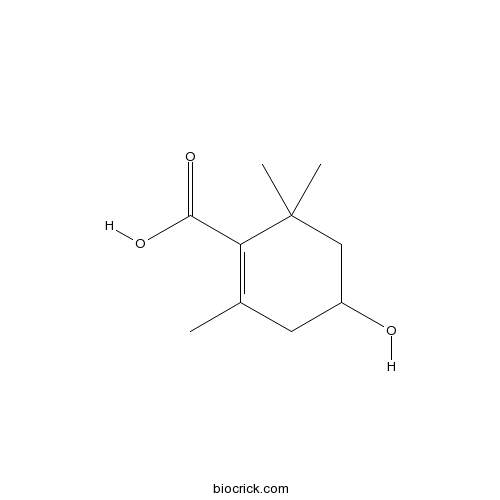
4-Hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenecarboxylic acidCAS# 62218-55-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 62218-55-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71307308 | Appearance | Cryst. |
| Formula | C10H16O3 | M.Wt | 184.2 |
| Type of Compound | Monoterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(CC(C1)O)(C)C)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VLNNCUQICIFEOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Structure Identification | Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products, 2009, 29(6):61-64.Chemical Constituents of the Fruits of Gardenia jasminoides form.grandiflora (Lour.) Makino.[Reference: WebLink]
|

4-Hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenecarboxylic acid Dilution Calculator

4-Hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenecarboxylic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.4289 mL | 27.1444 mL | 54.2888 mL | 108.5776 mL | 135.722 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0858 mL | 5.4289 mL | 10.8578 mL | 21.7155 mL | 27.1444 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5429 mL | 2.7144 mL | 5.4289 mL | 10.8578 mL | 13.5722 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1086 mL | 0.5429 mL | 1.0858 mL | 2.1716 mL | 2.7144 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0543 mL | 0.2714 mL | 0.5429 mL | 1.0858 mL | 1.3572 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3-O-Methylducheside A
Catalog No.:BCN4153
CAS No.:62218-23-9
- alpha-Viniferin
Catalog No.:BCN4152
CAS No.:62218-13-7
- epsilon-Viniferin
Catalog No.:BCN4151
CAS No.:62218-08-0
- 1,2,3-Triacetyl-5-deoxy-D-ribose
Catalog No.:BCC8408
CAS No.:62211-93-2
- 12-O-Methylcarnosic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7655
CAS No.:62201-71-2
- Hordenine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC8184
CAS No.:622-64-0
- 1,2-Bis(phenylthio)ethane
Catalog No.:BCC8415
CAS No.:622-20-8
- Benzyl L-(+)-mandelate
Catalog No.:BCC8873
CAS No.:62173-99-3
- Mirandin B
Catalog No.:BCN6581
CAS No.:62163-24-0
- (-)-Syringaresinol
Catalog No.:BCN3417
CAS No.:6216-81-5
- Z-Prolinol
Catalog No.:BCC2709
CAS No.:6216-63-3
- N-Methylcyclohexaneethaneamine
Catalog No.:BCN1795
CAS No.:62141-38-2
- Bifemelane hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6786
CAS No.:62232-46-6
- 1-Hydroxy-9-medroxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN3103
CAS No.:622408-85-9
- JLK 6
Catalog No.:BCC2343
CAS No.:62252-26-0
- Ponceau S Staining Solution
Catalog No.:BCC8032
CAS No.:6226-79-5
- (-)-p-Bromotetramisole Oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC5449
CAS No.:62284-79-1
- Desmopressin Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC1526
CAS No.:62288-83-9
- 4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN4154
CAS No.:623-05-2
- H-Gly-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2950
CAS No.:623-33-6
- H-Tyr(Me)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3133
CAS No.:6230-11-1
- Rutaevin 7-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7991
CAS No.:62306-81-4
- 5-Hydroxy-2-pyrrolidinone
Catalog No.:BCN4155
CAS No.:62312-55-4
- Ki20227
Catalog No.:BCC1678
CAS No.:623142-96-1
Trans-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal is a neurotoxic product of docosahexaenoic (22:6; n-3) acid oxidation.[Pubmed:18194211]
J Neurochem. 2008 May;105(3):714-24.
Lipid peroxidation of docosahexaenoic (22:6; n-3) acid (DHA) is elevated in the CNS in patients with Alzheimer's disease and in animal models of seizure and ethanol withdrawal. One product of DHA oxidation is trans-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (HHE), a six carbon analog of the n-6 fatty acid derived trans-4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE). In this work, we studied the neurotoxic potential of HHE. HHE and HNE were toxic to primary cultures of cerebral cortical neurons with LD(50)'s of 23 and 18 micromol/L, respectively. Toxicity was prevented by the addition of thiol scavengers. HHE and HNE depleted neuronal GSH content identically with depletion observed with 10 micromol/L of either compound. Using an antibody raised against HHE-protein adducts, we show that HHE modified specific proteins of 75, 50, and 45 kDa in concentration- and time-dependent manners. The time-dependent formation of HHE differed from that of F4-neuroprostanes following in vitro DHA oxidation likely as a result of the different oxidation pathways involved. Using purified mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH5A, we found that HHE was oxidized 6.5-fold less efficiently than HNE. Our data demonstrate that HHE and HNE have similarities but also differences in their neurotoxic mechanisms and metabolism.
1,6-Dimethyl-4-hydroxy-3-pyridinecarboxylic acid and 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-pyridinecarboxylic acid as new possible chelating agents for iron and aluminium.[Pubmed:19240917]
Dalton Trans. 2009 Mar 14;(10):1815-24.
1,6-Dimethyl-4-hydroxy-3-pyridinecarboxylic acid (DQ716) and 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-pyridinecarboxylic acid (DQ2) were evaluated for possible application to iron (Fe) and aluminium (Al) chelation therapy. Metal/ligand solution chemistry, electrochemistry, cytotoxicity, octanol/water partitioning (D(o/w)), and chelation efficiency, were studied. The Fe(iii)/DQ716, Fe(iii)/DQ2, Al(iii)/DQ716, and Al(iii)/DQ2 solution chemistry was investigated in aqueous 0.6 mol kg(-1) (Na)Cl at 25 degrees C by means of potentiometric titrations, UV-vis spectrophotometry, and (1)H-NMR spectroscopy. DQ716 exhibited the highest coordination efficiency towards Fe(iii) and Al(iii) among all hydroxypyridinecarboxylic acids examined so far, whereas DQ2 complexes were significantly less stable. These results were confirmed by chelation efficiency measurements performed in an octanol-aqueous solution in the presence of those ligands and metals. Partitioning experiments at pH 7.4 showed both DQ716 and DQ2, and their Fe(iii) and Al(iii) complexes, to be hydrophilic. According to the voltammetric data, the free ligands (DQ716 and DQ2) and their metal complexes are not predicted to undergo redox cycling at in vivo conditions. The standard reduction potentials of these complexes, and the kinetics of their formation and dissociation, were obtained. The toxicity of DQ716 and of DQ2 was investigated with human cancer cell lines and normal human fibroblasts. Cytotoxic effects were observed only for DQ2 at 0.1 mM, following 3 d exposure. According to our results, DQ716 has the required favourable properties to be a chelating agent for Fe and Al.
One-step electrochemical synthesis of 6-amino-4-hydroxy-2-napthalene-sulfonic acid functionalized graphene for green energy storage electrode materials.[Pubmed:23958735]
Nanotechnology. 2013 Sep 13;24(36):365706.
A green approach for the one-step electrochemical synthesis of water dispersible graphene is reported. An alkaline solution of 6-amino-4-hydroxy-2-naphthalene-sulfonic acid (ANS) serves the role of electrolyte as well as surface modifier. High-purity graphite rods are used as electrodes which can be exfoliated under a constant electrical potential ( approximately 20 V) to form ANS functionalized graphene (ANEG). The aqueous dispersion of ANEG obeyed Beer's law at moderate concentrations, as evidenced from ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy analysis. X-ray diffraction analysis suggests complete exfoliation of graphite into graphene. Fourier transform infrared and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy not only confirm the functionalization of graphene with ANS, but also suggest the formation of oxygen containing functional groups on the surface of ANEG. Raman spectra analysis indicates the presence of defects in ANEG as compared to pure graphite. Cyclic voltammetry and charge-discharge measurements of ANEG using three electrode systems show a specific capacitance of 115 F g(-1) at a current density of 4 A g(-1). The ANEG electrode exhibits 93% retention in specific capacitance after 1000 charge-discharge cycles, confirming its utility as a green energy storage electrode material.
Structural and theoretical studies of [6-bromo-1-(4-fluorophenylmethyl)-4(1H)-quinolinon-3-yl)]-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-3-buten oic acid as HIV-1 integrase inhibitor.[Pubmed:19556126]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Aug 15;19(16):4806-9.
Ethyl [6-bromo-1-(4-fluorophenylmethyl)-4(1H)-quinolinon-3-yl]-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-3-buteno ate 1 and [6-bromo-1-(4-fluorophenylmethyl)-4(1H)-quinolinon-3-yl)]-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-3-buten oic acid 2 were synthesized as potential HIV-1 integrase inhibitors and evaluated for their enzymatic and antiviral activity, acidic compound 2 being more potent than ester compound 1. X-ray diffraction analyses and theoretical calculations show that the diketoacid chain of compound 2 is preferentially coplanar with the quinolinone ring (dihedral angle of 0-30 degrees ). Docking studies suggest binding modes in agreement with structure-activity relationships.


