Decynium 22PMAT inhibitor CAS# 977-96-8 |
- Brefeldin A
Catalog No.:BCC4387
CAS No.:20350-15-6
- Ceramide
Catalog No.:BCC2458
CAS No.:3102-57-6
- Vitamin D3
Catalog No.:BCN2186
CAS No.:67-97-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 977-96-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5484462 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H23IN2 | M.Wt | 454.35 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 10 mM in DMSO | ||
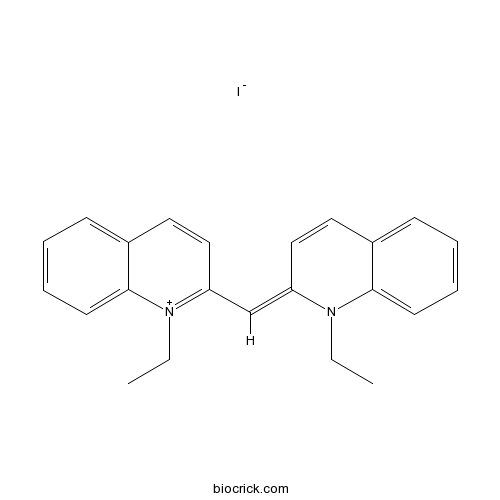
| Chemical Name | (2E)-1-ethyl-2-[(1-ethylquinolin-1-ium-2-yl)methylidene]quinoline;iodide | ||
| SMILES | CCN1C(=CC2=[N+](C3=CC=CC=C3C=C2)CC)C=CC4=CC=CC=C41.[I-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GMYRVMSXMHEDTL-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H23N2.HI/c1-3-24-20(15-13-18-9-5-7-11-22(18)24)17-21-16-14-19-10-6-8-12-23(19)25(21)4-2;/h5-17H,3-4H2,1-2H3;1H/q+1;/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of the plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT) (Ki = 0.10 μM). |

Decynium 22 Dilution Calculator

Decynium 22 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2009 mL | 11.0047 mL | 22.0095 mL | 44.0189 mL | 55.0237 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4402 mL | 2.2009 mL | 4.4019 mL | 8.8038 mL | 11.0047 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2201 mL | 1.1005 mL | 2.2009 mL | 4.4019 mL | 5.5024 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.044 mL | 0.2201 mL | 0.4402 mL | 0.8804 mL | 1.1005 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.022 mL | 0.11 mL | 0.2201 mL | 0.4402 mL | 0.5502 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Boldenone propionate
Catalog No.:BCC8895
CAS No.:977-32-2
- Irinotecan
Catalog No.:BCC2490
CAS No.:97682-44-5
- Latrepirdine
Catalog No.:BCC4541
CAS No.:97657-92-6
- Ganoderic acid D2
Catalog No.:BCC8989
CAS No.:97653-94-6
- Lucidone B
Catalog No.:BCN8242
CAS No.:97653-93-5
- Eticlopride hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7193
CAS No.:97612-24-3
- Isoscoparin-2''-Beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN7807
CAS No.:97605-25-9
- Canrenone
Catalog No.:BCC7626
CAS No.:976-71-6
- 6-Methylgenistein
Catalog No.:BCN6852
CAS No.:97575-49-0
- Quinelorane hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7100
CAS No.:97548-97-5
- 3-O-Caffeoyloleanolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3959
CAS No.:97534-10-6
- Ceftibuten
Catalog No.:BCC5216
CAS No.:97519-39-6
- Chuanxiongzine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8147
CAS No.:97747-88-1
- S186
Catalog No.:BCC5285
CAS No.:97759-16-5
- 2,6-Dimethyl-3-O-methyl-4-isobutyrylphloroglucinol
Catalog No.:BCN7355
CAS No.:97761-90-5
- 2,6-Dimethyl-3-O-methyl-4-(2-methylbutyryl)phloroglucinol
Catalog No.:BCN7356
CAS No.:97761-91-6
- Jasmoside
Catalog No.:BCN7552
CAS No.:97763-17-2
- Lappaconitine Hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCN2505
CAS No.:97792-45-5
- IMD 0354
Catalog No.:BCC4556
CAS No.:978-62-1
- Penciclovir Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC5635
CAS No.:97845-62-0
- 8,9-Didehydro-7-hydroxydolichodial
Catalog No.:BCN6674
CAS No.:97856-19-4
- Norfloxacin lactate
Catalog No.:BCC9104
CAS No.:97867-34-0
- Estradiol valerate
Catalog No.:BCC4482
CAS No.:979-32-8
- 3,4'-Dihydroxy-3,5',7-trimethoxyflavan
Catalog No.:BCN4528
CAS No.:97914-19-7
Membrane potential and pH-dependent accumulation of decynium-22 (1,1'-diethyl-2,2'-cyanine iodide) flourencence through OCT transporters in astrocytes.[Pubmed:23875515]
Bol Asoc Med P R. 2010 Jul-Sep;102(3):5-12.
1,1 '-Diethyl-2,2'-cyanine iodide (decynium22; D22) is a potent blocker of the organic cation family of transporters (EMT/OCT) known to move endogenous monoamines like dopamine and norepinephrine across cell membranes. Decynium22 is a cation with a relatively high affinity for all members of the OCT family in both human and rat cells. The mechanism through which decynium22 blocks OCT transporters are poorly understood. We tested the hypothesis that denynium22 may compete with monoamines utilizing OCT to permeate the cells. Using the ability of D22 to aggregate and produce fluorescence at 570 nm, we measured D22 uptake in cultured astrocytes. The rate of D22 uptake was strongly depressed by acid pH and by elevated external K+. The rate of uptake was similar to that displayed by 4-(4-(dimethylamino)-styryl)-N-methylpyridinium (ASP+), a well established substrate for OCT and high-affinity Na+-dependent monoamine transporters. These data were supported by measurement of electrogenic uptake using whole cell voltage clamp recording. Decynium22 depressed norepinephrine, but not glutamate uptake. These data are also consistent with the described OCT transporter characteristics. Taken together, our results suggest that decynium22 accumulation might be a useful instrument to study monoamine transport in the brain, and particularly in astrocytes, where they may play a prominent role in monoamine uptake during brain dysfunction related to monoamines (like Parkinson disease) and drug addiction.
Modulation of OCT3 expression by stress, and antidepressant-like activity of decynium-22 in an animal model of depression.[Pubmed:25597272]
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015 Apr;131:33-41.
The organic cation transporter-3 (OCT3) is a glucocorticoid-sensitive uptake mechanism that has been shown to regulate the bioavailability of monoamines in brain regions that are implicated in the pathophysiology of depression. In the present study, the relative impacts of acute stress alone and acute stress with a history of repeated stress (chronic+acute) were evaluated in two strains of rats: the stress-vulnerable Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) strain and the somewhat more stress-resilient Long-Evans (LE) strain. OCT3 mRNA was significantly upregulated in the hippocampus of LE rats 2h after exposure to acute restraint stress, but not in acutely-restrained rats with a history of repeated social defeat stress. WKY rats exhibited a very different pattern. OCT3 mRNA was unaffected by acute restraint stress alone but was robustly upregulated after repeated+acute stress. There was also a corresponding increase in cytosolic OCT3 protein following repeated+acute stress in WKY rats 3h after presentation of the acute stressor. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that altered expression of the OCT3 may play a role in stress coping, and strain differences in regulation of this expression may contribute to differences in physiological and behavioral responses to stress. Furthermore, the OCT3 inhibitor, Decynium 22 (1 and 10mug/kg, i.p.) reduced immobility of WKY rats, but not that of LE rats, in the forced swim test, suggesting that blockade of the OCT3 has antidepressant-like effects. Since WKY rats also appear to be resistant to the behavioral effects of traditional antidepressants, this also suggests that OCT3 antagonism may be an alternative therapeutic strategy for the treatment of depression in individuals who do not respond to conventional antidepressants.
Decynium-22 enhances SSRI-induced antidepressant-like effects in mice: uncovering novel targets to treat depression.[Pubmed:23785165]
J Neurosci. 2013 Jun 19;33(25):10534-43.
Mood disorders cause much suffering and lost productivity worldwide, compounded by the fact that many patients are not effectively treated by currently available medications. The most commonly prescribed antidepressant drugs are the selective serotonin (5-HT) reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which act by blocking the high-affinity 5-HT transporter (SERT). The increase in extracellular 5-HT produced by SSRIs is thought to be critical to initiate downstream events needed for therapeutic effects. A potential explanation for their limited therapeutic efficacy is the recently characterized presence of low-affinity, high-capacity transporters for 5-HT in brain [i.e., organic cation transporters (OCTs) and plasma membrane monoamine transporter], which may limit the ability of SSRIs to increase extracellular 5-HT. Decynium-22 (D-22) is a blocker of these transporters, and using this compound we uncovered a significant role for OCTs in 5-HT uptake in mice genetically modified to have reduced or no SERT expression (Baganz et al., 2008). This raised the possibility that pharmacological inactivation of D-22-sensitive transporters might enhance the neurochemical and behavioral effects of SSRIs. Here we show that in wild-type mice D-22 enhances the effects of the SSRI fluvoxamine to inhibit 5-HT clearance and to produce antidepressant-like activity. This antidepressant-like activity of D-22 was attenuated in OCT3 KO mice, whereas the effect of D-22 to inhibit 5-HT clearance in the CA3 region of hippocampus persisted. Our findings point to OCT3, as well as other D-22-sensitive transporters, as novel targets for new antidepressant drugs with improved therapeutic potential.
Interaction of organic cations with a newly identified plasma membrane monoamine transporter.[Pubmed:16099839]
Mol Pharmacol. 2005 Nov;68(5):1397-407.
Many endogenous compounds and xenobiotics are organic cations that rely on polyspecific organic cation transporters (OCTs) to traverse cell membranes. We recently cloned a novel human plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT) that belongs to the equillibrative nucleoside transporter (ENT) family. We have reported previously that, unlike other ENTs, PMAT (also known as ENT4) is a Na+-independent and membrane potential-sensitive transporter that transports monoamine neurotransmitters and the neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+). These compounds are the known substrates for OCTs, which raises the possibility that PMAT functions as a polyspecific transporter like the OCTs. In the present study, we analyzed the interaction of PMAT with a series of structurally diverse organic cations using MDCK cells stably expressing human PMAT. Our study showed that PMAT interacts with many organic cations that have heterogeneous chemical structures. PMAT transports classic OCT substrates, such as tetraethylammonium, guanidine, and histamine. Prototype OCT inhibitors, including cimetidine, and type II cations (e.g., quinidine, quinine, verapamil, and rhodamine123) are also PMAT inhibitors. An analysis of molecular structures and apparent binding affinities revealed that charge and hydrophobicity are the principal determinants for transporter-substrate/inhibitor interaction. A planar aromatic mass seems to be important for high affinity interaction. trans-Stimulation and efflux studies demonstrate that PMAT is able to mediate bidirectional transport. These functional properties of PMAT are strikingly similar to those of the OCTs. We therefore conclude that PMAT can function as a polyspecific organic cation transporter, which may play a role in organic cation transport in vivo.


