Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Peptide (985-996)EGFR Peptide (985-996) CAS# 96249-43-3 |
- Laminin (925-933)
Catalog No.:BCC1015
CAS No.:110590-60-8
- Cadherin Peptide, avian
Catalog No.:BCC1018
CAS No.:127650-08-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 96249-43-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 102601502 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C61H93N13O23 | M.Wt | 1376.46 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
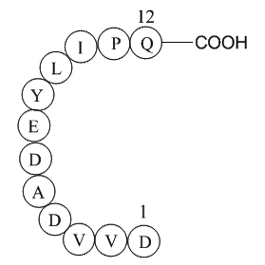
| Sequence | H2N-Asp-Val-Val-Asp-Ala-Asp-Glu-Tyr-Leu-Ile-Pro-Gln-OH | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-5-amino-2-[[(2S)-1-[(2S,3S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-3-methylpentanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)N)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC2=CC=C(C=C2)O)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CHCIQWQBUPWRLJ-XJSWDNOJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C61H93N13O23/c1-10-30(8)49(60(95)74-21-11-12-41(74)57(92)66-36(61(96)97)17-19-42(63)76)73-56(91)37(22-27(2)3)68-54(89)38(23-32-13-15-33(75)16-14-32)69-52(87)35(18-20-43(77)78)65-55(90)40(26-46(83)84)67-50(85)31(9)64-53(88)39(25-45(81)82)70-58(93)47(28(4)5)72-59(94)48(29(6)7)71-51(86)34(62)24-44(79)80/h13-16,27-31,34-41,47-49,75H,10-12,17-26,62H2,1-9H3,(H2,63,76)(H,64,88)(H,65,90)(H,66,92)(H,67,85)(H,68,89)(H,69,87)(H,70,93)(H,71,86)(H,72,94)(H,73,91)(H,77,78)(H,79,80)(H,81,82)(H,83,84)(H,96,97)/t30-,31-,34-,35-,36-,37-,38-,39-,40-,41-,47-,48-,49-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Peptide (985-996) Dilution Calculator

Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Peptide (985-996) Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) exists on the cell surface and is activated by the binding of its specific ligands, including epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor α. EGFR dimerization stimulates its intrinsic intracellular protein-tyrosine kinase activity. As a result, autophosphorylation of several tyrosine (Y) residues on the C-terminal domain of EGFR occurs. These include Y992, Y1045, Y1068, Y1148 and Y1173. This autophosphorylation elicits downstream activation and signaling by several other proteins that associate with the phosphorylated tyrosines through their own phosphotyrosine-binding SH2 domains. These downstream signaling proteins initiate several signal transduction cascades, principally the MAPK, Akt and JNK pathways, which lead to DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. Such proteins modulate phenotypes such as cell migration, adhesion, and proliferation. Activation of the receptor is important for the innate immune response in human skin.
Many therapeutic approaches are aimed at EGFR. The monoclonal antibodies block the extracellular ligand binding domain. With the binding site blocked, signal molecules can no longer attach and activate the tyrosine kinase. Another therapeutic method involves using small molecules to inhibit the EGFR tyrosine kinase on the cytoplasmic side of the receptor. Without kinase activity, EGFR is unable to activate itself, which is a prerequisite for the binding of downstream adaptor proteins. Ostensibly by halting the signaling cascade in cells that rely on this pathway for growth, tumor proliferation and migration is diminished.
Ref:
1. Yan. L, Beckman RA (October 2005). "Pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics in oncology therapeutic antibody development". BioTechniques 39 (4): 565–8.
2. Yosef Yarden and Joseph Schlessinger (1987). "Epidermal Growth-Factor Induces Rapid, Reversible Aggregation of the Purified Epidermal Growth-Factor Receptor". Biochemistry 26 (5): 1443–1451.
3. Downward J, Parker P, Waterfield MD (1984). "Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor". Nature 311 (5985): 483–5.
4. Oda K, Matsuoka Y, Funahashi A, Kitano H (2005). "A comprehensive pathway map of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling". Mol. Syst. Biol. 1 (1): 2005.0010.
5. David K. Moscatello2, Marina Holgado-Madruga2. "Frequent Expression of a Mutant Epidermal Growth Factor. Receptor in Multiple Human Tumors". Cancer Res December 1, 1995 55; 5536
- MPEP
Catalog No.:BCC4594
CAS No.:96206-92-7
- Isoliquiritigenin
Catalog No.:BCN4512
CAS No.:961-29-5
- 2'-Deoxyguanosine
Catalog No.:BCC5433
CAS No.:961-07-9
- Stylopine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN6964
CAS No.:96087-21-7
- Massoniresinol
Catalog No.:BCN4511
CAS No.:96087-10-4
- ent-17-Hydroxykauran-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN4510
CAS No.:960589-81-5
- Jatrorrhizine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8193
CAS No.:960383-96-4
- ONX-0914 (PR-957)
Catalog No.:BCC2095
CAS No.:960374-59-8
- Meropenem
Catalog No.:BCC2489
CAS No.:96036-03-2
- Vortioxetine (Lu AA21004) HBr
Catalog No.:BCC1213
CAS No.:960203-27-4
- SD 1008
Catalog No.:BCC2442
CAS No.:960201-81-4
- 2-hexyl-4-Pentynoic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC6480
CAS No.:96017-59-3
- Methyl 8-hydroxy-3-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl)-6-methyl-9-oxo-9H-furo[3,4-b]chromene-1-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCN7465
CAS No.:96287-41-1
- Androst-2-en-17-one
Catalog No.:BCC8821
CAS No.:963-75-7
- Huzhangoside D
Catalog No.:BCN2527
CAS No.:96315-53-6
- Metaphit
Catalog No.:BCC5664
CAS No.:96316-00-6
- Neonuezhenide
Catalog No.:BCN7461
CAS No.:96382-91-1
- H-ß-HoLeu-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3238
CAS No.:96386-92-4
- Fmoc-1-Nal-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3285
CAS No.:96402-49-2
- Goniotriol
Catalog No.:BCN4745
CAS No.:96405-62-8
- Amygdaloside
Catalog No.:BCC8231
CAS No.:96420-61-0
- Goniodiol
Catalog No.:BCN3958
CAS No.:96422-52-5
- Goniodiol 7-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN4793
CAS No.:96422-53-6
- Nifuroxazide
Catalog No.:BCC4686
CAS No.:965-52-6
The juxtamembrane, cytosolic region of the epidermal growth factor receptor is involved in association with alpha-subunit of Gs.[Pubmed:9038141]
J Biol Chem. 1997 Feb 28;272(9):5413-20.
Previously, we have demonstrated that epidermal growth factor (EGF) can stimulate adenylyl cyclase activity via activation of Gs in the heart. Moreover, we have recently shown that Gsalpha is phosphorylated by the EGF receptor protein tyrosine kinase and that the juxtamembrane region of the EGF receptor can stimulate Gs directly. Therefore, employing isolated cardiac membranes, the two-hybrid assay, and in vitro association studies with purified EGF receptor and Gsalpha we have investigated Gsalpha complex formation with the EGF receptor and elucidated the region in the receptor involved in this interaction. In isolated cardiac membranes, immunoprecipitation of EGF receptor was accompanied by co-immunoprecipitation of Gsalpha. In the yeast two-hybrid assay, the cytosolic domain of the EGF receptor and the N-terminal 64 amino acids of this region (Met644-Trp707) associated with Gsalpha. However, interactions of these regions of the EGF receptor with constitutively active Gsalpha were diminished in the two-hybrid assay. Employing purified proteins, our studies demonstrate that the EGF receptor, directly and stoichiometrically, associates with Gsalpha (1 mol of Gsalpha/mol of EGF receptor). This association was not altered in the presence or absence of ATP and therefore, was independent of tyrosine phosphorylation of either of the proteins. Peptides corresponding to the juxtamembrane region of the receptor decreased association of the EGF receptor with Gsalpha. However, neither the C-terminally truncated EGF receptor (Delta1022-1186) nor a peptide corresponding to residues 985-996 of the receptor altered association with Gsalpha, thus indicating the selectivity of the G protein interaction with the juxtamembrane region. Interestingly, peptides corresponding to N and C termini of Gsalpha did not alter the association of Gsalpha with the EGF receptor. Consistent with the findings from the two-hybrid assay where constitutively active Gsalpha poorly associated with the EGF receptor, in vitro experiments with purified proteins also demonstrated that activation of Gsalpha by guanosine 5'-3-O-(thio)triphosphate decreased the association of G protein with the EGF receptor. Thus we conclude that the juxtamembrane region of the EGF receptor, directly and stoichiometrically, associates with Gsalpha and that upon activation of Gsalpha this association is decreased.


