BalanophoninCAS# 118916-57-7 |
- (+)-Balanophonin
Catalog No.:BCX0627
CAS No.:215319-47-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 118916-57-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23252258 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H20O6 | M.Wt | 356.4 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (+)-Balanophonin;215319-47-4 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
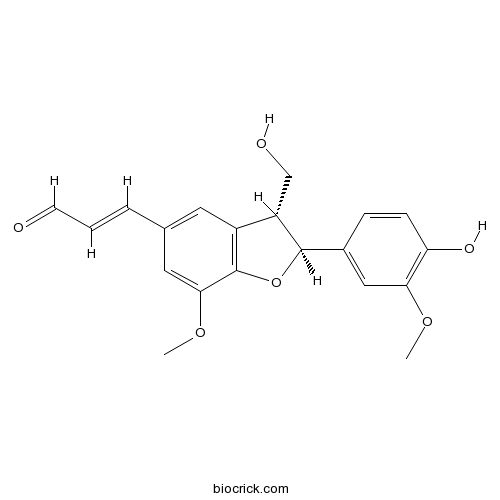
| Chemical Name | (E)-3-[(2S,3R)-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-(hydroxymethyl)-7-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-5-yl]prop-2-enal | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC2=C1OC(C2CO)C3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)OC)C=CC=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GWCSSLSMGCFIFR-LNFBDUAVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H20O6/c1-24-17-10-13(5-6-16(17)23)19-15(11-22)14-8-12(4-3-7-21)9-18(25-2)20(14)26-19/h3-10,15,19,22-23H,11H2,1-2H3/b4-3+/t15-,19+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Balanophonin shows potent α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, it has antioxidant, and anti-cancer activities. (±)-Balanophonin shows significant antibacterial activity against cariogenic oral streptococci, Streptococcus mutans and S. sobrinus. |
| Targets | α-glucosidase |
| In vitro | Antioxidant phenolic compounds of cassava (Manihot esculenta) from Hainan.[Pubmed: 22157579]Molecules. 2011 Dec 7;16(12):10157-67.
Aquilarin A, a new benzenoid derivative from the fresh stem of Aquilaria sinensis.[Pubmed: 20657422 ]Molecules. 2010 Jun 1;15(6):4011-6.
Constituents of the seeds of Cornus officinalis with Inhibitory Activity on the Formation of Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)[Reference: WebLink]J. Korean Soc. Appl.Biol.Chem., 2008, 51(4):316- 20.Ten compounds, (+)-pinoresinol (1), (-)-Balanophonin (2), gallicin (3), vanillin (4), 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde (5), coniferaldehyde (6), betulinic acid (7), ursolic acid (8), 5-hydroxymethyl furfural (9), and malic acid (10), were isolated from a EtOAc-soluble fraction of the seeds of Cornus officinalis. Bioactive Phenolic constituents from the culms of Phyllostachys bambusoides[Reference: WebLink]Natural Product Sciences, 2011, 17(4):267-72.
|
| Kinase Assay | Screening of α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of Vietnamese medicinal plants: Isolation of Active Principles from Oroxylum indicum[Reference: WebLink]Natural Product Sciences, 2014, 18(1):47-51.Among 38 Vietnamese medicinal plant extracts investigated for their α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, 35 extracts showed IC 50 values below 250 µg/mL. |
| Structure Identification | J Chromatogr A. 2012 Nov 16;1264:143-7.The role of harmonized, gas and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry in the discovery of the neolignan balanophonin in the fruit wall of Cirsium vulgare.[Pubmed: 23068765]In order to identify and quantify fruit-lignans of Cirsium vulgare - authors introduced a special analysis system: with particular attention to the lignans enrichment/separation course. |

Balanophonin Dilution Calculator

Balanophonin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8058 mL | 14.0292 mL | 28.0584 mL | 56.1167 mL | 70.1459 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5612 mL | 2.8058 mL | 5.6117 mL | 11.2233 mL | 14.0292 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2806 mL | 1.4029 mL | 2.8058 mL | 5.6117 mL | 7.0146 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0561 mL | 0.2806 mL | 0.5612 mL | 1.1223 mL | 1.4029 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0281 mL | 0.1403 mL | 0.2806 mL | 0.5612 mL | 0.7015 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Denudaquinol
Catalog No.:BCN8035
CAS No.:1189105-40-5
- Lettowienolide
Catalog No.:BCN8038
CAS No.:1189105-39-2
- Fmoc-D-Allo-Ile-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3508
CAS No.:118904-37-3
- Alstoyunine E
Catalog No.:BCN4782
CAS No.:1188932-15-1
- CEP-32496
Catalog No.:BCC1079
CAS No.:1188910-76-0
- KN-93 Phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC5638
CAS No.:1188890-41-6
- ABT 702 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5905
CAS No.:1188890-28-9
- NBQX
Catalog No.:BCC6624
CAS No.:118876-58-7
- Anti-Inflammatory Peptide 1
Catalog No.:BCC1006
CAS No.:118850-71-8
- Ustusolate C
Catalog No.:BCN6755
CAS No.:1188398-15-3
- Ustusol C
Catalog No.:BCN6757
CAS No.:1188398-13-1
- 15,16-Di-O-acetyldarutoside
Catalog No.:BCN6071
CAS No.:1188282-02-1
- 5-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-7-methoxybenzofuran
Catalog No.:BCN1606
CAS No.:118930-92-0
- 1,3-Dihydroxy-4-methoxy-10-methylacridin-9(10H)-one
Catalog No.:BCN1605
CAS No.:1189362-86-4
- (S,S)-2,6-Bis(4-isopropyl-2-oxazolin-2-yl)pyridine
Catalog No.:BCC8402
CAS No.:118949-61-4
- Ethyl ganoderate J
Catalog No.:BCN3486
CAS No.:1189555-95-0
- Mephedrone hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6183
CAS No.:1189726-22-4
- Fumitremorgin C
Catalog No.:BCC7507
CAS No.:118974-02-0
- 1-O-Deacetyl-2alpha-hydroxykhayanolide E
Catalog No.:BCN1604
CAS No.:1189801-51-1
- Viscumneoside III
Catalog No.:BCN7698
CAS No.:118985-27-6
- 8-Amino-2-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8783
CAS No.:119-28-8
- Methyl salicylate
Catalog No.:BCN5372
CAS No.:119-36-8
- 7-Anilino-4-hydroxy-2-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8777
CAS No.:119-40-4
- p-Anisoin
Catalog No.:BCC9113
CAS No.:119-52-8
Aquilarin A, a new benzenoid derivative from the fresh stem of Aquilaria sinensis.[Pubmed:20657422]
Molecules. 2010 Jun 1;15(6):4011-6.
Chemical investigation of the EtOH extract of the fresh stem of Aquilaria sinensis collected in Hainan Province of China resulted in the isolation of a new benzenoid, named aquilarin A (1), together with two known compounds Balanophonin (2) and (+)-lariciresinol (3). Their structures were elucidated by a study of their physical and spectral data. Compounds 2 and 3 exhibited cytotoxicity against SGC-7901 and SMMC-7721 cell lines.
Isolation of cytotoxic compounds from the seeds of Crataegus pinnatifida.[Pubmed:23845552]
Chin J Nat Med. 2013 Jul;11(4):411-4.
AIM: To study the chemical constituents and bioactivity of the seeds of Crataegus pinnatifida. METHODS: The chemical constituents were isolated and purified by macroporous adsorptive resin D101, silica gel, and ODS column chromatography, and preparative HPLC. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic methods. In addition, the cytotoxic activities of compounds 1-4 were investigated on OPM2 and RPMI-8226 cells. RESULTS: Four compounds were obtained and their structures were identified as (7S, 8S)-4-[2-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]-3, 5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (1), (+)-Balanophonin (2), erythro-guaiacylglycerol-beta-coniferyl aldehyde ether (3), buddlenol A (4). CONCLUSION: Compound 1 is a novel norlignan, while compounds 1-4 exhibited marginal inhibition on the proliferation of OPM2 and RPMI-8226 cells.
Antioxidant phenolic compounds of cassava (Manihot esculenta) from Hainan.[Pubmed:22157579]
Molecules. 2011 Dec 7;16(12):10157-67.
An activity-directed fractionation and purification process was used to isolate antioxidant components from cassava stems produced in Hainan. The ethyl acetate and n-butanol fractions showed greater DPPH and ABTS.+ scavenging activities than other fractions. The ethyl acetate fraction was subjected to column chromatography, to yield ten phenolic compounds: Coniferaldehyde (1), isovanillin (2), 6-deoxyjacareubin (3), scopoletin (4), syringaldehyde (5), pinoresinol (6), p-coumaric acid (7), ficusol (8), Balanophonin (9) and ethamivan (10), which possess significant antioxidant activities. The relative order of DPPH. scavenging capacity for these compounds was ascorbic acid (reference) > 6 > 1 > 8 > 10 > 9 > 3 > 4 > 7 > 5 > 2, and that of ABTS.+ scavenging capacity was 5 > 7 > 1 > 10 > 4 > 6 > 8 > 2 > Trolox (reference compound) > 3 > 9. The results showed that these phenolic compounds contributed to the antioxidant activity of cassava.
The role of harmonized, gas and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry in the discovery of the neolignan balanophonin in the fruit wall of Cirsium vulgare.[Pubmed:23068765]
J Chromatogr A. 2012 Nov 16;1264:143-7.
In order to identify and quantify fruit-lignans of Cirsium vulgare - authors introduced a special analysis system: with particular attention to the lignans enrichment/separation course. These synchronized, germination and enzymatic hydrolysis processes were followed by complementary gas and liquid chromatography, coupled with special mass selective detections (GC-MS, LC-MS/MS, LC-TOF/MS) and confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Mass fragmentations and NMR evidences, proved that the two main medicinal lignan constituents of the fruits of Cirsium vulgare are the neolignan-type, free Balanophonin and the butyrolactone-type tracheloside. As novelty to the field, these two lignans of different chemical structures could be quantitatively extracted, separately from each others, without impurities. Balanophonin and tracheloside do accumulate in the fruits of C. vulgare, separately: Balanophonin was found, in enormous high concentrations, in the fruit wall (23.2-24.9 mg/g), while in embryo part tracheloside was determined (20.3mg/g), exclusively. Consequently, the optimum source of Balanophonin proved to be the fruit wall, while tracheloside, - providing trachelogenin upon enzymatic hydrolysis, - could be obtained from the embryo parts of fruits. As further novelties of the study Balanophonin was identified and quantified at the first time with on-line chromatographic technique, in free form, without authentic standard compound.


