6-ChloromelatoninMelatonin agonist CAS# 63762-74-3 |
- Edoxaban tosylate monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1545
CAS No.:1229194-11-9
- Otamixaban
Catalog No.:BCC1827
CAS No.:193153-04-7
- Betrixaban
Catalog No.:BCC5118
CAS No.:330942-05-7
- Rivaroxaban
Catalog No.:BCC2292
CAS No.:366789-02-8
- Edoxaban
Catalog No.:BCC1543
CAS No.:480449-70-5
- Apixaban
Catalog No.:BCC2295
CAS No.:503612-47-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 63762-74-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1858 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H15ClN2O2 | M.Wt | 266.73 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
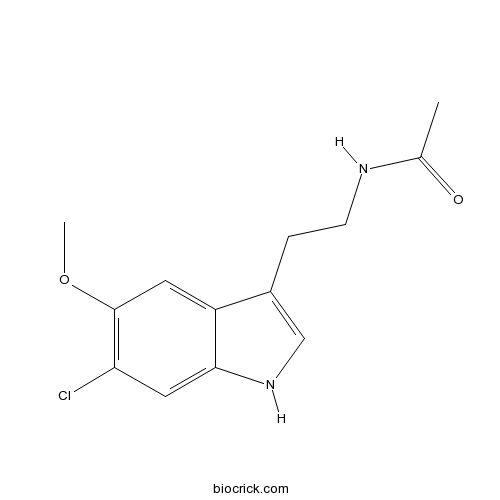
| Chemical Name | N-[2-(6-chloro-5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]acetamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)NCCC1=CNC2=CC(=C(C=C21)OC)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LUINDDOUWHRIPW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H15ClN2O2/c1-8(17)15-4-3-9-7-16-12-6-11(14)13(18-2)5-10(9)12/h5-7,16H,3-4H2,1-2H3,(H,15,17) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent melatonin agonist (pKi values are 9.10 and 9.77 for human recombinant MT1 and MT2 receptors respectively). Displays higher affinity for binding to hamster brain membrane and chicken retina than melatonin. |

6-Chloromelatonin Dilution Calculator

6-Chloromelatonin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7491 mL | 18.7455 mL | 37.4911 mL | 74.9822 mL | 93.7277 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7498 mL | 3.7491 mL | 7.4982 mL | 14.9964 mL | 18.7455 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3749 mL | 1.8746 mL | 3.7491 mL | 7.4982 mL | 9.3728 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.075 mL | 0.3749 mL | 0.7498 mL | 1.4996 mL | 1.8746 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0375 mL | 0.1875 mL | 0.3749 mL | 0.7498 mL | 0.9373 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3'-Amino-4'-methoxyacetanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8611
CAS No.:6375-47-9
- AEG 3482
Catalog No.:BCC8088
CAS No.:63735-71-7
- Pseudoprotogracillin
Catalog No.:BCC8354
CAS No.:637349-03-2
- Paspalinine
Catalog No.:BCN7386
CAS No.:63722-91-8
- Z-Phenylalaninol
Catalog No.:BCC2716
CAS No.:6372-14-1
- (R)-Baclofen hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4123
CAS No.:63701-55-3
- 2-(Dimethylamino)ethanesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1752
CAS No.:637-95-6
- Pramoxine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4705
CAS No.:637-58-1
- Clofibrate
Catalog No.:BCC5308
CAS No.:637-07-0
- Boc-D-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3447
CAS No.:6368-20-3
- Nisoldipine
Catalog No.:BCC4809
CAS No.:63675-72-9
- H-D-Asp-Obzl
Catalog No.:BCC2895
CAS No.:6367-42-6
- 12alpha-Hydroxygrandiflorenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4823
CAS No.:63768-17-2
- Cyclosporin D
Catalog No.:BCC6444
CAS No.:63775-96-2
- trans-Methylisoeugenol
Catalog No.:BCN6558
CAS No.:6379-72-2
- Desonide
Catalog No.:BCC4967
CAS No.:638-94-8
- alpha-Amyrin
Catalog No.:BCN3341
CAS No.:638-95-9
- beta-Amyrone
Catalog No.:BCN4179
CAS No.:638-97-1
- 2-Amino-3-dodecanol
Catalog No.:BCN4175
CAS No.:
- Erythrinin C
Catalog No.:BCN4176
CAS No.:63807-85-2
- Erythrinin A
Catalog No.:BCN3203
CAS No.:63807-86-3
- Dihydroalpinumisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4177
CAS No.:63807-90-9
- 5-(3-Chlorophenyl)-N-[4-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)phenyl]furan-2-carboxamide
Catalog No.:BCC3636
CAS No.:638156-11-3
- Z-D-Arg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3575
CAS No.:6382-93-0
A single blind, placebo controlled, across groups dose escalation study of the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the melatonin analog beta-methyl-6-chloromelatonin.[Pubmed:15302228]
Life Sci. 2004 Aug 27;75(15):1843-56.
Clinical investigation of melatonin agonists has been hampered by side effects such as hypothermia, hypotension and bradycardia. The availability of a melatonin agonist devoid of these side effects would improve our understanding of the mechanisms by which melatonin agonists affect sleep. This study investigated the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of the melatonin agonist beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin at doses up to 100 mg in healthy volunteers. The design was a single blind, across subjects, placebo controlled, group wise dose escalation using doses of 20, 35, 50 and 100 mg beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin. Eight subjects received one dose of study drug or placebo. Pharmacokinetic analysis showed a consistent Tmax across all doses with a mean of 1.12 +/- 0.11 hr for all groups (mean +/- SD). The half-life was also consistent across dose, with a mean of 1.04 +/- 0.04 hr. Maximum plasma concentrations increased with increasing dose with values of 44.83 +/- 29.79, 100.3 +/- 41.08, 79.84 +/- 26.36 and 410.3 +/- 129.4 ng/ml at doses of 20, 35, 50 and 100 mg, respectively. Area under the curve showed similar increases. No consistent changes in vital signs occurred as a function of dose or time after study drug. The incidence of all adverse events, the severity of the event or the event's relationship to treatment did not increase with higher doses of beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin. Sleepiness was reported after all doses of beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin. beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin appears safe and well tolerated at doses up to 100 mg. These doses are not associated with hypothermia, bradycardia or hypotension. A melatonin agonist lacking these side effects should allow investigation of the direct soporific effects of melatonin agonists.
The efficacy and safety of the melatonin agonist beta-methyl-6-chloromelatonin in primary insomnia: a randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover clinical trial.[Pubmed:15766306]
J Clin Psychiatry. 2005 Mar;66(3):384-90.
BACKGROUND: While melatonin agonists are known to regulate circadian sleep rhythms, it is not clear whether melatonin agonists have a direct soporific effect. It has been suggested that melatonin's soporific effect is secondary to its ability to induce hypothermia. beta-Methyl-6-Chloromelatonin is a high-affinity melatonin receptor agonist that is not associated with hypothermia. The purpose of the present study was to determine if the melatonin agonist beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin has a direct soporific effect in subjects with primary insomnia. METHOD: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover safety and efficacy study of 20 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg of beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin and placebo was conducted in subjects with DSM-IV-TR primary insomnia. Of 84 subjects screened, 40 progressed to randomly receive each of 3 beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin doses or placebo on each of 2 consecutive nights with 5-day washout periods between treatments. The effect of treatment on both polysomnographic and subjectively measured sleep parameters, next-morning psychomotor performance, and safety measures was determined. The primary outcome measure was latency to persistent sleep measured by polysomnography. RESULTS: A significant effect of beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin on the primary efficacy variable, latency to persistent sleep, was observed (p = .0003). The 20-mg dose resulted in a significant 31% improvement in sleep latency compared with placebo, while significant 32% and 41% improvements were observed at the 50-mg and 100-mg doses, respectively (20 mg, p = .0082; 50 mg, p = .0062; 100 mg, p < .0001). Similarly, a significant effect of beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin on subjective measures of time to fall asleep occurred (p = .0050), with significant improvement observed at both the 50-mg and 100-mg doses (p = .0350 and .0198, respectively) and a trend toward improvement observed at the 20-mg dose (p = .0582). Adverse events were mild to moderate in severity and did not differ in frequency between beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin and placebo treatments. CONCLUSION: beta-Methyl-6-Chloromelatonin significantly decreases both objective and subjective measures of sleep latency in subjects with primary insomnia. Thus, these data suggest that mel-atonin agonists may exert a direct soporific effect, as previous research indicates that beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin is not associated with changes in body temperature, heart rate, or blood pressure.
Melatonin-analog, beta-methyl-6-chloromelatonin, supplementation in spinal cord injury.[Pubmed:20420812]
Brain Res. 2010 Jun 22;1340:81-5.
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a devastating condition. Melatonin supplementation has been shown to lessen SCI, but its use has been limited by its side effect profile. In this work, rats underwent a moderate-to-severe contussional SCI with either placebo or beta-methyl-6-Chloromelatonin, 10mg/kg or 100mg/kg supplementation. The 10mg/kg supplementation demonstrated benefit; the 100mg/kg dosage was limited by toxicity. This is the first work to assess a melatonin analog in SCI.
Human malignant melanoma cells express high-affinity receptors for melatonin: antiproliferative effects of melatonin and 6-chloromelatonin.[Pubmed:8397097]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul 15;246(2):89-96.
In order to explore the potential oncostatic properties of the pineal hormone, melatonin, we have investigated its binding characteristics and functional effects in a human malignant melanoma (M-6) cell line. Binding studies in M-6 membranes showed the coexistence of 2-[125I]iodomelatonin binding sites with picomolar and nanomolar affinities. Guanine nucleotides caused conversion of all high-affinity sites to a low-affinity state without a change in binding capacity. Melatonin induced a marked concentration-dependent reduction in forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation in intact M-6 cells, indicating that it binds to a functional receptor in this cell line. The in vitro proliferation of M-6 cells was significantly inhibited by melatonin and its analogues 6-Chloromelatonin, and 2-iodomelatonin, at concentrations ranging from 10(-9) to 10(-4) M, as demonstrated by cell counts and measurements of DNA content. These findings indicate that M-6 cells express functional receptors for melatonin which may be involved in mediating the antiproliferative effects of this hormone.
Pharmacological characterization of human recombinant melatonin mt(1) and MT(2) receptors.[Pubmed:10696085]
Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Mar;129(5):877-86.
We have pharmacologically characterized recombinant human mt(1) and MT(2) receptors, stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO-mt(1) and CHO-MT(2)), by measurement of [(3)H]-melatonin binding and forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP (cAMP) production. [3H]-melatonin bound to mt(1) and MT(2) receptors with pK(D) values of 9.89 and 9.56 and B(max) values of 1.20 and 0.82 pmol mg(-1) protein, respectively. Whilst most melatonin receptor agonists had similar affinities for mt(1) and MT(2) receptors, a number of putative antagonists had substantially higher affinities for MT(2) receptors, including luzindole (11 fold), GR128107 (23 fold) and 4-P-PDOT (61 fold). In both CHO-mt(1) and CHO-MT(2) cells, melatonin inhibited forskolin-stimulated accumulation of cyclic AMP in a concentration-dependent manner (pIC(50) 9.53 and 9.74, respectively) causing 83 and 64% inhibition of cyclic AMP production at 100 nM, respectively. The potencies of a range of melatonin receptor agonists were determined. At MT(2) receptors, melatonin, 2-iodomelatonin and 6-Chloromelatonin were essentially equipotent, whilst at the mt(1) receptor these agonists gave the rank order of potency of 2-iodomelatonin>melatonin>6-Chloromelatonin. In both CHO-mt(1) and CHO-MT(2) cells, melatonin-induced inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP production was antagonized in a concentration-dependent manner by the melatonin receptor antagonist luzindole, with pA(2) values of 5.75 and 7.64, respectively. Melatonin-mediated responses were abolished by pre-treatment of cells with pertussis toxin, consistent with activation of G(i)/G(o) G-proteins. This is the first report of the use of [(3)H]-melatonin for the characterization of recombinant mt(1) and MT(2) receptors. Our results demonstrate that these receptor subtypes have distinct pharmacological profiles.
Melatonin receptors: are there multiple subtypes?[Pubmed:7762083]
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 Feb;16(2):50-6.
There is now evidence for more than one site of action for the hormone melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxy-tryptamine). Recent pharmacological and molecular advances are providing the tools to address the characterization of melatonin receptor subtypes. The development of novel melatonin receptor agonists and antagonists, high-affinity radioligands, quantitative bioassays, and the recent cloning of melatonin receptors are furthering our understanding of native and recombinant melatonin receptors. In this article, Margarita Dubocovich discusses the properties of melatonin receptors, and the basis for their classification into at least two subtypes, the ML1 and ML2.
Luzindole (N-0774): a novel melatonin receptor antagonist.[Pubmed:2843633]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Sep;246(3):902-10.
The pharmacological potencies of 2-substituted N-acetyltryptamines were determined on the presynaptic melatonin receptor site of rabbit retina labeled in vitro with [3H]dopamine. Calcium-dependent release of [3H]dopamine was elicited by electrical stimulation at 3 Hz for 2 min (20 mA, 2 msec). Melatonin (5-OCH3-N-acetyltryptamine) and 6-Chloromelatonin were equipotent in inhibiting the calcium-dependent release of [3H]dopamine (IC50 = 40 pM). 2-Substituted N-acetyltryptamines with a methyl (i.e., 6,7-dichloro-2-methylmelatonin, IC50 = 10 pM) or iodine (i.e., 2-iodomelatonin, IC50 = 5 pM) group were more potent than melatonin in inhibiting [3H]dopamine release. I report here the pharmacological properties of the novel N-acetyltryptamine, 2-benzyl-N-acetyltryptamine (N-0774, luzindole) on the presynaptic melatonin receptor of rabbit retina. Luzindole (0.1-10 microM) did not affect the spontaneous outflow of radioactivity or the stimulation-evoked release of [3H]dopamine when added alone. However, luzindole (0.1-10 microM) shifted the concentration effect curve for melatonin to the right in a parallel fashion. The pA2 extrapolated from the Schild plot (slope, 0.91) was 7.7, with a KB = 20 nM. The dissociation constants for luzindole (KB), determined in the presence of 6,7-dichloro-2-methylmelatonin (10 pM-1 nM) or 6-Chloromelatonin (10 pM-100 nM) were 16 and 40 nM, respectively. These data suggest that luzindole and the various melatonin agonists are competing for the same presynaptic melatonin receptor site in the rabbit retina.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
2-[125I]iodomelatonin binding sites in hamster brain membranes: pharmacological characteristics and regional distribution.[Pubmed:2834175]
Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):1825-33.
Studies in a variety of seasonally breeding mammals have shown that melatonin mediates photoperiodic effects on reproduction. Relatively little is known, however, about the site(s) or mechanisms of action of this hormone for inducing reproductive effects. Although binding sites for [3H]melatonin have been reported previously in bovine, rat, and hamster brain, the pharmacological selectivity of these sites was never demonstrated. In the present study, we have characterized binding sites for a new radioligand, 2-[125I]iodomelatonin, in brains from a photoperiodic species, the Syrian hamster. 2-[125I]Iodomelatonin labels a high affinity binding site in hamster brain membranes. Specific binding of 2-[125I]iodomelatonin is rapid, stable, saturable, and reversible. Saturation studies demonstrated that 2-[125I]iodomelatonin binds to a single class of sites with an affinity constant (Kd) of 3.3 +/- 0.5 nM and a total binding capacity (Bmax) of 110.2 +/- 13.4 fmol/mg protein (n = 4). The Kd value determined from kinetic analysis (3.1 +/- 0.9 nM; n = 5) was very similar to that obtained from saturation experiments. Competition experiments showed that the relative order of potency of a variety of indoles for inhibition of 2-[125I]iodomelatonin binding site to hamster brain membranes was as follows: 6-Chloromelatonin greater than or equal to 2-iodomelatonin greater than N-acetylserotonin greater than or equal to 6-methoxymelatonin greater than or equal to melatonin greater than 6-hydroxymelatonin greater than or equal to 6,7-dichloro-2-methylmelatonin greater than 5-methoxytryptophol greater than 5-methoxytryptamine greater than or equal to 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine greater than N-acetyltryptamine greater than serotonin greater than 5-methoxyindole (inactive). Compounds known to act at serotonergic, adrenergic, or dopaminergic receptors were either inactive or relatively ineffective as compared to melatonin. These results suggest that 2-[125I]iodomelatonin is a selective, high affinity probe for identifying melatonin receptor binding sites in rodent brain.


