAS No.:526214-79-9
- Isomorellic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3074
CAS No.:5262-69-1
- Ponicidin
Catalog No.:BCN3231
CAS No.:52617-37-5
- Ginsenoside Rd
Catalog No.:BCN1074
CAS No.:52705-93-8
- Scillascillin
Catalog No.:BCN5684
CAS No.:52706-07-7
- Isoelemicin
Catalog No.:BCN4760
CAS No.:5273-85-8
- beta-Asarone
Catalog No.:BCN5685
CAS No.:5273-86-9
- Medicarpin 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7773
CAS No.:52766-70-8
- PHA 568487
Catalog No.:BCC7574
CAS No.:527680-57-5
- H-D-Phe(3,4-DiCl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3179
CAS No.:52794-98-6
- H-Phe(3,4-DiCl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3178
CAS No.:52794-99-7
- Magnolol
Catalog No.:BCN5687
CAS No.:528-43-8
- Fisetin
Catalog No.:BCN5024
CAS No.:528-48-3
- Delphinidin chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3015
CAS No.:528-53-0
- Cyanidin Chloride
Catalog No.:BCN1231
CAS No.:528-58-5
Herbacetin induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells: Involvements of ROS and PI3K/Akt pathway.[Pubmed:23063593]
Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Jan;51:426-33.
Herbacetin (HER) is a natural flavonoid compound that can be extracted from Ramose Scouring Rush Herb, and its biological and pharmacological activities lack of corresponding attention. In this study, the apoptotic effect of HER against the human hepatoma cell line (HepG2) was investigated. The results showed that HepG2 cells apoptosis occurred in a dose-dependent manner within 48h incubated with HER, which was confirmed by DNA fragmentation, nuclear shrinkage, and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage. HER at 25-100muM induced a mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway associated with Bcl-2/Bax ratio decrease, mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsi) collapse, cytochrome c release, and caspase-3 activation. Increasing expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha) was also observed in HER-treated cells. Furthermore, the addition of a ROS inhibitor (N-Acetyl-l-cysteine, NAC) significantly attenuated the apoptosis induced by HER and also blocked the expression of PGC-1alpha protein. Additionally, HER effectively inhibited the phosphorylation of Akt and the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002 increased the inhibition effect of HER on Akt phosphorylation. These findings provide evidences that HER induces HepG2 apoptosis in a ROS-mediated mitochondria-dependent manner that correlate with the inactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway.
Herbacetin inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase via JNK and nuclear factor-kappaB in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.[Pubmed:26297979]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 15;765:115-23.
Herbacetin (3,4',5,7,8-pentahydroxyflavone), an active flavonol compound within flavonoid, has been shown to induce apoptosis in HepG2 cells and suppress hepatocyte growth factor-induced motility of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. However, the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of Herbacetin have not been researched. In this study, we examined the inflammatory responses stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in RAW264.7 macrophage cells after pretreatment with different concentrations of Herbacetin. We found that Herbacetin decreased nitric oxide (NO) production in LPS-induced RAW264.7 and mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. In addition, Herbacetin inhibited the LPS-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA and protein in RAW264.7 cells. Treatment with Herbacetin decreased the release of proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. Moreover, Herbacetin inhibited the activity of JNK kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB, signaling molecules involved in NO production. Cell signaling analysis using Bay 11-7082 (an inhibitory kappaB kinase 2 inhibitor) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitors (SB203580 for p38, SP600125 for JNK, and PD 98059 for ERK) suggested that LPS induced iNOS expression via activation of the JNK and NF-kappaB pathway, but not the p38 and ERK pathway. These findings suggest that Herbacetin exerts an anti-inflammatory effect through suppression of LPS-induced JNK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways and diminished production of proinflammatory cytokines and mediators.
Herbacetin, a constituent of ephedrae herba, suppresses the HGF-induced motility of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by inhibiting c-Met and Akt phosphorylation.[Pubmed:24081687]
Planta Med. 2013 Nov;79(16):1525-30.
Ephedrae herba suppresses hepatocyte growth factor-induced cancer cell motility by inhibiting tyrosine phosphorylation of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-Met, and the PI3K/Akt pathway. Moreover, Ephedrae herba directly inhibits the tyrosine-kinase activity of c-Met. Ephedrine-type alkaloids, which are the active component of Ephedrae herba, do not affect hepatocyte growth factor-c-Met-Akt signalling, prompting us to study other active molecules in the herb. We recently discovered Herbacetin glycosides and found that their aglycon, Herbacetin, inhibits hepatocyte growth factor-c-Met-Akt signalling. This study revealed a novel biological activity of Herbacetin. Herbacetin suppressed hepatocyte growth factor-induced motility in human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by inhibiting c-Met and Akt phosphorylation and directly inhibiting c-Met tyrosine kinase activity. The effects of Herbacetin were compared to those of kaempferol, apigenin, and isoscutellarein, all of which have similar structures. Herbacetin inhibition of hepatocyte growth factor-induced motility was the strongest of those for the tested flavonols, and only Herbacetin inhibited the hepatocyte growth factor-induced phosphorylation of c-Met. These data suggest that Herbacetin is a novel Met inhibitor with a potential utility in cancer therapeutics.


