BenzoinCAS# 119-53-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

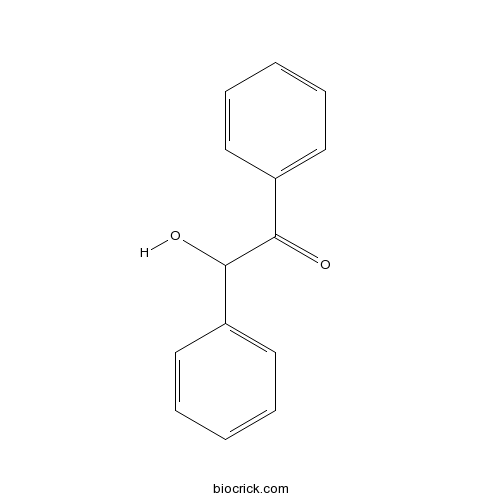
Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 119-53-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 8400 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H12O2 | M.Wt | 212 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-hydroxy-1,2-diphenylethanone | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ISAOCJYIOMOJEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H12O2/c15-13(11-7-3-1-4-8-11)14(16)12-9-5-2-6-10-12/h1-10,13,15H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Benzoin Dilution Calculator

Benzoin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.717 mL | 23.5849 mL | 47.1698 mL | 94.3396 mL | 117.9245 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9434 mL | 4.717 mL | 9.434 mL | 18.8679 mL | 23.5849 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4717 mL | 2.3585 mL | 4.717 mL | 9.434 mL | 11.7925 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0943 mL | 0.4717 mL | 0.9434 mL | 1.8868 mL | 2.3585 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0472 mL | 0.2358 mL | 0.4717 mL | 0.9434 mL | 1.1792 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- p-Anisoin
Catalog No.:BCC9113
CAS No.:119-52-8
- 7-Anilino-4-hydroxy-2-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8777
CAS No.:119-40-4
- Methyl salicylate
Catalog No.:BCN5372
CAS No.:119-36-8
- 8-Amino-2-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8783
CAS No.:119-28-8
- Viscumneoside III
Catalog No.:BCN7698
CAS No.:118985-27-6
- 1-O-Deacetyl-2alpha-hydroxykhayanolide E
Catalog No.:BCN1604
CAS No.:1189801-51-1
- Fumitremorgin C
Catalog No.:BCC7507
CAS No.:118974-02-0
- Mephedrone hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6183
CAS No.:1189726-22-4
- Ethyl ganoderate J
Catalog No.:BCN3486
CAS No.:1189555-95-0
- (S,S)-2,6-Bis(4-isopropyl-2-oxazolin-2-yl)pyridine
Catalog No.:BCC8402
CAS No.:118949-61-4
- 1,3-Dihydroxy-4-methoxy-10-methylacridin-9(10H)-one
Catalog No.:BCN1605
CAS No.:1189362-86-4
- 5-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-7-methoxybenzofuran
Catalog No.:BCN1606
CAS No.:118930-92-0
- Benzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8859
CAS No.:119-61-9
- 2-Carboxybenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN2274
CAS No.:119-67-5
- 5-Amino-2-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8732
CAS No.:119-79-9
- 3,4-Dihydrocoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN6793
CAS No.:119-84-6
- 2,2'-Biquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8489
CAS No.:119-91-5
- Abiesinol F
Catalog No.:BCN6418
CAS No.:1190070-91-7
- 4-[2-[(3-Ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-3-pyrrolin-1-yl)carboxamido]ethyl]benzenesulfonamide
Catalog No.:BCC8672
CAS No.:119018-29-0
- M2 ion channel blocker
Catalog No.:BCC1726
CAS No.:1190215-03-2
- Sarcandrone A
Catalog No.:BCN6073
CAS No.:1190225-47-8
- Sarcandrone B
Catalog No.:BCN6074
CAS No.:1190225-48-9
- PSI-7977
Catalog No.:BCC1871
CAS No.:1190307-88-0
- PSI-7976
Catalog No.:BCC5138
CAS No.:1190308-01-0
Supramolecular chirality and crystallization from biocatalytic self-assembly in lipidic cubic mesophases.[Pubmed:30874704]
Nanoscale. 2019 Mar 28;11(13):5891-5895.
Biocatalytic self-assembly in a nanoconfined environment is widely used in nature to construct complex structures that endow special characteristics to life. There is tremendous interest in mimicking such bottom-up processes to fabricate functional materials. In this study, we have investigated a novel biomimetic scaffold based on lipidic cubic mesophases (LCMs), which provide a special nanoconfined environment for biocatalytic self-assembly and subsequent formation of organic crystals. (R)-Benzoin generated in situ from benzaldehyde in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme benzaldehyde lyase (BAL) exhibits - when confined within LCMs - enhanced chirality compared to (R)-Benzoin in solution or (R)-Benzoin-doped LCMs. We infer that a metastable state is formed under kinetic control that displays enhanced supramolecular chirality. As they age, these metastable structures can further grow into thermodynamically stable crystals. The biomimetic, nanoconfined environment provided by the LCMs plays a key role in the development of supramolecular chirality and subsequent crystallization.
Comparing Negative Pressure Wound Therapy with Instillation and Conventional Dressings for Sternal Wound Reconstructions.[Pubmed:30859044]
Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019 Jan 4;7(1):e2087.
Background: Muscle flap reconstruction has become a mainstay of therapy following treatment of sternal wound complications; however, success depends on removing wound exudate and infectious material from the wound before reconstruction and closure. Importantly, time to closure is a key factor affecting morbidity/mortality and cost-to-treat for this wound type. Methods: A retrospective analysis of 30 patients who were treated for sternal wound complications between June 2015 and October 2017 was performed. After surgical debridement, group 1 patients (n = 15) received negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) with instillation and dwell time (NPWTi-d), instilling 1/8-strength Dakin's solution with a 20-minute dwell time followed by 2 hours of NPWT (-125 mm Hg); group 2 patients (n = 15) were treated with wet-to-moist dressings soaked in 1/8-strength Dakin's solution. After muscle flap reconstruction and closure with sutures, group 1 patients received closed incision negative pressure therapy, and group 2 patients received Benzoin and wound closure strips. Data collected included time to closure, therapy duration, number of debridements/dressing changes, drain duration, and complications. Results: There was a significantly shorter time to closure (P < 0.0001) for group 1 when compared with group 2. In addition, there were fewer therapy days (P = 0.0041), fewer debridements/dressing changes (P = 0.0011), and shorter drain duration (P = 0.0001) for group 1 when compared with group 2. Conclusions: We describe a novel regimen consisting of adjunctive NPWTi-d, along with debridement and systemic antibiotics, followed by closed incision negative pressure therapy after muscle flap reconstruction and closure, to help manage preexisting sternal wounds that had failed to close following a previous cardiac procedure.
Can the Radical Channel Contribute to the Catalytic Cycle of N-Heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) in Benzoin Condensation?[Pubmed:30457867]
J Org Chem. 2018 Nov 20.
NHC can catalyze Benzoin condensation via the key Breslow intermediate. EPR spectroscopy recently confirmed the existence of the radical species, but its catalytic role is still unclear. Herein, we use density functional approaches to study the radical-associated pathway in comparison with the non-radical mechanism reported previously. Theoretical investigations show that the non-radical path (DeltaG = 18.7 kcal/mol) is more kinetically favorable than the radical route (DeltaG = 27.6 kcal/mol), which is initialized by the hydrogen abstraction between the Breslow intermediate and benzaldehyde, leading to a radical pair. The product formation is thus dominated by the non-radical pathway. In addition, the Breslow intermediate is less stable than its keto form, which blocks the Benzoin condensation and the radical species could play an important role to assist the tautomerization and to promote the catalytic reaction.
Benzoins and cyclobenzoins in supramolecular and polymer chemistry.[Pubmed:30264062]
Chem Commun (Camb). 2018 Oct 23;54(85):11989-11997.
Benzoin condensation is one of the oldest rigorously described organic reactions, having been discovered in 1832 by Liebig and Wohler. It creates a new C-C bond and a stereocenter from ubiquitous aldehyde starting materials under simple cyanide-catalyzed conditions. We have recently discovered cycloBenzoins: a class of macrocyclic compounds prepared by a Benzoin cyclooligomerization of simple aromatic dialdehydes. CycloBenzoins' internal cavities suggest they should be intriguing solution-phase supramolecular hosts, while their crystallographic packing aligns these cavities into potentially useful pores in the solid state. Well-precedented derivatization chemistry allows rapid functionalization into heteroacenes, which are optoelectronic materials and models for graphene defects. This Feature Article summarizes our work on cycloBenzoins, together with other applications of Benzoins in supramolecular chemistry and materials science.


