Chebulic acidCAS# 23725-05-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 23725-05-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71308174 | Appearance | Powder |
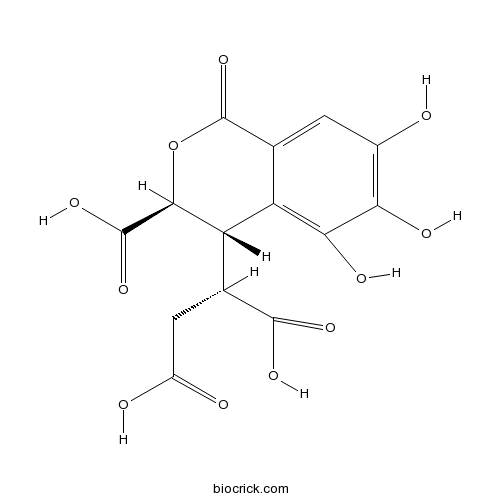
| Formula | C14H12O11 | M.Wt | 356.2 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[(3S,4S)-3-carboxy-5,6,7-trihydroxy-1-oxo-3,4-dihydroisochromen-4-yl]butanedioic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=C2C(=C(C(=C1O)O)O)C(C(OC2=O)C(=O)O)C(CC(=O)O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | COZMWVAACFYLBI-XJEVXTIOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H12O11/c15-5-1-4-7(10(19)9(5)18)8(3(12(20)21)2-6(16)17)11(13(22)23)25-14(4)24/h1,3,8,11,15,18-19H,2H2,(H,16,17)(H,20,21)(H,22,23)/t3-,8-,11-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Chebulic acid at both doses (25 and 50 mg/kg) improves biochemical alterations caused by renal ischemia in diabetic rats. 2. Chebulic acid has effects against the progression of AGE-induced endothelial cell dysfunction, may constitute a promising intervention agent against diabetic vascular complications. 3. Chebulic acid significantly reduced the tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced cell cytotoxicity, intracellular reactive oxygen species level, and the ratio of GSSH, oxidized form of glutathione (GSH) to the over total GSH (GSH + GSSG) (4.42%) as compared to that with t-BHP alone (8.33%). |
| Targets | VEGFR | ROS |

Chebulic acid Dilution Calculator

Chebulic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8074 mL | 14.0371 mL | 28.0741 mL | 56.1482 mL | 70.1853 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5615 mL | 2.8074 mL | 5.6148 mL | 11.2296 mL | 14.0371 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2807 mL | 1.4037 mL | 2.8074 mL | 5.6148 mL | 7.0185 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0561 mL | 0.2807 mL | 0.5615 mL | 1.123 mL | 1.4037 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0281 mL | 0.1404 mL | 0.2807 mL | 0.5615 mL | 0.7019 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Nardosinone
Catalog No.:BCN2324
CAS No.:23720-80-1
- Platycoside E
Catalog No.:BCN6385
CAS No.:237068-41-6
- Damascenone
Catalog No.:BCN8355
CAS No.:23696-85-7
- Olaquindox
Catalog No.:BCN2538
CAS No.:23696-28-8
- Boc-Ser(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3442
CAS No.:23680-31-1
- Levosulpiride
Catalog No.:BCC4463
CAS No.:23672-07-3
- Stigmast-4-ene-3,6-dione
Catalog No.:BCN5778
CAS No.:23670-94-2
- Vicenin -2
Catalog No.:BCN3013
CAS No.:23666-13-9
- Neogrifolin
Catalog No.:BCN7526
CAS No.:23665-96-5
- Ardisiacrispin A
Catalog No.:BCN2323
CAS No.:23643-61-0
- Clerosterol
Catalog No.:BCN2905
CAS No.:2364-23-0
- Triapine
Catalog No.:BCC5112
CAS No.:236392-56-6
- 6-Hydroxy-4-Methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCC9206
CAS No.:2373-31-1
- trans-Methylkhellactone
Catalog No.:BCN6919
CAS No.:23733-92-8
- trans-3'-O-Benzoyl-4'-O-methylkhellactone
Catalog No.:BCN6921
CAS No.:23733-95-1
- 4-Amino-3-hydroxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8681
CAS No.:2374-03-0
- Rivulobirin E
Catalog No.:BCN5090
CAS No.:237407-59-9
- Methylprednisolone Sodium Succinate
Catalog No.:BCC5629
CAS No.:2375-03-3
- 4-Aminopyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine
Catalog No.:BCC8690
CAS No.:2380-63-4
- Homovanillyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN7173
CAS No.:2380-78-1
- 6-Hydroxyindole
Catalog No.:BCN8310
CAS No.:2380-86-1
- Pogostone
Catalog No.:BCN2696
CAS No.:23800-56-8
- Hinesol
Catalog No.:BCC9232
CAS No.:23811-08-7
- Trichokaurin
Catalog No.:BCN4851
CAS No.:23811-50-9
Preventive effects of chebulic acid isolated from Terminalia chebula on advanced glycation endproduct-induced endothelial cell dysfunction.[Pubmed:20659546]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Oct 5;131(3):567-74.
AIM OF THE STUDY: The aqueous extract of Terminalia chebular fruits was reported to have anti-hyperglycemia and anti-diabetic complication effects. The present study therefore investigated the protective mechanism of Chebulic acid, a phenolcarboxylic acid compound isolated from the ripe fruits of Terminalia chebula against advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs)-induced endothelial cell dysfunction. MATERIALS AND METHODS: To investigate the protective mechanism of Chebulic acid against vascular endothelial dysfunction human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were treated with Chebulic acid in the presence/absence of glyceraldehyde-related AGEs (glycer-AGEs). RESULTS: HUVEC incubated with 100 mug/ml of glycer-AGEs had significantly enhanced reactive oxygen species formation, whereas the treatment of Chebulic acid dose-dependently reduced glycer-AGE-induced formation to 108.2 +/- 1.9% for 25 muM versus 137.8 +/- 1.1% for glycer-AGEs treated alone. The transendothelial electrical resistance (TER) value of the glycer-AGEs group was dramatically decreased to 76.9 +/- 2.2% compared to the control, whereas Chebulic acid treatment prevented glycer-AGE-induced TER change with a value of 91.3 +/- 5.3%. The incubation of confluent HUVEC with 100 mug/ml of glycer-AGEs for 24h remarkably increased the adhesion of human monocytic THP-1 cells compared to non-stimulated HUVEC. These increases in HUVEC adhesiveness were dose-dependently reduced by Chebulic acid. CONCLUSIONS: The present study shows the effects of Chebulic acid against the progression of AGE-induced endothelial cell dysfunction suggesting that this compound may constitute a promising intervention agent against diabetic vascular complications.
Chebulic acid attenuates ischemia reperfusion induced biochemical alteration in diabetic rats.[Pubmed:22963650]
Pharm Biol. 2013 Jan;51(1):23-9.
CONTEXT: Diabetic nephropathy is one of the important microvascular complications of diabetes; however, the main problem remains is the control of progression of nephropathy in diabetes. Chebulic acid was selected, as tannins from Terminalia chebula are used as antidiabetic, renoprotective, antioxidant, hypotensive and an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor. OBJECTIVE: In this study, we evaluated the effect of Chebulic acid on ischemia reperfusion induced biochemical alteration in diabetic rats. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Chebulic acid (CA) was isolated from T. chebula; LD(50) and acute toxicity studies of CA were done. Renal ischemia and reperfusion technique was used to induce nephropathy in diabetic rats. Glibenclamide (10 mg/kg) was used as diabetic standard; CA at doses of 25 and 50 mg/kg were administered for 28 days and various biochemical parameters were monitored. RESULTS: The LD(50) was found to be 251 mg/kg; 25 and 50 mg/kg doses were selected as no toxic symptoms were observed at both doses, except slight diarrhea. CA significantly (p < 0.001) reduced the glucose, creatinine, urea nitrogen, glycosylated hemoglobulin, proteinuria, urine albumin excretion, glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and increased serum insulin and glycogen level. CA also restored glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, glutathione, superoxide dismutase, catalase and malondialdehyde levels. Improvement in kidney was also noted in histopathological studies. CONCLUSIONS: The statistical data indicated that Chebulic acid at both doses (25 and 50 mg/kg) improves biochemical alterations caused by renal ischemia in diabetic rats.
Isolation of chebulic acid from Terminalia chebula Retz. and its antioxidant effect in isolated rat hepatocytes.[Pubmed:16932919]
Arch Toxicol. 2007 Mar;81(3):211-8.
A hepatoprotective compound was isolated from the ethanolic extract of the fruits of Terminalia chebula Retz. by consecutive solvent partitioning, followed by silica gel and Sephadex LH-20 column chromatographies. The purified compound was identified as a mixture of Chebulic acid and its minor isomer, neoChebulic acid, with a ratio of 2:1 by spectroscopic analysis including 1D and 2D NMR and MS spectroscopy. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the protection of rat hepatocytes against oxidative toxicity by Chebulic acid obtained from T. chebula Retz. This compound exhibited in vitro a free radical-scavenging activity and ferric-reducing antioxidant activity. Also, the specific ESR spectrum for the (*)OOH radical signals consisting of three-line ESR spectra was within the field of 0.27 mT, whereas 2.5 and 0.25 mg/ml of Chebulic acid significantly reduced the signal intensity of the ESR spectra to 0.06 mT and 0.11 mT, respectively. Using isolated rat hepatocyte experiment, we demonstrated that the treatment of hepatocytes with Chebulic acid significantly reduced the tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced cell cytotoxicity, intracellular reactive oxygen species level, and the ratio of GSSH, oxidized form of glutathione (GSH) to the over total GSH (GSH + GSSG) (4.42%) as compared to that with t-BHP alone (8.33%).
Effects of chebulic acid on advanced glycation endproducts-induced collagen cross-links.[Pubmed:24759763]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37(7):1162-7. Epub 2014 Apr 24.
Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) have been implicated in the development of diabetic complications. We report the antiglycating activity of Chebulic acid (CA), isolated from Terminalia chebula on breaking the cross-links of proteins induced by AGEs and inhibiting the formation of AGEs. Aminoguanidine (AG) reduced 50% of glycated bovine serum albumin (BSA) with glycolaldehyde (glycol-BSA)-induced cross-links of collagen at a concentration of 67.8 +/- 2.5 mM, the level of CA required for exerting a similar antiglycating activity was 38.8 +/- 0.5 microM. Also, the breaking activity on collagen cross-links induced by glycol-BSA was potent with CA (IC50=1.46 +/- 0.05 mM), exhibiting 50-fold stronger breaking activity than with ALT-711, a well-known cross-link breaker (IC50=72.2 +/- 2.4 mM). IC50 values of DPPH. scavenging activity for CA and ascorbic acid (AA) were 39.2 +/- 4.9 and 19.0 +/- 1.2 microg dry matter (DM) mL(-1), respectively, and ferric reducing and antioxidant power (FRAP) activities for CA and AA were 4.70 +/- 0.06 and 11.4 +/- 0.1 mmol/FeSO4.7H2O/g DM, respectively. The chelating activities of CA, AG and ALT711 on copper-catalyzed oxidation of AA were compared, and in increasing order, ALT-711 (IC50 of 1.92 +/- 0.20 mM)


