9-AminocamptothecinCAS# 91421-43-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 91421-43-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 72402 | Appearance | Powder |
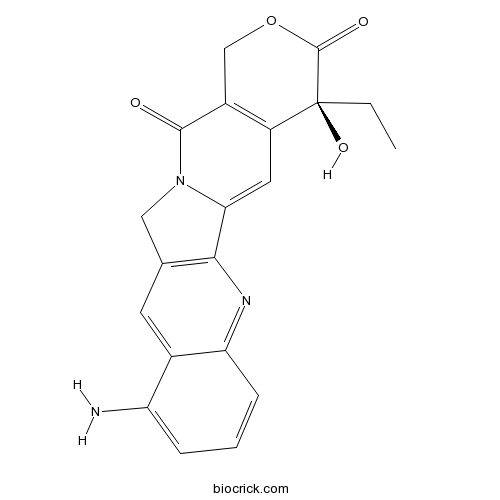
| Formula | C20H17N3O4 | M.Wt | 363.37 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 9-Amino-20(S)-camptothecin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 3.33 mg/mL (9.16 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| SMILES | CCC1(C2=C(COC1=O)C(=O)N3CC4=C(C3=C2)N=C5C=CC=C(C5=C4)N)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FUXVKZWTXQUGMW-FQEVSTJZSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 9-Aminocamptothecin is a topoisomerase I inhibitor with potent anticancer activity.In combination with 9-Aminocamptothecin, one 15-mer peptide (SAYAATVRGPLSSAS) has synergistic cytotoxic effects with 9-Aminocamptothecin both in the cytotoxicity assay and in nude mouse xenograft human tumor models. |
| Targets | P450 (e.g. CYP17) |
| In vitro | Cytochrome P450 3A-mediated metabolism of the topoisomerase I inhibitor 9-aminocamptothecin: impact on cancer therapy.[Pubmed: 24889073]Int J Oncol. 2014 Aug;45(2):877-86.The metabolism of 9-Aminocamptothecin (9-AC) was investigated in human and rat liver microsomes.
|
| In vivo | Antitumor efficacy of colon-specific HPMA copolymer/9-aminocamptothecin conjugates in mice bearing human-colon carcinoma xenografts.[Pubmed: 19685500 ]Macromol Biosci. 2009 Nov 10;9(11):1135-42.The antitumor activity of a colon-specific N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide (HPMA) copolymer - 9-Aminocamptothecin (9-AC) conjugate (P-9-AC) was assessed in orthotopic and subcutaneous animal (HT29 xenograft) tumor models.
Phase II study of 9-aminocamptothecin in previously treated lymphomas: results of Cancer and Leukemia Group B 9551.[Pubmed: 18648813]Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009 Apr;63(5):793-8.To evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of the topoisomerase I inhibitor, 9-Aminocamptothecin (9-AC), in patients with relapsed lymphoma and to correlate 9-AC plasma concentrations with response and toxicity.
|
| Kinase Assay | Identification of a small topoisomerase I-binding peptide that has synergistic antitumor activity with 9-aminocamptothecin.[Pubmed: 16546989]Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Mar;5(3):739-45.The topoisomerase I (top1)-targeted camptothecin class of anticancer drugs is important in the treatment of several types of cancers. This class of drug inhibits the top1 enzyme during its catalytic DNA relaxation cycle, stabilizing the transient covalent top1-DNA complex by simultaneous noncovalent interactions with DNA and top1.
|

9-Aminocamptothecin Dilution Calculator

9-Aminocamptothecin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.752 mL | 13.7601 mL | 27.5202 mL | 55.0403 mL | 68.8004 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5504 mL | 2.752 mL | 5.504 mL | 11.0081 mL | 13.7601 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2752 mL | 1.376 mL | 2.752 mL | 5.504 mL | 6.88 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.055 mL | 0.2752 mL | 0.5504 mL | 1.1008 mL | 1.376 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0275 mL | 0.1376 mL | 0.2752 mL | 0.5504 mL | 0.688 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
9-Aminocamptothecin is a topoisomerase I inhibitor with potent anticancer activity.
In Vitro:In human breast (MCF-7), bladder (MGH-U1), and colon (HT-29) cancer cell lines, 9-Aminocamptothecin cytotoxicity increases with both higher drug concentrations and longer exposure times. Minimal cell killing is also observed unless 9-Aminocamptothecin concentrations exceeds a threshold of 2.7 nm[1]. 9-Aminocamptothecin inhibits PC-3, PC-3M, DU145, and LNCaP cells with IC50 values of 34.1, 10, 6.5, and 8.9 nM, respectively after 96 h of drug exposure[2].
In Vivo:9-Aminocamptothecin inhibits tumor growth at the lowest oral dose (0.35 mg/kg/day), whereas higher oral doses (0.75 and 1 mg/kg/day) and s.c. administration (4 mg/kg/week) causes tumor regression. 9-Aminocamptothecin is well tolerated at all doses, with no toxic death or weight loss of more than 10% observed in any group[2]. 9-Aminocamptothecin induces complete remissions in 55 % of SCID mice engrafted with human myeloid leukemia. The oral and intravenous routes are equally effective. The results with this pre-clinical model support the evaluation of 9-Aminocamptothecin as antileukemic agent in a phase I trial in patients with AML[3].
References:
[1]. Li ML, et al. Pharmacological determinants of 9-aminocamptothecin cytotoxicity. Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Jan;7(1):168-74.
[2]. de Souza PL, et al. 9-Aminocamptothecin: a topoisomerase I inhibitor with preclinical activity in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1997 Feb;3(2):287-94.
[3]. Jeha S, et al. Activity of oral and intravenous 9-aminocamptothecin in SCID mice engrafted with human leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 1998 Dec;32(1-2):159-64.
- 9-Nitrocamptothecin
Catalog No.:BCN8448
CAS No.:91421-42-0
- 25-O-ethylcimigenol-3-O-beta-D-xylopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1309
CAS No.:914086-57-0
- PluriSIn #1 (NSC 14613)
Catalog No.:BCC2305
CAS No.:91396-88-2
- Lu AA 47070
Catalog No.:BCC7977
CAS No.:913842-25-8
- CS 2100
Catalog No.:BCC6221
CAS No.:913827-99-3
- SC75741
Catalog No.:BCC5448
CAS No.:913822-46-5
- Ropinirole HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4939
CAS No.:91374-20-8
- 1''-Hydroxyerythrinin C
Catalog No.:BCN4066
CAS No.:913690-46-7
- Brexpiprazole
Catalog No.:BCC4118
CAS No.:913611-97-9
- AMG-458
Catalog No.:BCC3721
CAS No.:913376-83-7
- Almorexant hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5123
CAS No.:913358-93-7
- LY 2087101
Catalog No.:BCC7869
CAS No.:913186-74-0
- R788 disodium hexahydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5127
CAS No.:914295-16-2
- INCB024360 analogue
Catalog No.:BCC1647
CAS No.:914471-09-3
- Palomid 529
Catalog No.:BCC3905
CAS No.:914913-88-5
- BEZ235 (NVP-BEZ235)
Catalog No.:BCC3655
CAS No.:915019-65-7
- MDV3100 (Enzalutamide)
Catalog No.:BCC1268
CAS No.:915087-33-1
- 3-[4-[(2-Chloro-5-iodophenyl)methyl]phenoxy]tetrahydro-furan
Catalog No.:BCC8601
CAS No.:915095-94-2
- Bakkenolide IIIa
Catalog No.:BCN7352
CAS No.:915289-60-0
- Cot inhibitor-2
Catalog No.:BCC1497
CAS No.:915363-56-3
- Cot inhibitor-1
Catalog No.:BCC1496
CAS No.:915365-57-0
- ABC294640
Catalog No.:BCC4192
CAS No.:915385-81-8
- WAY 316606
Catalog No.:BCC2052
CAS No.:915759-45-4
- Dovitinib (TKI258) Lactate
Catalog No.:BCC6473
CAS No.:915769-50-5
Identification of a small topoisomerase I-binding peptide that has synergistic antitumor activity with 9-aminocamptothecin.[Pubmed:16546989]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Mar;5(3):739-45.
The topoisomerase I (top1)-targeted camptothecin class of anticancer drugs is important in the treatment of several types of cancers. This class of drug inhibits the top1 enzyme during its catalytic DNA relaxation cycle, stabilizing the transient covalent top1-DNA complex by simultaneous noncovalent interactions with DNA and top1. We examined top1 using phage display because of the significance of this known top1-directed drug action. Several peptides that bind top1 were discovered and these were examined for top1 affinity, top1 catalytic and cleavage complex effects, and cytotoxic effects in cultured cell lines and in an in vivo tumor model. Although several peptides exhibited nanomolar and low-micromolar affinity for top1, none had cytotoxic effects when administered alone. However, in combination with 9-Aminocamptothecin, one 15-mer peptide (SAYAATVRGPLSSAS) had synergistic cytotoxic effects with 9-Aminocamptothecin both in the cytotoxicity assay and in nude mouse xenograft human tumor models. This report details the investigation of this peptide.
Antitumor efficacy of colon-specific HPMA copolymer/9-aminocamptothecin conjugates in mice bearing human-colon carcinoma xenografts.[Pubmed:19685500]
Macromol Biosci. 2009 Nov 10;9(11):1135-42.
The antitumor activity of a colon-specific N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide (HPMA) copolymer - 9-Aminocamptothecin (9-AC) conjugate (P-9-AC) was assessed in orthotopic and subcutaneous animal (HT29 xenograft) tumor models. P-9-AC treatment of mice bearing orthotopic colon tumors, with a dose of 3 mg/kg of 9-AC equivalent every other day for 6 weeks, resulted in regression of tumors in 9 of 10 mice. A lower dose of P-9-AC (1.25 mg/kg of 9-AC equivalent) every other day for 8 weeks inhibited subcutaneous tumor growth in all mice. No liver metastases were observed. Colon-specific release of 9-AC from polymer conjugates enhanced antitumor activity and minimized the systemic toxicity.
Phase II study of 9-aminocamptothecin in previously treated lymphomas: results of Cancer and Leukemia Group B 9551.[Pubmed:18648813]
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009 Apr;63(5):793-8.
PURPOSE: To evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of the topoisomerase I inhibitor, 9-Aminocamptothecin (9-AC), in patients with relapsed lymphoma and to correlate 9-AC plasma concentrations with response and toxicity. METHODS: Eligible patients had relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) treated with one or two prior regimens, low grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) treated with one or two prior regimens, or aggressive NHL treated with one prior regimen. The first nine patients received 9-AC dimethylacetamide 0.85 mg/m(2) per day intravenously over 72 h every 2 weeks and the remaining 27 patients received 9-AC/colloidal dispersion 1.1 mg/m(2) per day. Patients received a minimum of three cycles unless progression or intolerable toxicity occurred. Responding patients received two cycles past best response with a minimum of six cycles. RESULTS: CALGB 9551 accrued 37 patients from April 1996 through October 2000; one patient with HD, 18 patients with indolent lymphoma, and 17 patients with aggressive lymphoma. The overall response rate was 17%, with response rates of 11% (2 partial responses) in patients with indolent histologies and 23% (1 complete response, 3 partial responses) in patients with aggressive histologies. The patient with HD did not respond. Response rates were similar for both drug formulations. The median remission duration for the six responders was 6.5 months, with one remission lasting longer than 12 months. Significant grade 3 and 4 toxicities included neutropenia (66%), anemia (31%), and thrombocytopenia (36%), with 20% of patients experiencing grade 3 or 4 infection. No treatment related deaths occurred. Steady state serum concentrations did not correlate with patient response or toxicity. CONCLUSION: Single agent 9-AC has modest activity in aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.
Cytochrome P450 3A-mediated metabolism of the topoisomerase I inhibitor 9-aminocamptothecin: impact on cancer therapy.[Pubmed:24889073]
Int J Oncol. 2014 Aug;45(2):877-86.
The metabolism of 9-Aminocamptothecin (9-AC) was investigated in human and rat liver microsomes. In both species 9-AC was almost exclusively biotransformed to dihydroxy-9-AC (M1) and monohydroxy-9-AC (M2). The enzymatic efficiencies of the formation of M1 and M2 (V(max)/K(m)) were 1.7- and 2.7fold higher in rat than in human liver microsomes indicating species-related differences in 9-AC hydroxylation. Incubation in the presence of human recombinant cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes demonstrated that the formation of M1 and M2 is mainly catalyzed by CYP3A4 and only to a minor extent by extrahepatic CYP1A1. The predominant role of CYP3A4 was further supported by a dramatic inhibition of metabolite formation in the presence of the CYP3A4 substrates troleandomycin and ketoconazole. Experiments conducted in isolated perfused rat livers further demonstrated that biliary excretion of 9-AC, M1 and M2 during 60 min of perfusion was pronounced and accounted for 17.7+/-2.59, 0.05+/-0.01 and 2.75+/-0.14% of total 9-AC applied to the liver, respectively. In summary, this study established that CYP3A-dependent hydroxylation is the main metabolic pathway for 9-AC in rat and human liver, which have to be taken into consideration during cancer therapy of patients.


