BAY 60-6583Potent A2B receptor agonist CAS# 910487-58-0 |
- QNZ (EVP4593)
Catalog No.:BCC2249
CAS No.:545380-34-5
- Andrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN5735
CAS No.:5508-58-7
- Tanshinone IIA
Catalog No.:BCN5763
CAS No.:568-72-9
- JSH-23
Catalog No.:BCC4610
CAS No.:749886-87-1
- SC75741
Catalog No.:BCC5448
CAS No.:913822-46-5
- IMD 0354
Catalog No.:BCC4556
CAS No.:978-62-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 910487-58-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11717831 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H17N5O2S | M.Wt | 379.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
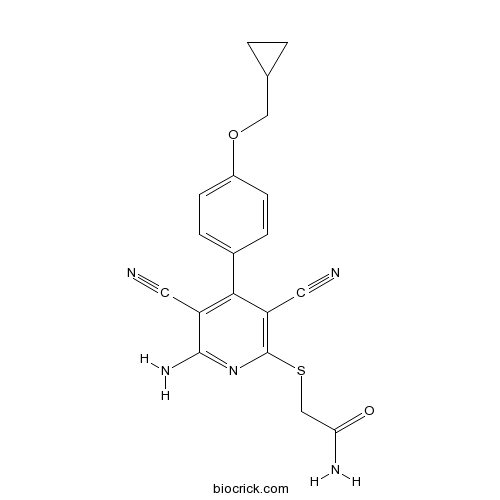
| Chemical Name | 2-[6-amino-3,5-dicyano-4-[4-(cyclopropylmethoxy)phenyl]pyridin-2-yl]sulfanylacetamide | ||
| SMILES | C1CC1COC2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=C(C(=NC(=C3C#N)SCC(=O)N)N)C#N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZTYHZMAZUWOXNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H17N5O2S/c20-7-14-17(12-3-5-13(6-4-12)26-9-11-1-2-11)15(8-21)19(24-18(14)23)27-10-16(22)25/h3-6,11H,1-2,9-10H2,(H2,22,25)(H2,23,24) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent adenosine A2B receptor agonist (EC50 = 2.83 nM for murine A2B receptor). Displays selectivity for A2B over A1, A2A and A3 receptors. Decreases fMLP-induced superoxide production in neutrophils at low concentrations (1-10 nM). Cardioprotective; attenuates infarct size in a mouse model of myocardial ischemia. |

BAY 60-6583 Dilution Calculator

BAY 60-6583 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6355 mL | 13.1773 mL | 26.3546 mL | 52.7093 mL | 65.8866 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5271 mL | 2.6355 mL | 5.2709 mL | 10.5419 mL | 13.1773 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2635 mL | 1.3177 mL | 2.6355 mL | 5.2709 mL | 6.5887 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0527 mL | 0.2635 mL | 0.5271 mL | 1.0542 mL | 1.3177 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0264 mL | 0.1318 mL | 0.2635 mL | 0.5271 mL | 0.6589 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- RGDS peptide
Catalog No.:BCC7694
CAS No.:91037-65-9
- CGI-1746
Catalog No.:BCC1473
CAS No.:910232-84-7
- Impurity of Calcipotriol
Catalog No.:BCC5388
CAS No.:910133-69-6
- Fmoc-Arg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3039
CAS No.:91000-69-0
- N,N'-Bis(acetoacetyl)-o-toluidine
Catalog No.:BCC9062
CAS No.:91-96-3
- Benzoguanamine
Catalog No.:BCC8853
CAS No.:91-76-9
- Coumarin
Catalog No.:BCN6309
CAS No.:91-64-5
- Syringol
Catalog No.:BCN3534
CAS No.:91-10-1
- 2,6-Bis(hydroxymethyl)-p-cresol
Catalog No.:BCC8505
CAS No.:91-04-3
- 2-Benzoylpyridine
Catalog No.:BCC8562
CAS No.:91-02-1
- 8-Methoxybonducellin
Catalog No.:BCN4453
CAS No.:90996-27-3
- A 83-01
Catalog No.:BCC1319
CAS No.:909910-43-6
- Danshenol C
Catalog No.:BCN6681
CAS No.:910856-25-6
- 8-Epidiosbulbin E acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7812
CAS No.:91095-48-6
- 3,6,19,23-Tetrahydroxy-12-ursen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1310
CAS No.:91095-51-1
- Furowanin A
Catalog No.:BCN4790
CAS No.:911004-72-3
- Isotussilagine
Catalog No.:BCN1985
CAS No.:91108-32-6
- SB 706504
Catalog No.:BCC5615
CAS No.:911110-38-8
- Adapalene sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC4285
CAS No.:911110-93-5
- Cefoselis hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4093
CAS No.:911212-25-4
- LY2603618
Catalog No.:BCC3923
CAS No.:911222-45-2
- MPP dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7225
CAS No.:911295-24-4
- EC 144
Catalog No.:BCC5600
CAS No.:911397-80-3
- SLx-2119
Catalog No.:BCC1954
CAS No.:911417-87-3
Environmental changes in Jiaozhou Bay of northern China during the past 90years using metals and biogenic elements in sediments.[Pubmed:28372756]
J Environ Sci (China). 2017 Mar;53:301-312.
Metals and biogenic elements were analyzed from surface sediments and a 100cm core collected from Jiaozhou Bay in July 2009, to determine how the environment has changed over the past 90years due to increasing anthropogenic influences in this region. High concentrations of biogenic silica (BSi) represented the dominance of diatoms in the bay. Most metals were lower than the marine sediment quality guidelines; however, Hg, Zn, and Mn were at polluted levels. The vertical profiles of biogenic elements and metals in the sediment core suggest that the most significant environmental changes occurred since the 1990s, and three stages could be defined: (1) before 1950, characterized by low concentrations of biogenic elements and metals; (2) between 1950 and 1990, displaying an obvious increase of Hg and a slow increase of biogenic elements; (3) after 1990, reflected by a significant increase of total organic carbon (TOC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphate (TP), and most metals, but a decrease of BSi. Correlation and principal component analyses indicated that most metals originated from lithogenic sources, industrial and domestic discharges as well as maricultural activities.
Source levels and call parameters of harbor seal breeding vocalizations near a terrestrial haulout site in Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve.[Pubmed:28372144]
J Acoust Soc Am. 2017 Mar;141(3):EL274.
Source levels of harbor seal breeding vocalizations were estimated using a three-element planar hydrophone array near the Beardslee Islands in Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve, Alaska. The average source level for these calls was 144 dBRMS re 1 muPa at 1 m in the 40-500 Hz frequency band. Source level estimates ranged from 129 to 149 dBRMS re 1 muPa. Four call parameters, including minimum frequency, peak frequency, total duration, and pulse duration, were also measured. These measurements indicated that breeding vocalizations of harbor seals near the Beardslee Islands of Glacier Bay National Park are similar in duration (average total duration: 4.8 s, average pulse duration: 3.0 s) to previously reported values from other populations, but are 170-220 Hz lower in average minimum frequency (78 Hz).
Classification of underwater vocalizations of wild spotted seals (Phoca largha) in Liaodong Bay, China.[Pubmed:28372138]
J Acoust Soc Am. 2017 Mar;141(3):2256.
Underwater vocalizations were recorded and classified from wild spotted seals (Phoca largha) in Liaodong Bay, China. The spotted seals exhibited an extensive underwater vocal repertoire but with limited complexity. Four major call types, representing 77.8% of all calls recorded, were identified using multivariate analyses of ten acoustic parameters; knock, growl, drum, and sweep. The calls were relatively brief (12-270 ms, mean of -10 dB duration) pulsating sounds of low-frequency (peak frequency <600 Hz) and narrow bandwidth (169-232 Hz, mean of -3 dB bandwidth; 237-435 Hz, mean of -6 dB bandwidth). Frequency variables (-3/-6 dB frequency bandwidth, center frequency, and top three peak frequencies) were the primary descriptors used to differentiate the call types. Comparing the spotted seal underwater vocalizations with those of the closely related Pacific harbor seal (Phoca vitulina richardii) indicated that the two species use similar bandwidths and peak frequencies but spotted seal calls were generally shorter. Knowledge of underwater vocalizations of wild spotted seals is important for understanding the species behavior and for planning future acoustic surveys of its distribution and occurrence.
Assessment of health risk related to the ingestion of trace metals through fish consumption in Todos os Santos Bay.[Pubmed:28374187]
Environ Monit Assess. 2017 May;189(5):204.
This study was carried out to evaluate the concentration of trace elements (As, Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) in the muscle of carnivorous fish species from three different areas of Todos os Santos Bay (BTS), Bahia State, Brazil. Trace elements were analyzed using inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), and consumption rates advisory for minimizing chronic systemic effects in children and adults were estimated. As concentrations in fish samples from Jiribatuba were higher than legal limits set by FAO, and Cd concentrations in fish from Iguape Bay were high in comparison with FAO and EC. This study provides information about the fish consumption limits, considering the elements concentrations observed in the analyses, in particular As and Cd, necessary for minimizing potential health risks.
A role for the low-affinity A2B adenosine receptor in regulating superoxide generation by murine neutrophils.[Pubmed:21693629]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Sep;338(3):1004-12.
The formation of adenosine dampens inflammation by inhibiting most cells of the immune system. Among its actions on neutrophils, adenosine suppresses superoxide generation and regulates chemotactic activity. To date, most evidence implicates the G(s) protein-coupled A(2A) adenosine receptor (AR) as the primary AR subtype responsible for mediating the actions of adenosine on neutrophils by stimulating cAMP production. Given that the A(2B)AR is now known to be expressed in neutrophils and that it is a G(s) protein-coupled receptor, we examined in this study whether it signals to suppress neutrophil activities by using 2-[6-amino-3,5-dicyano-4-[4-(cyclopropylmethoxy)phenyl]pyridin-2-ylsulfanyl]aceta mide (BAY 60-6583), a new agonist for the human A(2B)AR that was confirmed in preliminary studies to be a potent and highly selective agonist for the murine A(2B)AR. We found that treating mouse neutrophils with low concentrations (10(-9) and 10(-8) M) of BAY 60-6583 inhibited formylated-methionine-leucine-phenylalanine (fMLP)-stimulated superoxide production by either naive neutrophils, tumor necrosis factor-alpha-primed neutrophils, or neutrophils isolated from mice treated systemically with lipopolysaccharide. This inhibitory action of BAY 60-6583 was confirmed to involve the A(2B)AR in experiments using neutrophils obtained from A(2B)AR gene knockout mice. It is noteworthy that BAY 60-6583 increased fMLP-stimulated superoxide production at higher concentrations (>1 muM), which was attributed to an AR-independent effect. In a standard Boyden chamber migration assay, BAY 60-6583 alone did not stimulate neutrophil chemotaxis or influence chemotaxis in response to fMLP. These results indicate that the A(2B)AR signals to suppress oxidase activity by murine neutrophils, supporting the idea that this low-affinity receptor for adenosine participates along with the A(2A)AR in regulating the proinflammatory actions of neutrophils.
Characterization of the A2B adenosine receptor from mouse, rabbit, and dog.[Pubmed:19141710]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Apr;329(1):2-13.
We have cloned and pharmacologically characterized the A(2B) adenosine receptor (AR) from the dog, rabbit, and mouse. The full coding regions of the dog and mouse A(2B)AR were obtained by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, and the rabbit A(2B)AR cDNA was obtained by screening a rabbit brain cDNA library. It is noteworthy that an additional clone was isolated by library screening that was identical in sequence to the full-length rabbit A(2B)AR, with the exception of a 27-base pair deletion in the region encoding amino acids 103 to 111 (A(2B)AR(103-111)). This 9 amino acid deletion is located in the second intracellular loop at the only known splice junction of the A(2B)AR and seems to result from the use of an additional 5' donor site found in the rabbit and dog but not in the human, rat, or mouse sequences. [(3)H]3-Isobutyl-8-pyrrolidinoxanthine and 8-[4-[((4-cyano-[2,6-(3)H]-phenyl)carbamoylmethyl)oxy]phenyl]-1,3-di(n-propyl)xan thine ([(3)H]MRS 1754) bound with high affinity to membranes prepared from human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells expressing mouse, rabbit, and dog A(2B)ARs. Competition binding studies performed with a panel of agonist (adenosine and 2-amino-3,5-dicyano-4-phenylpyridine analogs) and antagonist ligands identified similar potency orders for the A(2B)AR orthologs, although most xanthine antagonists displayed lower binding affinity for the dog A(2B)AR compared with A(2B)ARs from rabbit and mouse. No specific binding could be detected with membranes prepared from HEK 293 cells expressing the rabbit A(2B)AR(103-111) variant. Furthermore, the variant failed to stimulate adenylyl cyclase or calcium mobilization. We conclude that significant differences in antagonist pharmacology of the A(2B)AR exist between species and that some species express nonfunctional variants of the A(2B)AR due to "leaky" splicing.
Cardioprotection by ecto-5'-nucleotidase (CD73) and A2B adenosine receptors.[Pubmed:17353435]
Circulation. 2007 Mar 27;115(12):1581-90.
BACKGROUND: Ecto-5'-nucleotidase (CD73)-dependent adenosine generation has been implicated in tissue protection during acute injury. Once generated, adenosine can activate cell-surface adenosine receptors (A1 AR, A2A AR, A2B AR, A3 AR). In the present study, we define the contribution of adenosine to cardioprotection by ischemic preconditioning. METHODS AND RESULTS: On the basis of observations of CD73 induction by ischemic preconditioning, we found that inhibition or targeted gene deletion of cd73 abolished infarct size-limiting effects. Moreover, 5'-nucleotidase treatment reconstituted cd73-/- mice and attenuated infarct sizes in wild-type mice. Transcriptional profiling of adenosine receptors suggested a contribution of A2B AR because it was selectively induced by ischemic preconditioning. Specifically, in situ ischemic preconditioning conferred cardioprotection in A1 AR-/-, A2A AR-/-, or A3 AR-/- mice but not in A2B AR-/- mice or in wild-type mice after inhibition of the A2B AR. Moreover, A2B AR agonist treatment significantly reduced infarct sizes after ischemia. CONCLUSIONS: Taken together, pharmacological and genetic evidence demonstrate the importance of CD73-dependent adenosine generation and signaling through A2B AR for cardioprotection by ischemic preconditioning and suggests 5'-nucleotidase or A2B AR agonists as therapy for myocardial ischemia.


