DL-AP4Broad spectrum EAA antagonist CAS# 20263-07-4 |
- Calyculin A
Catalog No.:BCC2457
CAS No.:101932-71-2
- Fumonisin B1
Catalog No.:BCC2461
CAS No.:116355-83-0
- Calcineurin Autoinhibitory Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2456
CAS No.:148067-21-4
- Ceramide
Catalog No.:BCC2458
CAS No.:3102-57-6
- Fostriecin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2460
CAS No.:87860-39-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 20263-07-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2207 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C4H10NO5P | M.Wt | 183.1 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 33 mM in water | ||
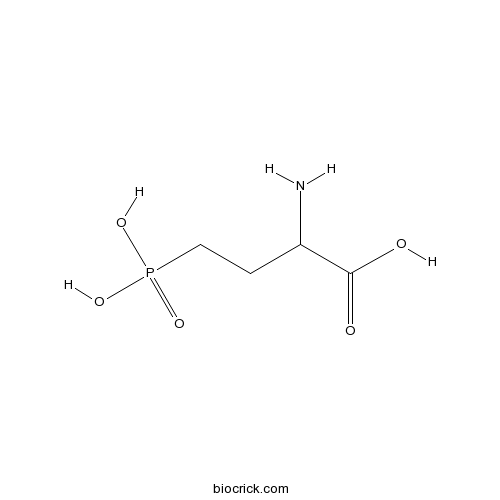
| Chemical Name | 2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C(CP(=O)(O)O)C(C(=O)O)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DDOQBQRIEWHWBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C4H10NO5P/c5-3(4(6)7)1-2-11(8,9)10/h3H,1-2,5H2,(H,6,7)(H2,8,9,10) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Broad spectrum EAA ligand. Separate isomers D-AP4 and L-AP4 also available. |

DL-AP4 Dilution Calculator

DL-AP4 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.4615 mL | 27.3075 mL | 54.615 mL | 109.2299 mL | 136.5374 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0923 mL | 5.4615 mL | 10.923 mL | 21.846 mL | 27.3075 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5461 mL | 2.7307 mL | 5.4615 mL | 10.923 mL | 13.6537 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1092 mL | 0.5461 mL | 1.0923 mL | 2.1846 mL | 2.7307 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0546 mL | 0.2731 mL | 0.5461 mL | 1.0923 mL | 1.3654 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- DL-AP3
Catalog No.:BCC2459
CAS No.:20263-06-3
- Ginkgolic acid C13:0
Catalog No.:BCN5333
CAS No.:20261-38-5
- H-Valinol
Catalog No.:BCC2696
CAS No.:2026-48-4
- Calyxin H
Catalog No.:BCN4888
CAS No.:202596-22-3
- OTX-015
Catalog No.:BCC1829
CAS No.:202590-98-5
- 13-O-Ethylpiptocarphol
Catalog No.:BCN7448
CAS No.:202522-40-5
- 13(18)-Oleanen-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN4887
CAS No.:20248-08-2
- JANEX-1
Catalog No.:BCC1668
CAS No.:202475-60-3
- Glomeratose A
Catalog No.:BCN8400
CAS No.:202471-84-9
- Ro 04-6790
Catalog No.:BCC7512
CAS No.:202466-68-0
- AM 281
Catalog No.:BCC6944
CAS No.:202463-68-1
- 1,3,7-Trihydroxy-2-prenylxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN4886
CAS No.:20245-39-0
- JHW 007 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7923
CAS No.:202645-74-7
- 3α-Bis-(4-fluorophenyl) methoxytropane hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6846
CAS No.:202646-03-5
- Nicotinamide N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN1969
CAS No.:1986-81-8
- Forsythenside A
Catalog No.:BCN6440
CAS No.:202721-09-3
- Homodihydrocapsaicin I
Catalog No.:BCN7844
CAS No.:20279-06-5
- 4-Methoxycoumarine
Catalog No.:BCN6536
CAS No.:20280-81-3
- Orexin B (mouse)
Catalog No.:BCC5766
CAS No.:202801-92-1
- Licoagrochalcone A
Catalog No.:BCC8197
CAS No.:202815-28-9
- BMS 191011
Catalog No.:BCC7448
CAS No.:202821-81-6
- Ralfinamide mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC7844
CAS No.:202825-45-4
- Safinamide Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC2320
CAS No.:202825-46-5
- Rosmarinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5893
CAS No.:20283-92-5
Phenylglycines can evoke quisqualate-primed depolarizations in rat cingulate cortex: an effect associated with [3H]DL-AP4 uptake.[Pubmed:8996809]
Eur J Neurosci. 1996 Dec;8(12):2599-604.
Depolarization could be evoked in slices of rat cingulate cortex by the normally non-excitatory compound L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate (L-AP4) if the slices had been sensitized by exposure to quisqualate. The magnitude of the response to L-AP4 was dependent on the concentrations of both L-AP4 and quisqualate and was inhibited by alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate receptor antagonism. A series of phenylglycine analogues were capable of evoking similar dose-dependent depolarizations in the rat cingulate cortex following quisqualate sensitization, the most potent being (S)-4-carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycine. If the superfusate collected during application of (S)-4-carboxy-3-hydroxyphenylglycine to a quisqualate-sensitized slice was administered to a slice not previously exposed to quisqualate, a small depolarization was obtained. All the compounds shown to be capable of evoking the quisqualate-sensitized response showed affinity for the L-AP4 uptake site whilst having no affinity at ionotropic glutamate receptors and different profiles of activity at metabotropic glutamate receptors. None of the compounds was active at the metabotropic glutamate 4a receptor. There was a statistically significant correlation between a compound's effectiveness in inhibiting [3H]DL-AP4 uptake into rat cortical synaptosomes and its potency in evoking quisqualate-sensitized depolarization. It is concluded that this response may be the result of hetero-exchange between L-AP4 ligands and quisqualate.
The effects of a series of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and excitant amino acid-induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations.[Pubmed:7042024]
Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):65-75.
1 The depressant actions on evoked electrical activity and the excitant amino acid antagonist properties of a range of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids have been investigated in the isolated spinal cord preparations of the frog or immature rat. 2 When tested on dorsal root-evoked ventral root potentials, members of the homologous series from 2- amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid to 2-amino-8-phosphonooctanoic acid showed depressant actions which correlated with the ability of the substances to antagonize selectivity motoneuronal depolarizations induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate. 3 2-Amino-5-phosphonovalerate was the most potent substance of the series giving an apparent KD of 1.4 microM for the antagonism of responses to N-methyl-D-aspartate. 4 A comparison of the (+)- and (-)-forms of 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate indicated that the N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist activity and the neuronal depressant action of this substance were both due mainly to the (-)-isomer. 5 The (-)- and (+)-forms of 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate had different actions. The (-)-forms of this substance had a relatively weak and non-selective antagonist action on depolarizations induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate, quisqualate and kainate and a similarly weak depressant effect when tested on evoked electrical activity. The (+)-form was more potent than he (-)-form in depressing electrically evoked activity but did not antagonize responses to amino acid excitants. At concentrations higher than those required to depress electrically evoked activity, the (+)-form produced depolarization. This action was blocked by 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate.
Antagonism of excitatory amino acid-induced responses and of synaptic excitation in the isolated spinal cord of the frog.[Pubmed:316343]
Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;67(4):591-603.
1. A range of compounds has been tested for excitatory amino acid agonist or antagonist activity and for effects on synaptic activity on isolated hemisected spinal cords of frogs. 2. L-Monoamino dicarboxylic acids of chain length up to 8 carbon atoms (L-alpha-aminosuberate) were all agonists. 3. Within a series of D-monoamino dicarboxylic acids, and with diamino dicarboxylic acids (mainly unresolved mixtures of diasteroisomers), there was a progression from agonist activity, for compounds of chain length equal to or shorter than glutamate, to antagonist activity, for compounds of longer chain length equal to or shorter than glutamate, to antagonist activity, for compounds of longer chain length, D-alpha-Aminosuberate (D alpha SD) was the most potent antagonist. 4. The antagonist actions of these substances showed a Mg2+--like selectivity with respect to depolarizations produced by different excitants. N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) was the most susceptible agonist and quisqualate and kainate the least susceptible. Responses to other excitatory amino acids, including L-glutamate and L-aspartate, showed intermediate sensitivity to the antagonists. 5. A parallelism was observed between the relative potencies of mono- and diamino dicarboxylic acids as NMDA antagonists and their relative potencies as depressants of synaptic responses. 6. The results support the concept of different types of excitatory amino acid receptors, with NMDA and its antagonists acting predominantly on one type. These NMDA receptors are probably transmitter receptors activated by an excitatory amino acid transmitter.


