BassianolideCAS# 64763-82-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 64763-82-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 137699675 | Appearance | Powder |
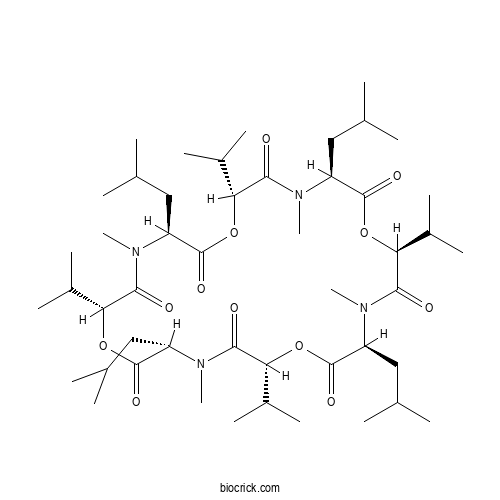
| Formula | C48H84N4O12 | M.Wt | 909.2 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (3S,6R,9S,12R,15S,18S,21S,24R)-4,10,16,22-tetramethyl-3,9,15,21-tetrakis(2-methylpropyl)-6,12,18,24-tetra(propan-2-yl)-1,7,13,19-tetraoxa-4,10,16,22-tetrazacyclotetracosane-2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23-octone | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC1C(=O)OC(C(=O)N(C(C(=O)OC(C(=O)N(C(C(=O)OC(C(=O)N(C(C(=O)OC(C(=O)N1C)C(C)C)CC(C)C)C)C(C)C)CC(C)C)C)C(C)C)CC(C)C)C)C(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QVZZPLDJERFENQ-GWUCKCKXSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C48H84N4O12/c1-25(2)21-33-45(57)61-38(30(11)12)42(54)50(18)35(23-27(5)6)47(59)63-40(32(15)16)44(56)52(20)36(24-28(7)8)48(60)64-39(31(13)14)43(55)51(19)34(22-26(3)4)46(58)62-37(29(9)10)41(53)49(33)17/h25-40H,21-24H2,1-20H3/t33-,34-,35-,36-,37-,38+,39+,40+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Bassianolide Dilution Calculator

Bassianolide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.0999 mL | 5.4993 mL | 10.9987 mL | 21.9974 mL | 27.4967 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.22 mL | 1.0999 mL | 2.1997 mL | 4.3995 mL | 5.4993 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.11 mL | 0.5499 mL | 1.0999 mL | 2.1997 mL | 2.7497 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.022 mL | 0.11 mL | 0.22 mL | 0.4399 mL | 0.5499 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.011 mL | 0.055 mL | 0.11 mL | 0.22 mL | 0.275 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Glochidionionoside D
Catalog No.:BCX0583
CAS No.:620598-43-8
- Hydrangeifolin I
Catalog No.:BCX0582
CAS No.:88510-10-5
- 9-Oxoailanthoidol
Catalog No.:BCX0581
CAS No.:912280-23-0
- Balanophonin B
Catalog No.:BCX0580
CAS No.:92216-41-6
- Noueloside D
Catalog No.:BCX0579
CAS No.:2088336-76-7
- 3,4,6-Tri-O-galloyl-D-glucose
Catalog No.:BCX0578
CAS No.:99523-99-6
- Comososide
Catalog No.:BCX0577
CAS No.:1123534-26-8
- γ-Thujaplicatene
Catalog No.:BCX0576
CAS No.:29725-59-5
- Plicatinaphthol
Catalog No.:BCX0575
CAS No.:22127-07-7
- Ananasin A
Catalog No.:BCX0574
CAS No.:2242607-05-0
- Pyrroside A
Catalog No.:BCX0573
CAS No.:116271-36-4
- Piperafizine B
Catalog No.:BCX0572
CAS No.:74720-33-5
- Beauvericin A
Catalog No.:BCX0585
CAS No.:165467-50-5
- Laurotetanine
Catalog No.:BCX0586
CAS No.:128-76-7
- 6'-O-Acetyldaucosterol
Catalog No.:BCX0587
CAS No.:870093-75-7
- Cyclocarioside I
Catalog No.:BCX0588
CAS No.:1644624-82-7
- ent-11α,12α,15α-Trihydroxykaur-16-en-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0589
CAS No.:57719-84-3
- Thujaplicatin
Catalog No.:BCX0590
CAS No.:6512-66-9
- 7,2',4'-Trihydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCX0591
CAS No.:128837-33-2
- Noueloside B
Catalog No.:BCX0592
CAS No.:2172630-88-3
- Genkwanol A
Catalog No.:BCX0593
CAS No.:111103-90-3
- Cyclocarioside K
Catalog No.:BCX0594
CAS No.:2093058-16-1
- Wikstrol B
Catalog No.:BCX0595
CAS No.:160963-92-8
- Stelleranoid B
Catalog No.:BCX0596
CAS No.:2957870-90-3
Rapid analysis of insecticidal metabolites from the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana 331R using UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS.[Pubmed:37968430]
Mycotoxin Res. 2024 Feb;40(1):123-132.
Beauveria bassiana, a representative entomopathogenic fungus, is increasingly being utilized as an eco-friendly pest management alternative to chemical insecticides. This fungus produces a range of insecticidal secondary metabolites that act as antimicrobial and immunosuppressive agents. However, detailed qualitative and quantitative analysis related to these compounds remains scarce, we developed a method for the rapid analysis of these metabolites. Eight secondary metabolites (bassianin, Bassianolide, beauvericin, beauveriolide I, enniatin A, A1, and B, and tenellin) were efficiently extracted when B. bassiana-infected Tenebrio molitor larvae were ground in 70% EtOH extraction solvent and subsequently subjected to ultrasonic treatment for 30 min. The eight metabolites were rapidly and simultaneously analyzed using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS). Bassianolide (20.6-51.1 microg/g) and beauvericin (63.6-109.8 microg/g) were identified as the main metabolites in B. basssiana-infected larvae, indicating that they are likely major toxins of B. bassiana. Validation of the method exhibited recovery rates in the range of 80-115% and precision in the range of 0.1-8.0%, indicating no significant interference from compounds in the matrix. We developed a method to rapidly analyze eight insecticidal metabolites using UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS. This can be extensively utilized for detecting and producing insecticidal fungal secondary metabolites.
Hydroxy Acid Activation in Fungal Non-Ribosomal Peptide Synthesis Assessed by Site-Directed Mutagenesis.[Pubmed:37252886]
Chembiochem. 2023 Jul 3;24(13):e202300233.
The fungal cyclodepsipeptides (CDPs) enniatin, beauvericin, Bassianolide, and PF1022 consist of alternating N-methylated l-amino and d-hydroxy acids. They are synthesized by non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS). The amino acid and hydroxy acid substrates are activated by adenylation (A) domains. Although various A domains have been characterized thus giving insights into the mechanism of substrate conversion, little is known about the utilization of hydroxy acids in NRPSs. Therefore, we used homology modelling and molecular docking of the A(1) domain of enniatin synthetase (EnSyn) to gain insights into the mechanism of hydroxy acid activation. We introduced point mutations into the active site and used a photometric assay to study the substrate activation. The results suggest that the hydroxy acid is selected by interaction with backbone carbonyls rather than by a specific side chain. These insights enhance the understanding of non-amino acid substrate activation and could contribute to the engineering of depsipeptide synthetases.
Metabolomic Analysis Demonstrates the Impacts of Polyketide Synthases PKS14 and PKS15 on the Production of Beauvericins, Bassianolide, Enniatin A, and Ferricrocin in Entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana.[Pubmed:36984865]
Metabolites. 2023 Mar 14;13(3):425.
Beauveria bassiana is a globally distributed entomopathogenic fungus that produces various secondary metabolites to support its pathogenesis in insects. Two polyketide synthase genes, pks14 and pks15, are highly conserved in entomopathogenic fungi and are important for insect virulence. However, understanding of their mechanisms in insect pathogenicity is still limited. Here, we overexpressed these two genes in B. bassiana and compared the metabolite profiles of pks14 and pks15 overexpression strains to those of their respective knockout strains in culture and in vivo using tandem liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking (GNPS). The pks14 and pks15 clusters exhibited crosstalk with biosynthetic clusters encoding insect-virulent metabolites, including beauvericins, Bassianolide, enniatin A, and the intracellular siderophore ferricrocin under certain conditions. These secondary metabolites were upregulated in the pks14-overexpressing strain in culture and the pks15-overexpressing strain in vivo. These data suggest that pks14 and pks15, their proteins or their cluster components might be directly or indirectly associated with key pathways in insect pathogenesis of B. bassiana, particularly those related to secondary metabolism. Information about interactions between the polyketide clusters and other biosynthetic clusters improves scientific understanding about crosstalk among biosynthetic pathways and mechanisms of pathogenesis.
The Toxins of Beauveria bassiana and the Strategies to Improve Their Virulence to Insects.[Pubmed:34512581]
Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 26;12:705343.
The long-term and excessive usage of pesticides is an enormous burden on the environment, which also increases pest resistance. To overcome this problem, research and application of entomopathogenic fungi, which are both environmentally friendly and cause lower resistance, have gained great momentum. Entomopathogenic fungi have a wide range of prospects. Apart from Bacillus thuringiensis, Beauveria bassiana is the most studied biopesticide. After invading insect hosts, B. bassiana produces a variety of toxins, which are secondary metabolites such as beauvericin, bassianin, Bassianolide, beauverolides, tenellin, oosporein, and oxalic acid. These toxins help B. bassiana to parasitize and kill the hosts. This review unequivocally considers beauveria toxins highly promising and summarizes their attack mechanism(s) on the host insect immune system. Genetic engineering strategies to improve toxin principles, genes, or virulent molecules of B. bassiana have also been discussed. Lastly, we discuss the future perspective of Beauveria toxin research, including newly discovered toxins.
Sarocladium and Lecanicillium Associated with Maize Seeds and Their Potential to Form Selected Secondary Metabolites.[Pubmed:33451141]
Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):98.
The occurrence and diversity of Lecanicillium and Sarocladium in maize seeds and their role in this cereal are poorly understood. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate Sarocladium and Lecanicillium communities found in endosphere of maize seeds collected from fields in Poland and their potential to form selected bioactive substances. The sequencing of the internally transcribed spacer regions 1 (ITS 1) and 2 (ITS2) and the large-subunit (LSU, 28S) of the rRNA gene cluster resulted in the identification of 17 Sarocladium zeae strains, three Sarocladium strictum and five Lecanicillium lecanii isolates. The assay on solid substrate showed that S. zeae and S. strictum can synthesize Bassianolide, vertilecanin A, vertilecanin A methyl ester, 2-decenedioic acid and 10-hydroxy-8-decenoic acid. This is also the first study revealing the ability of these two species to produce beauvericin and enniatin B1, respectively. Moreover, for the first time in the present investigation, pyrrocidine A and/or B have been annotated as metabolites of S. strictum and L. lecanii. The production of toxic, insecticidal and antibacterial compounds in cultures of S. strictum, S. zeae and L. lecanii suggests the requirement to revise the approach to study the biological role of fungi inhabiting maize seeds.
Application of untargeted tandem mass spectrometry with molecular networking for detection of enniatins and beauvericins from complex samples.[Pubmed:33166889]
J Chromatogr A. 2020 Dec 20;1634:461626.
An untargeted LC-MS/MS-based molecular networking method was established for the automatic determination of variants of enniatin and beauvericin from both fungal cultures and naturally contaminated samples. Using this method, a large number of samples can be efficiently analyzed for the presence of enniatin- and beauvericin-related compounds. As proof of concept, 26 cultures, derived from 13 fungal strains in the genera of Fusarium, Beauveria, and Diaporthe, as well as 46 food samples were analyzed. Four enniatin- and three beauvericin-producing fungi were newly discovered. Among them, the production of beauvericin by Fusarium sp. 190-20-2 was further confirmed by the presence of a beauvericin biosynthesis gene cluster in its genomic sequence. Additionally, 17 enniatin congeners, including one new isomer of enniatin A, and three previously unreported Bassianolide analogues were detected from an enniatin-producing fungus, Fusarium sp. 17-048, and a beauvericin-producing fungus, Beauveria sp. 186-069, respectively. The structures of the detected compounds were tentatively determined by a series of product ions of their sodium adducts. The new isomer of enniatin A was further confirmed by NMR spectra. A preliminary survey of food samples showed that enniatins were prevalent in the tested wheat flour and noodle samples, whereas beauvericin was only discovered in cornflour powder samples.
Characterization of mycotoxins from entomopathogenic fungi (Cordyceps fumosorosea) and their toxic effects to the development of asian citrus psyllid reared on healthy and diseased citrus plants.[Pubmed:33058930]
Toxicon. 2020 Dec;188:39-47.
Entomopathogenic fungi (EPF) produce multiple mycotoxins, which play an essential role in improving fungal pathogenesis and virulence. To characterize various mycotoxins from the crude methanol extract of Cordyceps fumosorosea, a major EPF against various insect pests, we performed ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometer (UPLC-QTOF MS) technique, and all compounds were identified through molecular mass and formulae. Bassianolide was assessed against the nymphs and adults of Diaphorina citri reared on healthy and Huanglongbing (HLB)-diseased Citrus spp. Plants under laboratory conditions. Overall, 17 compounds were identified from the fungal extract and categorized into three groups, i.e. (1) alkaloids (Isariotins A-C), (2) peptides (Bassianolide, Beauverolides, Beauvericin A, Isaridins and Destruxin E) and (3) polyketide (Tenuipyrone). The detected beauverolides (B, C, F, I, Ja) from C. fumosorosea were novel mycotoxins, and their detection intensity was the highest in the fungal extract. Furthermore, Bassianolide caused more than 70% and 80% mortality of D. citri nymphs and adults after two days of application, respectively. After three days of chemical application, all nymphal and adult populations of D. citri were killed by Bassianolide. However, the mortality rates of both populations, nymphs and adults, were higher on HLB-diseased plants as compared to healthy plants.
Isolation of Beauveria bassiana from the Chagas Disease Vector Triatoma infestans in the Gran Chaco Region of Argentina: Assessment of Gene Expression during Host-Pathogen Interaction.[Pubmed:33053646]
J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Oct 12;6(4):219.
A native strain of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana (Bb-C001) was isolated from a naturally infected Triatoma infestans, Klug (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) adult cadaver in the Gran Chaco region, Salta province, Argentina. The isolate was both phenotypic and molecularly characterized in a context of fungus-insect interaction, by measuring the expression pattern of toxin genes during infection and immune response of T. infestans. The commercial strain GHA of B. bassiana, which was previously used in field interventions to control these vectors, was used as reference in this study. The phylogenetic trees based on both ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) and elongation factor 1-alpha (EF1-alpha) indicated that Bb-C001 fits into a B. bassiana cluster, and the sequence-characterized amplified regions (SCAR) showed that Bb-C001 is different from the GHA strain. There were no differences between both strains regarding viability, radial growth, and conidia production, either in the median survival time or insect mortality. However, Bb-C001 showed a higher expression than GHA of the Bassianolide synthetase gene (BbbslS) during infection, and similar levels of the beauvericin synthetase gene (BbbeaS). Immune-related genes of T. infestans nymphs (limpet-2 and defensin-1, -2, and -6) were later expressed and thus insects failed to stop the infection process. These results showed that B. bassiana Bb-C001 is a promised fungal strain to be incorporated in the current biological control programs of T. infestans in Salta province, Argentina.
Lack of involvement of chitinase in direct toxicity of Beauveria bassiana cultures to the aphid Myzus persicae.[Pubmed:31715183]
J Invertebr Pathol. 2020 Jan;169:107276.
The fungal insect pathogen Beauveria bassiana produces a range of insecticidal metabolites and enzymes, including chitinases and proteases, which may assist the disease progression. The enzymes often play a predominant role in the pathogenicity pathway and both chitinases and proteases have previously been shown to be important in host infection. Spray application of supernatants of B. bassiana broth cultures of an isolate from New Zealand caused significant mortality in the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae, within 24 h, demonstrating an apparent contact toxicity. Three-day-old broth cultures were the most effective, with less insect mortality seen using six-day-old broth. However, aphicidal activity increased again when treating aphids with seven-day-old broth. Cultures grew substantially better and produced more potent aphicidal cultures when cultured in media with an initial pH above 5.5. Chitinase was produced a day earlier than the serine protease Pr1, but the peak production periods of these enzymes did not correlate with the aphicidal activities of three- or six-day-old cultures. Cultures treated with EDTA or heated to inactivate the enzymes still showed strong insecticidal activity. Neither beauvericin nor Bassianolide, two known insecticidal metabolites, were detected in the supernatants. Therefore the key aphicidal components of B. bassiana cultures were not associated with chitinase nor Pr1 and are yet to be identified.
Modified substrate specificity of a methyltransferase domain by protein insertion into an adenylation domain of the bassianolide synthetase.[Pubmed:31388353]
J Biol Eng. 2019 Jul 31;13:65.
BACKGROUND: Creating designer molecules using a combination of select domains from polyketide synthases and/or nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) continues to be a synthetic goal. However, an incomplete understanding of how protein-protein interactions and dynamics affect each of the domain functions stands as a major obstacle in the field. Of particular interest is understanding the basis for a class of methyltransferase domains (MT) that are found embedded within the adenylation domain (A) of fungal NRPS systems instead of in an end-to-end architecture. RESULTS: The MT domain from Bassianolide synthetase (BSLS) was removed and the truncated enzyme BSLS-DeltaMT was recombinantly expressed. The biosynthesis of Bassianolide was abolished and N-desmethylBassianolide was produced in low yields. Co-expression of BSLS-DeltaMT with standalone MT did not recover Bassianolide biosynthesis. In order to address the functional implications of the protein insertion, we characterized the N-methyltransferase activity of the MT domain as both the isolated domain (MT(BSLS)) and as part of the full NRPS megaenzyme. Surprisingly, the MT(BSLS) construct demonstrated a relaxed substrate specificity and preferentially methylated an amino acid (L-Phe-SNAC) that is rarely incorporated into the final product. By testing the preference of a series of MT constructs (BSLS, MT(BSLS), cMT, XLcMT, and aMT) to L-Phe-SNAC and L-Leu-SNAC, we further showed that restricting and/or fixing the termini of the MT(BSLS) by crosslinking or embedding the MT within an A domain narrowed the substrate specificity of the methyltransferase toward L-Leu-SNAC, the preferred substrate for the BSLS megaenzyme. CONCLUSIONS: The embedding of MT into the A2 domain of BSLS is not required for the product assembly, but is critical for the overall yields of the final products. The substrate specificity of MT is significantly affected by the protein context within which it is present. While A domains are known to be responsible for selecting and activating the biosynthetic precursors for NRPS systems, our results suggest that embedding the MT acts as a secondary gatekeeper for the assembly line. This work thus provides new insights into the embedded MT domain in NRPSs, which will facilitate further engineering of this type of biosynthetic machinery to create structural diversity in natural products.
Cyclic Octamer Peptoids: Simplified Isosters of Bioactive Fungal Cyclodepsipeptides.[Pubmed:30029532]
Molecules. 2018 Jul 19;23(7):1779.
Cyclic peptoids have recently emerged as an important class of bioactive scaffolds with unique conformational properties and excellent metabolic stabilities. In this paper, we describe the design and synthesis of novel cyclic octamer peptoids as simplified isosters of mycotoxin depsipeptides Bassianolide, verticilide A1, PF1022A and PF1022B. We also examine their complexing abilities in the presence of sodium tetrakis[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]borate (TFPB) salt and explore their general insecticidal activity. Finally, we discuss the possible relationship between structural features of free and Na(+)-complexed cyclic octamer peptoids and bioactivities in light of conformational isomerism, a crucial factor affecting cyclic peptoids' biomimetic potentials.
Investigation and molecular docking studies of Bassianolide from Lecanicillium lecanii against Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae).[Pubmed:29551387]
Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;206-207:65-72.
Entomopathogenic fungi are rich sources of bioactive secondary metabolites that possess insecticidal properties. The present study reported a novel approach for the identification of insecticidal compounds produced by Lecanicillium lecanii 09 and to assess their toxicity against the diamondback moth Plutella xylostella L. The cyclic peptides groups of toxic substances were separated from L. lecanii 09 through submerged liquid state fermentation. The most abundant toxic metabolite, Bassianolide was purified by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and its molecular weight and purity were determined by Liquid chromatography - mass spectroscopy (LC-MS), Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and H(1) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) respectively. Subsequently, the toxicity of Bassianolide was tested against third instar larvae of P. xylostella at three different concentrations (0.01, 0.1, 0.5 mg/ml). The results showed that higher concentration of 0.5 mg/ml had significant maximum mortality at 120 hour post inoculation. Furthermore, we investigated the ligand-target interaction of secondary metabolite binding with target insect immune receptor proteins and predicted the role of toxicity against insect host. This is the first study to report the infection process and the interaction of fungal mediated cyclicdepsipeptide compound (Bassianolide) from L. lecanii 09 against the insect host P. xylostella. This novel approach provides a potential impact on biological control using natural toxic compound which acts as good inhibitor on pest insect and prevents toxicity hazards, pollution as well as ecocidal effects killing several beneficial insects.
Aspergillus niger is a superior expression host for the production of bioactive fungal cyclodepsipeptides.[Pubmed:29507740]
Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2018 Mar 2;5:4.
BACKGROUND: Fungal cyclodepsipeptides (CDPs) are non-ribosomally synthesized peptides produced by a variety of filamentous fungi and are of interest to the pharmaceutical industry due to their anticancer, antimicrobial and anthelmintic bioactivities. However, both chemical synthesis and isolation of CDPs from their natural producers are limited due to high costs and comparatively low yields. These challenges might be overcome by heterologous expression of the respective CDP-synthesizing genes in a suitable fungal host. The well-established industrial fungus Aspergillus niger was recently genetically reprogrammed to overproduce the cyclodepsipeptide enniatin B in g/L scale, suggesting that it can generally serve as a high production strain for natural products such as CDPs. In this study, we thus aimed to determine whether other CDPs such as beauvericin and Bassianolide can be produced with high titres in A. niger, and whether the generated expression strains can be used to synthesize new-to-nature CDP derivatives. RESULTS: The beauvericin and Bassianolide synthetases were expressed under control of the tuneable Tet-on promoter, and titres of about 350-600 mg/L for Bassianolide and beauvericin were achieved when using optimized feeding conditions, respectively. These are the highest concentrations ever reported for both compounds, whether isolated from natural or heterologous expression systems. We also show that the newly established Tet-on based expression strains can be used to produce new-to-nature beauvericin derivatives by precursor directed biosynthesis, including the compounds 12-hydroxyvalerate-beauvericin and bromo-beauvericin. By feeding deuterated variants of one of the necessary precursors (d-hydroxyisovalerate), we were able to purify deuterated analogues of beauvericin and Bassianolide from the respective A. niger expression strains. These deuterated compounds could potentially be used as internal standards in stable isotope dilution analyses to evaluate and quantify fungal spoilage of food and feed products. CONCLUSION: In this study, we show that the product portfolio of A. niger can be expanded from enniatin to other CDPs such as beauvericin and Bassianolide, as well as derivatives thereof. This illustrates the capability of A. niger to produce a range of different peptide natural products in titres high enough to become industrially relevant.


