GNE-7915Potent and selective LRRK2 inhibitor CAS# 1351761-44-8 |
- HG-10-102-01
Catalog No.:BCC4271
CAS No.:1351758-81-0
- GNE0877
Catalog No.:BCC5369
CAS No.:1374828-69-9
- GNE-9605
Catalog No.:BCC5458
CAS No.:1536200-31-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1351761-44-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 58539171 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H21F4N5O3 | M.Wt | 443.4 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 14.33 mg/mL (32.32 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
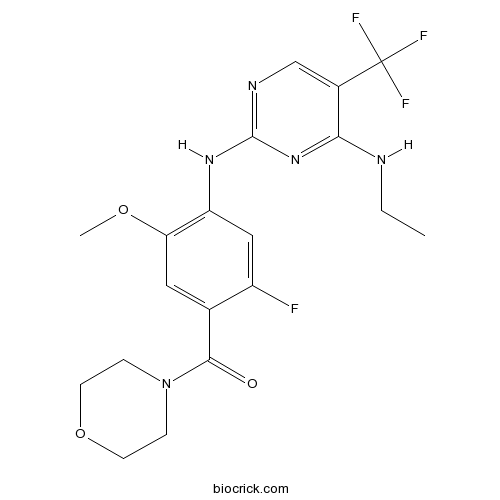
| Chemical Name | [4-[[4-(ethylamino)-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]-2-fluoro-5-methoxyphenyl]-morpholin-4-ylmethanone | ||
| SMILES | CCNC1=NC(=NC=C1C(F)(F)F)NC2=C(C=C(C(=C2)F)C(=O)N3CCOCC3)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XCFLWTZSJYBCPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H21F4N5O3/c1-3-24-16-12(19(21,22)23)10-25-18(27-16)26-14-9-13(20)11(8-15(14)30-2)17(29)28-4-6-31-7-5-28/h8-10H,3-7H2,1-2H3,(H2,24,25,26,27) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | GNE-7915 is a potent, selective and brain-penetrant inhibitor of LRRK2 with an IC50 of 9 nM.In Vitro:Maintaining the methoxy/fluoro arrangement at C-2′/C-5′ and varying aminoalkyl R1 substitution resultes in single-digit nanomolar LRRK2 cellular activities for GNE-7915 and compound 19. Expanded Invitrogen kinase profiling (187 kinases) at 0.1 μM for both GNE-7915 (100-fold over LRRK2 Ki) and 19 (250-fold over LRRK2 Ki) resultes in only TTK showing greater than 50% inhibition. Selectivity profiling using the DiscoverX KinomeScan55 competitive binding assay panel, which includes 392 unique kinases, is also performed for GNE-7915 at 0.1 μM. Binding of >50% probe displacement is detected for 10 kinases and of >65% for only LRRK2, TTK, and ALK, further supporting the excellent LRRK2 selectivity for GNE-7915. Cerep receptor profiling, including expanded brain panels, suggestes that GNE-7915 and 19 only inhibite 5-HT2B with >70% inhibition at 10 μM. GNE-7915 and 19 are confirmed to be moderately potent 5-HT2B antagonists in vitro functional assays[2]. References: | |||||

GNE-7915 Dilution Calculator

GNE-7915 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2553 mL | 11.2765 mL | 22.553 mL | 45.106 mL | 56.3825 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4511 mL | 2.2553 mL | 4.5106 mL | 9.0212 mL | 11.2765 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2255 mL | 1.1276 mL | 2.2553 mL | 4.5106 mL | 5.6382 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0451 mL | 0.2255 mL | 0.4511 mL | 0.9021 mL | 1.1276 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0226 mL | 0.1128 mL | 0.2255 mL | 0.4511 mL | 0.5638 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
GNE-7915 is a highly potent, selective, and brain-penetrable leucine-rich repeat kinase2 (LRRK2) inhibitor, with Ki and IC50 of 1 nM and 9 nM, respectively.
GEN-7915 is extensive inhibitor across 187 screened kinases, except TTK kinase. In an extended profile across 392 kinases, GNE-7915 only bound to 10 enzymes to a significant extent (>50% probe displaced at 100 nM). GNE-7915 and its progenitors are the first selective LRRK2 inhibitors to penetrating the brain barrier. [1]
GEN-7915 has been shown to induce dephosphorylation of LRRK2 in the brain of transgenic mice. GNE-7915 is not reported to cause cellular or genetic toxicity, and has progressed into preclinical studies in cynomolgus monkeys [3]. The use of in silico modelling, extensive in vitro assays and resource-efficient in vivo techniques to produce GNE-7915, reflects a trend towards the concerted optimisation of potency, selectivity and pharmacokinetic properties in early-stage drug development [1]. GNE-7915 can inhibit TNFαand CXCL10 at higher concentrations (≥ 3 μM) in both WT and LRRK2 KO experiments [2].
References:
1.Kavanagh ME, Doddareddy MR, Kassiou M. The development of CNS-active LRRK2 inhibitors using property-directed optimisation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Jul 1;23(13):3690-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.04.086. Epub 2013 May 9.
2.Luerman GC, Nguyen C, Samaroo H et al. Phosphoproteomic evaluation of pharmacological inhibition of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 reveals significant off-target effects of LRRK-2-IN-1. J Neurochem. 2014 Feb;128(4):561-76. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12483. Epub 2013 Nov 11.
3.Estrada AA, Liu X, Baker-Glenn C et al. Discovery of highly potent, selective, and brain-penetrable leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) small molecule inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2012 Nov 26;55(22):9416-33. doi: 10.1021/jm301020q. Epub 2012 Oct 15.
- HG-10-102-01
Catalog No.:BCC4271
CAS No.:1351758-81-0
- ONO-4059
Catalog No.:BCC6463
CAS No.:1351635-67-0
- 21,23:24,25-Diepoxy-21,23-dimethoxytirucall-7-en-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN1581
CAS No.:1351617-74-7
- Amooracetal
Catalog No.:BCN6876
CAS No.:1351617-73-6
- Sarpogrelate hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5247
CAS No.:135159-51-2
- H-DL-Ala-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2854
CAS No.:13515-97-4
- H-Sar-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3335
CAS No.:13515-93-0
- 2',7-Dihydroxy-5,8-dimethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN4041
CAS No.:1351338-14-1
- Z-Tyr-OMe
Catalog No.:BCC2746
CAS No.:13512-31-7
- Fmoc-Nva-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3302
CAS No.:135112-28-6
- Camelliaside A
Catalog No.:BCN3871
CAS No.:135095-52-2
- kb-NB77-78
Catalog No.:BCC5462
CAS No.:1350622-33-1
- H-Val-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3143
CAS No.:13518-40-6
- Sanggenol P
Catalog No.:BCN4766
CAS No.:1351931-30-0
- 3Beta-acetoxy-eupha-7,25-dien-24(R)-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1580
CAS No.:1352001-09-2
- AMG232
Catalog No.:BCC3992
CAS No.:1352066-68-2
- Schineolignin B
Catalog No.:BCN3623
CAS No.:1352185-26-2
- AZD6738
Catalog No.:BCC6505
CAS No.:1352226-88-0
- Pindolol
Catalog No.:BCC6881
CAS No.:13523-86-9
- Trijuganone C
Catalog No.:BCN3685
CAS No.:135247-94-8
- Pulchinenoside B
Catalog No.:BCN6554
CAS No.:135247-95-9
- EW-7197
Catalog No.:BCC6467
CAS No.:1352608-82-2
- 2''-O-Rhamnosylicariside II
Catalog No.:BCN3464
CAS No.:135293-13-9
- MEN 10376
Catalog No.:BCC7133
CAS No.:135306-85-3
LRRK2 G2019S-induced mitochondrial DNA damage is LRRK2 kinase dependent and inhibition restores mtDNA integrity in Parkinson's disease.[Pubmed:28973664]
Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Nov 15;26(22):4340-4351.
Mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) are associated with increased risk for developing Parkinson's disease (PD). Previously, we found that LRRK2 G2019S mutation carriers have increased mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage and after zinc finger nuclease-mediated gene mutation correction, mtDNA damage was no longer detectable. While the mtDNA damage phenotype can be unambiguously attributed to the LRRK2 G2019S mutation, the underlying mechanism(s) is unknown. Here, we examine the role of LRRK2 kinase function in LRRK2 G2019S-mediated mtDNA damage, using both genetic and pharmacological approaches in cultured neurons and PD patient-derived cells. Expression of LRRK2 G2019S induced mtDNA damage in primary rat midbrain neurons, but not in cortical neuronal cultures. In contrast, the expression of LRRK2 wild type or LRRK2 D1994A mutant (kinase dead) had no effect on mtDNA damage in either midbrain or cortical neuronal cultures. In addition, human LRRK2 G2019S patient-derived lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCL) demonstrated increased mtDNA damage relative to age-matched controls. Importantly, treatment of LRRK2 G2019S expressing midbrain neurons or patient-derived LRRK2 G2019S LCLs with the LRRK2 kinase inhibitor GNE-7915, either prevented or restored mtDNA damage to control levels. These findings support the hypothesis that LRRK2 G2019S-induced mtDNA damage is LRRK2 kinase activity dependent, uncovering a novel pathological role for this kinase. Blocking or reversing mtDNA damage via LRRK2 kinase inhibition or other therapeutic approaches may be useful to slow PD-associated pathology.
Effects of LRRK2 Inhibitors on Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurotransmission.[Pubmed:27943591]
CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017 Feb;23(2):162-173.
INTRODUCTION: Mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) are the most prevalent cause of familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease (PD). Because most pathogenic LRRK2 mutations result in enhanced kinase activity, it suggests that LRRK2 inhibitors may serve as a potential treatment for PD. To evaluate whether LRRK2 inhibitors are effective therapies for PD, it is crucial to know whether LRRK2 inhibitors will affect dopaminergic (DAergic) neurotransmission. However, to date, there is no study to investigate the impact of LRRK2 inhibitors on DAergic neurotransmission. AIMS: To address this gap in knowledge, we examined the effects of three types of LRRK2 inhibitors (LRRK2-IN-1, GSK2578215A, and GNE-7915) on dopamine (DA) release in the dorsal striatum using fast-scan cyclic voltammetry and DA neuron firing in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) using patch clamp in mouse brain slices. RESULTS: We found that LRRK2-IN-1 at a concentration higher than 1 muM causes off-target effects and decreases DA release, whereas GSK2578215A and GNE-7915 do not. All three inhibitors at 1 muM have no effect on DA release and DA neuron firing rate. We have further assessed the effects of the inhibitors in two preclinical LRRK2 mouse models (i.e., BAC transgenic hG2019S and hR1441G) and demonstrated that GNE-7915 enhances DA release and synaptic vesicle mobilization/recycling. CONCLUSION: GNE-7915 can be validated for further therapeutic development for PD.
The development of CNS-active LRRK2 inhibitors using property-directed optimisation.[Pubmed:23721803]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Jul 1;23(13):3690-6.
Mutations in PARK8/LRRK2 are the most common genetic cause of Parkinson's disease. Inhibition of LRRK2 kinase activity has neuroprotective benefits, and provides a means of addressing the underlying biochemical cause of Parkinson's disease for the first time. Initial attempts to develop LRRK2 inhibitors were largely unsuccessful and highlight shortcomings intrinsic to traditional, high throughput screening methods of lead discovery. Recently, amino-pyrimidine GNE-7915 was reported as a potent (IC50=9 nM) selective (1/187 kinases), brain-penetrant and non-toxic inhibitor of LRRK2. The use of in silico modelling, extensive in vitro assays and resource-efficient in vivo techniques to produce GNE-7915, reflects a trend towards the concerted optimisation of potency, selectivity and pharmacokinetic properties in early-stage drug development.
Discovery of highly potent, selective, and brain-penetrable leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) small molecule inhibitors.[Pubmed:22985112]
J Med Chem. 2012 Nov 26;55(22):9416-33.
There is a high demand for potent, selective, and brain-penetrant small molecule inhibitors of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) to test whether inhibition of LRRK2 kinase activity is a potentially viable treatment option for Parkinson's disease patients. Herein we disclose the use of property and structure-based drug design for the optimization of highly ligand efficient aminopyrimidine lead compounds. High throughput in vivo rodent cassette pharmacokinetic studies enabled rapid validation of in vitro-in vivo correlations. Guided by this data, optimal design parameters were established. Effective incorporation of these guidelines into our molecular design process resulted in the discovery of small molecule inhibitors such as GNE-7915 (18) and 19, which possess an ideal balance of LRRK2 cellular potency, broad kinase selectivity, metabolic stability, and brain penetration across multiple species. Advancement of GNE-7915 into rodent and higher species toxicity studies enabled risk assessment for early development.


