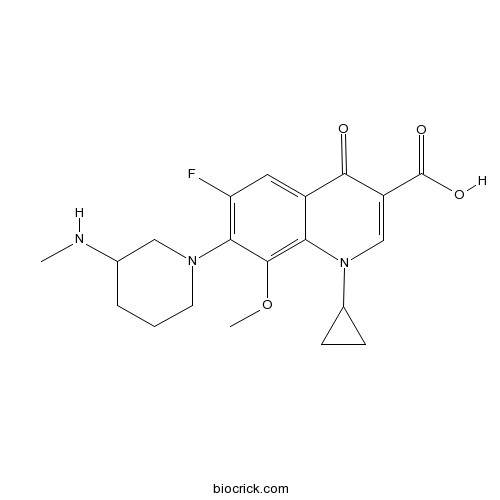
BalofloxacinCAS# 127294-70-6 |
- GW1929
Catalog No.:BCC1611
CAS No.:196808-24-9
- Inolitazone
Catalog No.:BCC1652
CAS No.:223132-37-4
- Inolitazone dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1653
CAS No.:223132-38-5
- Aleglitazar
Catalog No.:BCC1337
CAS No.:475479-34-6
- L-165041
Catalog No.:BCC1687
CAS No.:79558-09-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 127294-70-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 65958 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H24FN3O4 | M.Wt | 389.42 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) DMSO : 0.67 mg/mL (1.72 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-[3-(methylamino)piperidin-1-yl]-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CNC1CCCN(C1)C2=C(C=C3C(=C2OC)N(C=C(C3=O)C(=O)O)C4CC4)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MGQLHRYJBWGORO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H24FN3O4/c1-22-11-4-3-7-23(9-11)17-15(21)8-13-16(19(17)28-2)24(12-5-6-12)10-14(18(13)25)20(26)27/h8,10-12,22H,3-7,9H2,1-2H3,(H,26,27) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Balofloxacin is quinolone antibiotic, inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial DNA by interference with the enqyme DNA gyrase.
Target: Antibacterial; DNA gyrase.
Balofloxacin, an orally active fluoroquinolone antibiotic, has been developed by Choongwae Pharma in Korea, for the treatment of urinary tract infection (UTI). Chugai and Ciba were developing balofloxacin for respiratory tract infections (RTI) but discontinued development in 1995 due to changes in Chugai's R&D; focus and a lack of efficacy of the drug. Following phase II trials, Choongwae bought the rights to develop balofloxacin in Korea from Chugai. Phase III trials for UTI were completed in early 2001. Balofloxacin was approved by the Korean FDA in December 2001 for UTI. In March 2002, phase II trials were underway for RTI. References: | |||||

Balofloxacin Dilution Calculator

Balofloxacin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5679 mL | 12.8396 mL | 25.6792 mL | 51.3584 mL | 64.198 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5136 mL | 2.5679 mL | 5.1358 mL | 10.2717 mL | 12.8396 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2568 mL | 1.284 mL | 2.5679 mL | 5.1358 mL | 6.4198 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0514 mL | 0.2568 mL | 0.5136 mL | 1.0272 mL | 1.284 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0257 mL | 0.1284 mL | 0.2568 mL | 0.5136 mL | 0.642 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Balofloxacin is quinolone antibiotic, inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial DNA by interference with the enqyme DNA gyrase.
- Sitafloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC5164
CAS No.:127254-12-0
- Intermedin B
Catalog No.:BCN7317
CAS No.:127214-87-3
- Bisacurone C
Catalog No.:BCN7316
CAS No.:127214-86-2
- (3S,4S)-3-(Boc-amino)-4-methylpyrrolidine
Catalog No.:BCC4015
CAS No.:127199-54-6
- KN-62
Catalog No.:BCC3602
CAS No.:127191-97-3
- 7-(2'-Deoxyadenosin-N6-yl)aristolactam I
Catalog No.:BCN2559
CAS No.:127191-86-0
- 4-O-Demethylkadsurenin D
Catalog No.:BCN6649
CAS No.:127179-70-8
- MI-2
Catalog No.:BCC1746
CAS No.:1271738-62-5
- MI-3
Catalog No.:BCC1747
CAS No.:1271738-59-0
- BMS-911543
Catalog No.:BCC2204
CAS No.:1271022-90-2
- Glyceryl hexacosanoate
Catalog No.:BCC8991
CAS No.:127098-14-0
- Sulfo-NHS-LC-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3578
CAS No.:127062-22-0
- BRL 37344, sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6860
CAS No.:127299-93-8
- Zamifenacin fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC7418
CAS No.:127308-98-9
- PACAP 1-27
Catalog No.:BCC5726
CAS No.:127317-03-7
- YLF-466D
Catalog No.:BCC4086
CAS No.:1273323-67-3
- 2-Chloromethyl-3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8569
CAS No.:127337-60-4
- Rebaudioside G
Catalog No.:BCN7860
CAS No.:127345-21-5
- Coclauril
Catalog No.:BCN6150
CAS No.:127350-68-9
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- Odoroside A
Catalog No.:BCC8224
CAS No.:12738-19-1
- Y-27152
Catalog No.:BCC7254
CAS No.:127408-30-4
- Y-26763
Catalog No.:BCC7253
CAS No.:127408-31-5
- Calystegine B2
Catalog No.:BCN1879
CAS No.:127414-85-1
Alterations of protein complexes and pathways in genetic information flow and response to stimulus contribute to Escherichia coli resistance to balofloxacin.[Pubmed:22729160]
Mol Biosyst. 2012 Sep;8(9):2303-11.
Protein-protein interactions are important biological processes and essential for a global understanding of cell functions. To date, little is known about the protein interactions and roles of the protein interacting networks and protein complexes in bacterial resistance to antibiotics. In the present study, we investigated protein complexes in Escherichia coli exposed to an antibiotic Balofloxacin (BLFX). One homomeric and eight heteromeric protein complexes involved in BLFX resistance were detected. Potential roles of these complexes that are played in BLFX resistance were characterized and categorized into four functional areas: information streams, monosaccharide metabolism, response to stimulus and amino acid metabolic processes. Protein complexes involved in information streams and response to stimulus played more significant roles in the resistance. These results are consistent with previously published mechanisms on the acquired quinolone-resistance through the GyrA-GyrB complex, and two novel antibiotic-resistant pathways were identified: upregulation of genetic information flow and alteration of the response to a stimulus. The balance of the two pathways will be a viable means of reducing BLFX-resistance.
In vitro and in vivo effectiveness evaluation of balofloxacin in experimental Staphylococcus aureus keratitis.[Pubmed:24828089]
J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Aug;30(6):482-8.
PURPOSE: To evaluate the effectiveness of Balofloxacin for treatment of experimental Staphylococcus aureus keratitis. METHODS: In vitro testing compared the cellular toxicity of and bacterial susceptibility to Balofloxacin and levofloxacin in human corneal epithelial cells (HCECs). For in vivo testing, experimental bacterial keratitis was induced and treated with Balofloxacin eye drops (0.5%) and levofloxacin eye drops (0.5%). RESULTS: In vitro toxicity examinations showed that Balofloxacin, as well as levofloxacin, had low cytotoxicity in HCECs. Balofloxacin eye drops (0.5%) also showed a similar relative cytotoxicity to levofloxacin eye drops (0.5%). In bacterial susceptibility examinations, both Balofloxacin and levofloxacin significantly reduced S. aureus compared with the untreated control (P<0.001 for both Balofloxacin and levofloxacin). Balofloxacin was more effective than levofloxacin in the treatment of S. aureus bacterial keratitis (P<0.05). In experimental bacterial keratitis treatment testing, Balofloxacin was also more effective than levofloxacin with respect to the parameters of physiological score, histological observation, and bacterial quantitation (P<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: Balofloxacin was safe in the treatment of S. aureus bacterial keratitis, and more effective than levofloxacin. Therefore, Balofloxacin was shown to have potential clinical value in ophthalmic local application.
Myo-inositol improves the host's ability to eliminate balofloxacin-resistant Escherichia coli.[Pubmed:26030712]
Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 1;5:10720.
Antibiotic-resistant mechanisms are associated with fitness costs. However, why antibiotic-resistant bacteria usually show increasing adaptation to hosts is largely unknown, especially from the host's perspective. The present study reveals the host's varied response to Balofloxacin-resistant Escherichia coli (BLFX-R) using an integrated proteome and metabolome approach and identifies myo-inositol and phagocytosis-related proteins as crucial biomarkers. Originally, macrophages have an optimal attractive preference to BLFX-S due to more polarization of BLFX-S than BLFX-R, which renders faster elimination to BLFX-S than BLFX-R. The slower elimination to BLFX-R may be reversed by exogenous myo-inositol. Primarily, myo-inositol depolarizes macrophages, elevating adherence to both BLFX-S and BLFX-R. Since the altered adherence is equal to both strains, the myo-inositol-treated macrophages are free of the barrier to BLFX-R and thereby promote phagocytosis of BLFX-R. This work provides a novel strategy based on metabolic modulation for eliminating antibiotic-resistant bacteria with a high degree of host adaptation.
Downregulation of Na(+)-NQR complex is essential for Vibrio alginolyticus in resistance to balofloxacin.[Pubmed:22465713]
J Proteomics. 2012 May 17;75(9):2638-48.
Increasingly isolated frequency of antibiotic-resistant V. alginolyticus strains in clinic and aquaculture has been reported, but the mechanisms of V. alginolyticus antibiotic resistance are largely absent. In the present study, native/SDS-PAGE based proteomics, which may provide information on protein-protein interaction, was utilized to investigate differential proteins of V. alginolyticus in resistance to Balofloxacin. Ten proteins were altered, in which V12G01_04671, V12G01_00457, V12G01_15927, V12G01_15240, NqrA (spot 26), and NqrF (spot 30) were downregulated, while V12G01_22043, TolC, V12G01_15130, V12G01_19297 were upregulated. Importantly, the two components of Na(+)-NQR complex, NqrA and NqrF, were vertically lined and was further investigated. Western blotting assay indicated that downregulation of the two proteins contrasted sharply with upregulation of a control protein TolC, which was consistent with the result obtained from 2-DE gel analysis. Furthermore, overexpression of NqrA, NqrF and TolC resulted in decrease and elevation of bacterial survival ability in medium with Balofloxacin, respectively. These results indicate that downregulation of Na(+)-NQR complex is essential for V. alginolyticus resistance to Balofloxacin. This is the first report on the role of Na(+)-NQR complex in antibiotic resistance. This finding highlights the way to an understanding of antibiotic-resistant mechanisms in content of metabolic regulation.


