AlpinetinCAS# 36052-37-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 36052-37-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 154279 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C16H14O4 | M.Wt | 270.3 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 7-Hydroxy 5-methoxyflavanone; 5-O-Methylpinocembrin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (184.99 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
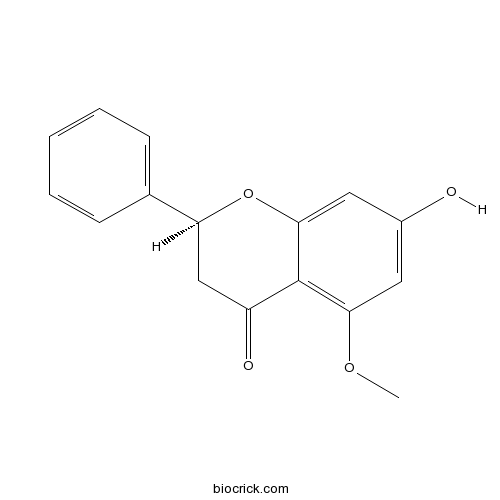
| Chemical Name | (2S)-7-hydroxy-5-methoxy-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C2C(=O)CC(OC2=CC(=C1)O)C3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QQQCWVDPMPFUGF-ZDUSSCGKSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Alpinetin has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer activities; it inhibits proliferation ,regulates of the Bcl-2 family and XIAP expression, releases of cytochrome c and activates caspases. |
| Targets | LDL | PPAR | TLR | NF-kB | ERK | JNK | IkB | TNF-α | p38MAPK | IL Receptor | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | Nrf2 | HO-1 | ROS | Calcium Channel | PKC | IKK |
| In vitro | Immunosuppressive activity of alpinetin on activation and cytokines secretion of murine T lymphocytes.[Pubmed: 24964870]Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2014 Aug;36(4):290-6.Alpinetin, a flavonoid compound extracted from the seeds of Alpinia katsumadai Hayata, has been known to possess antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and other important therapeutic activities. Antiproliferative effect of alpinetin in BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cells.[Pubmed: 22246103 ]Int J Mol Med. 2012 Apr;29(4):607-12.Alpinetin is a novel plant flavonoid derived from Alpinia katsumadai Hayata, found to possess strong anticancer effects. However, the antitumor effect of Alpinetin on pancreatic cancer cells and the detailed mechanism remain unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate Alpinetin's beneficial effect on pancreatic cancer and the possible molecular mechanism involved. Vasorelaxant effects of cardamonin and alpinetin from Alpinia henryi K. Schum.[Pubmed: 11336110]J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2001 May;37(5):596-606.The vascular effects of cardamonin and Alpinetin from Alpinia henryi K. Schum. were examined in the rat isolated mesenteric arteries.
|
| In vivo | Alpinetin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury in mice.[Pubmed: 26321118]Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Oct;28(2):1003-8.Alpinetin, a novel plant flavonoid isolated from Alpinia katsumadai Hayata, has been demonstrated to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. However, the effects of Alpinetin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute kidney injury have not been reported. |
| Kinase Assay | Alpinetin inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory mediator response by activating PPAR-γ in THP-1-derived macrophages.[Pubmed: 24104193]Alpinetin enhances cholesterol efflux and inhibits lipid accumulation in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-loaded human macrophages.[Pubmed: 25496323]Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2014 Dec 11.Alpinetin is a natural flavonoid abundantly present in the ginger family. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 5;721(1-3):96-102.Alpinetin, a novel plant flavonoid derived from Alpinia katsumadai Hayata, has been reported to have anti-inflammatory properties. However, the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Alpinetin has not been fully elucidated. |
| Cell Research | Alpinetin suppresses proliferation of human hepatoma cells by the activation of MKK7 and elevates sensitization to cis-diammined dichloridoplatium.[Pubmed: 22159816]Oncol Rep. 2012 Apr;27(4):1090-6.Alpinetin is a type of novel plant flavonoid derived from Alpinia katsumadai Hayata, found to possess strong anti-hepatoma effects. However, the detailed antitumor mechanism of Alpinetin remains unclear. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-7 (MKK7) can regulate cellular growth, differentiation and apoptosis. |

Alpinetin Dilution Calculator

Alpinetin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6996 mL | 18.498 mL | 36.9959 mL | 73.9919 mL | 92.4898 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7399 mL | 3.6996 mL | 7.3992 mL | 14.7984 mL | 18.498 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.37 mL | 1.8498 mL | 3.6996 mL | 7.3992 mL | 9.249 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.074 mL | 0.37 mL | 0.7399 mL | 1.4798 mL | 1.8498 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.037 mL | 0.185 mL | 0.37 mL | 0.7399 mL | 0.9249 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Diepiserratenediol
Catalog No.:BCN7433
CAS No.:3604-92-0
- Ecdysone
Catalog No.:BCN2629
CAS No.:3604-87-3
- 2',4'-Dihydroxy-6'-methoxyacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN5314
CAS No.:3602-54-8
- Nandrolone decanoate
Catalog No.:BCC9087
CAS No.:360-70-3
- Glycodeoxycholic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7250
CAS No.:360-65-6
- [Ala17]-MCH
Catalog No.:BCC6024
CAS No.:359784-84-2
- 3,6-Ditigloyloxynortropane
Catalog No.:BCN1877
CAS No.:359723-70-9
- Pterosin G
Catalog No.:BCN8148
CAS No.:35964-50-2
- Triptotin F
Catalog No.:BCN3482
CAS No.:359630-36-7
- Inotodiol
Catalog No.:BCN3331
CAS No.:35963-37-2
- 3-Acetoxy-11-ursen-28,13-olide
Catalog No.:BCN5313
CAS No.:35959-08-1
- 3-Hydroxy-11-ursen-28,13-olide
Catalog No.:BCN5312
CAS No.:35959-05-8
- Dihydrosanguinarine
Catalog No.:BCN3713
CAS No.:3606-45-9
- Tetrahydrocurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN2724
CAS No.:36062-04-1
- Hexahydrocurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN4641
CAS No.:36062-05-2
- Octahydrocurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN2725
CAS No.:36062-07-4
- B-HT 933 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7474
CAS No.:36067-72-8
- B-HT 920
Catalog No.:BCC1417
CAS No.:36085-73-1
- Sodium cholate
Catalog No.:BCN6981
CAS No.:361-09-1
- Propranolol glycol
Catalog No.:BCC6817
CAS No.:36112-95-5
- RBC8
Catalog No.:BCC5569
CAS No.:361185-42-4
- 3,4-Secolupa-4(23),20(29)-diene-3,28-dioic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7243
CAS No.:36138-41-7
- Saxagliptin
Catalog No.:BCC3934
CAS No.:361442-04-8
- JDTic
Catalog No.:BCC1670
CAS No.:361444-66-8
Alpinetin suppresses proliferation of human hepatoma cells by the activation of MKK7 and elevates sensitization to cis-diammined dichloridoplatium.[Pubmed:22159816]
Oncol Rep. 2012 Apr;27(4):1090-6.
Alpinetin is a type of novel plant flavonoid derived from Alpinia katsumadai Hayata, found to possess strong anti-hepatoma effects. However, the detailed antitumor mechanism of Alpinetin remains unclear. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-7 (MKK7) can regulate cellular growth, differentiation and apoptosis. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of MKK7 in the anti-hepatoma effect mediated by Alpinetin. HepG2 cells were treated with Alpinetin at various doses and for different times, and the levels of phosphorylated MKK7 (p-MKK7) and total MKK7 were tested by RT-PCR and western blotting. Following transient transfection with RNA interference, cell viability and cell cycle stage were determined using methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium assay and flow cytometry, in order to assess the antitumor action of Alpinetin. In addition, chemosensitization to cis-diammined dichloridoplatium (CDDP) by Alpinetin was assessed by cell counting array and the cell growth inhibitory rate was calculated. The results showed that Alpinetin suppressed HepG2 cell proliferation and arrested cells in the G0/G1 phase by up-regulating the expression levels of p-MKK7. On the contrary, inhibiting the expression of MKK7 reversed the antitumor effect of Alpinetin. Moreover, Alpinetin enhanced the sensitivity of HepG2 hepatoma cells to the chemotherapeutic agent CDDP. Taken together, our studies indicate that activation of MKK7 mediates the anti-hepatoma effect of Alpinetin. MKK7 may be a putative target for molecular therapy against hepatoma and Alpinetin could serve as a potential agent for the development of hepatoma therapy.
Immunosuppressive activity of alpinetin on activation and cytokines secretion of murine T lymphocytes.[Pubmed:24964870]
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2014 Aug;36(4):290-6.
Abstract Alpinetin, a flavonoid compound extracted from the seeds of Alpinia katsumadai Hayata, has been known to possess antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and other important therapeutic activities. In the current study, we investigated Alpinetin for its immunosuppressive effect on activation and cytokines secretion of murine T lymphocytes. The data showed that Alpinetin markedly suppressed ConA-induced murine splenocyte proliferation, Th1/Th2 cytokines production, CD4(+) T-cell populations and ratio of CD4(+)/CD8(+). This inspired us to further study the effects of Alpinetin in vivo. The results showed that administration of Alpinetin suppressed T-cell-mediated delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction in mice. In addition, we studied signal transduction pathways about T-cell activation on puried murine T lymphocytes by Western-blot assay. The data revealed that Alpinetin could shock the activation of NF-kappaB, NFAT2 signal transduction pathways. These observations indicated that Alpinetin have potential effects in downregulating the immune system and might be developed as a useful immunosuppressive agent in treating undesired immune responses.
Vasorelaxant effects of cardamonin and alpinetin from Alpinia henryi K. Schum.[Pubmed:11336110]
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2001 May;37(5):596-606.
The vascular effects of cardamonin and Alpinetin from Alpinia henryi K. Schum. were examined in the rat isolated mesenteric arteries. 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectra showed that cardamonin is present in trans-form, and single-crystal radiographic structure revealed that Alpinetin is present in S configuration. Both cardamonin and Alpinetin produced a rightward shift in the concentration-response curve for phenylephrine in a noncompetitive manner, and they induced relaxation of phenylephrine-preconstricted arteries with respective mean inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of 9.3+/-0.6 microM and 27.5+/-2.8 microM. Both compounds also relaxed arteries preconstricted by endothelin I or U46619. Their relaxant effects were decreased in endothelium-removed rings. Pretreatment with N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester or methylene blue inhibited relaxation induced by both agents, and pretreatment with L-arginine reversed the effect of N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester on cardamonin-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation. The relaxant effects of cardamonin and Alpinetin were unaffected by indomethacin (3 microM). Cardamonin and Alpinetin inhibited 60 mM K+-induced contraction with respective IC50 of 11.5+/-0.3 microM and 37.9+/-3.6 microM. In addition, both agents inhibited the transient contraction induced by 3 microM phenylephrine or by 10 mM caffeine in Ca2+-free Krebs solution. Finally, these two agents also concentration dependently relax the arteries preconstricted by 1 microM phorbol 12,13-diacetate in Ca2+-free Krebs solution. These results indicate that purified cardamonin and Alpinetin from A. henryi K. Schum. relaxed rat mesenteric arteries through multiple mechanisms. They induced both endothelium-dependent and -independent relaxation; the former is likely mediated by nitric oxide whereas the latter is probably mediated through nonselective inhibition of Ca2+ influx and intracellular Ca2+ release and inhibition of the protein kinase C-dependent contractile mechanism.
Alpinetin enhances cholesterol efflux and inhibits lipid accumulation in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-loaded human macrophages.[Pubmed:25496323]
Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2015 Nov-Dec;62(6):840-7.
Alpinetin is a natural flavonoid abundantly present in the ginger family. Here, we investigated the effect of Alpinetin on cholesterol efflux and lipid accumulation in oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-treated THP-1 macrophages and human peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages (HMDMs). After exposing THP-1 macrophages to Alpinetin, cholesterol efflux was determined by liquid scintillator. The mRNA and protein levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-gamma), liver X receptor alpha (LXR-alpha), ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1), and ABCG1 and scavenger receptor class B member 1 were determined by reverse-transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) and Western blot analysis, respectively. Alpinetin promoted apolipoprotein A-I- and high-density-lipoprotein-mediated cholesterol efflux and elevated PPAR-gamma and LXR-alpha mRNA and protein expression in a dose-dependent fashion in ox-LDL-treated THP-1 macrophages and HMDMs. Small interfering RNA-mediated silencing of PPAR-gamma or LXR-alpha dose dependently reversed Alpinetin-increased cholesterol efflux in THP-1 macrophages, indicating the involvement of PPAR-gamma and LXR-alpha in Alpinetin-promoted cholesterol efflux. Alpinetin inhibited ox-LDL-induced lipid accumulation and enhanced the expression of ABCA1 and ABCG1 mRNA and protein, which was reversed by specific knockdown of PPAR-gamma or LXR-alpha. Taken together, our results reveal that Alpinetin exhibits positive effects on cholesterol efflux and inhibits ox-LDL-induced lipid accumulation, which might be through PPAR-gamma/LXR-alpha/ABCA1/ABCG1 pathway.
Alpinetin inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory mediator response by activating PPAR-gamma in THP-1-derived macrophages.[Pubmed:24104193]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 5;721(1-3):96-102.
Alpinetin, a novel plant flavonoid derived from Alpinia katsumadai Hayata, has been reported to have anti-inflammatory properties. However, the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Alpinetin has not been fully elucidated. The purpose of this study was to investigate the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Alpinetin in modifying lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced signaling pathways in human THP-1 macrophages. The cells were stimulated with LPS in the presence or absence of Alpinetin. The pro-inflammatory cytokines were evaluated by ELISA and qRT-PCR. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB), inhibitory kappa B (IkappaBalpha) protein, p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and PPAR-gamma were determined by Western blotting. The results showed that Alpinetin inhibited TNF-alpha, IL-6 and IL-1beta expression in LPS-stimulated human THP-1 macrophages in a dose-dependent manner. Western blot analysis showed that Alpinetin suppressed LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation, IkappaBalpha degradation, phosphorylation of ERK, JNK and P38. Furthermore, Alpinetin could significantly down-regulated the expression of TLR4 stimulating by LPS. We also found that Alpinetin could activate PPAR-gamma and the anti-inflammatory effects of Alpinetin can be reversed by GW9662, a specific antagonist for PPAR-gamma. These results suggest that Alpinetin activates PPAR-gamma, thereby attenuating TLR4 expression and TLR4 mediated NF-kappaB and MAPK activation and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These findings suggest that Alpinetin may be a therapeutic agent against inflammatory diseases.
Antiproliferative effect of alpinetin in BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cells.[Pubmed:22246103]
Int J Mol Med. 2012 Apr;29(4):607-12.
Alpinetin is a novel plant flavonoid derived from Alpinia katsumadai Hayata, found to possess strong anticancer effects. However, the antitumor effect of Alpinetin on pancreatic cancer cells and the detailed mechanism remain unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate Alpinetin's beneficial effect on pancreatic cancer and the possible molecular mechanism involved. Pancreatic cancer cell lines were treated with Alpinetin at various doses and for different times, and the effect of Alpinetin on cell growth inhibition, apoptosis and the cell cycle was determined. The expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, XIAP and Bax, the activity of caspases and the levels of cytochrome c released were measured. The results showed that Alpinetin inhibited the viability of three pancreatic cancer cell lines and induced apoptosis of BxPC-3 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. This was accompanied by regulation of the expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, Bax and XIAP. Furthermore, Alpinetin treatment led to the release of cytochrome c and activation of caspases-3, -8 and -9 proteins. Taken together, our studies indicate that Alpinetin inhibited the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells possibly through the regulation of the Bcl-2 family and XIAP expression, release of cytochrome c and the activation of caspases. Alpinetin may serve as a potential agent for the development of pancreatic cancer cell therapies.
Alpinetin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury in mice.[Pubmed:26321118]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Oct;28(2):1003-8.
Alpinetin, a novel plant flavonoid isolated from Alpinia katsumadai Hayata, has been demonstrated to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. However, the effects of Alpinetin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute kidney injury have not been reported. In the present study, we investigated the protective effects and the underlying mechanism of Alpinetin against LPS-induced acute kidney injury in mice. The results showed that Alpinetin inhibited LPS-induced kidney histopathologic changes, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels. Alpinetin also inhibited LPS-induced ROS, MDA, and inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha, IL-6 and IL-1beta production in kidney tissues. Meanwhile, Western blot analysis showed that Alpinetin suppressed LPS-induced TLR4 expression and NF-kappaB activation in kidney tissues. In addition, Alpinetin was found to up-regulate the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 in a dose-dependent manner. In conclusion, Alpinetin protected LPS-induced kidney injury through activating Nrf2 and inhibiting TLR4 expression.


