3-ButylidenephthalideCAS# 551-08-6 |
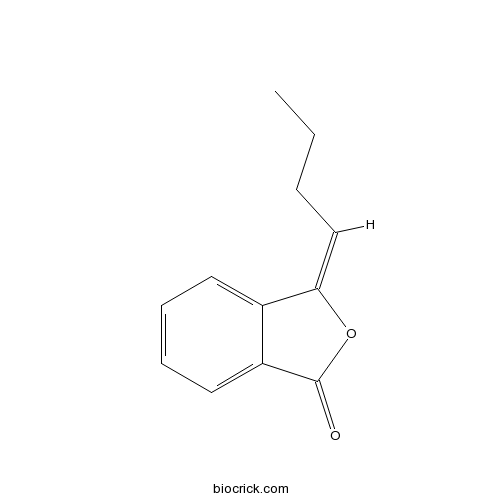
- (Z)-Butylidenephthalide
Catalog No.:BCN4007
CAS No.:72917-31-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 551-08-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5352899 | Appearance | Oil |
| Formula | C12H12O2 | M.Wt | 188.22 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 250 mg/mL (1328.23 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | (3E)-3-butylidene-2-benzofuran-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CCCC=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)O1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WMBOCUXXNSOQHM-DHZHZOJOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H12O2/c1-2-3-8-11-9-6-4-5-7-10(9)12(13)14-11/h4-8H,2-3H2,1H3/b11-8+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | (Z)-3-butylidenephthalide has antihyperglycemic effect is due to inhibition of α-glucosidase at the intestinal level, inhibited the activity of yeast-α-glucosidase (IC(50) 2.35 mM) in a noncompetitive fashion with a K(i) of 4.86 mM. It can induce a dose-dependent antinociceptive action in the hot-plate assay, it is also effective for controlling the pain provoked by chemical irritation at the doses of 10 and 31.6 mg/kg. |
| Targets | Nrf2 | TNF-α | NO | IL Receptor |
| In vivo | (Z)-3-butylidenephthalide from Ligusticum porteri , an α-glucosidase inhibitor.[Pubmed: 20879744]J Nat Prod. 2011 Mar 25;74(3):314-20.An extract from the roots of Ligusticum porteri, orally administered to groups of normal and diabetic mice, showed significant hypoglycemic and antihyperglycemic effects.
|
| Kinase Assay | Effects of natural phytochemicals in Angelica sinensis (Danggui) on Nrf2-mediated gene expression of phase II drug metabolizing enzymes and anti-inflammation.[Pubmed: 23640758]Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2013 Sep;34(6):303-11.The root of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (abbreviated as AS) (Danggui) has a long history in Asian herbal medicine. Recently, it was demonstrated that AS possesses anti-cancer and anti-oxidant activities. Because the transcription factor Nrf2 mediates the expression of many cellular anti-oxidative stress genes, including genes that are involved in phase II drug metabolism and anti-oxidative stress, this study sought to investigate whether pure compounds from AS or an AS extract could activate antioxidant response element (ARE)-mediated gene expression and induce anti-inflammatory activities.
|
| Animal Research | Antinociceptive activity of Ligusticum porteri preparations and compounds.[Pubmed: 24093628]Pharm Biol. 2014 Jan;52(1):14-20.The roots and rhizomes of Ligusticum porteri Coulter & Rose (Apiaceae) are widely used in Mexican folk medicine for several purposes, including painful complaints. The main goal of this work was to demonstrate the analgesic action in mice of some preparations and major compounds from L. porteri.
|
| Structure Identification | J Chromatogr A. 2013 Apr 5;1284:53-8.Online isolation and purification of four phthalide compounds from Chuanxiong rhizoma using high-speed counter-current chromatography coupled with semi-preparative liquid chromatography.[Pubmed: 23484653]The phthalide compounds of Chuanxiong rhizoma including senkyunolide A, levistolide A, Z-ligustilide and 3-Butylidenephthalide, have been reported as the biologically active compounds because of their therapeutic effects.
|

3-Butylidenephthalide Dilution Calculator

3-Butylidenephthalide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.3129 mL | 26.5647 mL | 53.1293 mL | 106.2586 mL | 132.8233 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0626 mL | 5.3129 mL | 10.6259 mL | 21.2517 mL | 26.5647 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5313 mL | 2.6565 mL | 5.3129 mL | 10.6259 mL | 13.2823 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1063 mL | 0.5313 mL | 1.0626 mL | 2.1252 mL | 2.6565 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0531 mL | 0.2656 mL | 0.5313 mL | 1.0626 mL | 1.3282 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- EVP-6124
Catalog No.:BCC1566
CAS No.:550999-75-2
- EVP-6124 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1567
CAS No.:550999-74-1
- Nalmefene - d3
Catalog No.:BCC6093
CAS No.:55096-26-9
- 5,6,7-Trimethoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN7590
CAS No.:55085-47-7
- Skullcapflavone II
Catalog No.:BCN3188
CAS No.:55084-08-7
- Andrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN5735
CAS No.:5508-58-7
- Acitretin
Catalog No.:BCC1189
CAS No.:55079-83-9
- Diversoside
Catalog No.:BCN7537
CAS No.:55062-36-7
- Protodioscin
Catalog No.:BCN6274
CAS No.:55056-80-9
- 2,6,4'-Trihydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCN7588
CAS No.:55051-85-9
- Dammar-20(21)-en-3,24,25-triol
Catalog No.:BCN5734
CAS No.:55050-69-6
- Isorhamnetin-3-O-neohespeidoside
Catalog No.:BCN1234
CAS No.:55033-90-4
- Liquiritin
Catalog No.:BCN5944
CAS No.:551-15-5
- 6-Aminopenicillanic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8765
CAS No.:551-16-6
- Viridiflorine
Catalog No.:BCN2045
CAS No.:551-57-5
- Supinine
Catalog No.:BCN1952
CAS No.:551-58-6
- Dimetridazole
Catalog No.:BCC8944
CAS No.:551-92-8
- 2'-Aminoacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1746
CAS No.:551-93-9
- 4beta-Carboxy-19-nortotarol
Catalog No.:BCN4065
CAS No.:55102-39-1
- (S)-3-Carboxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycine
Catalog No.:BCC6607
CAS No.:55136-48-6
- Kaempferol 3-sophoroside-7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7825
CAS No.:55136-76-0
- Oxohydrastinine
Catalog No.:BCN3299
CAS No.:552-29-4
- Paeonol
Catalog No.:BCN5738
CAS No.:552-41-0
- Isorhoifolin
Catalog No.:BCN5739
CAS No.:552-57-8
Antinociceptive activity of Ligusticum porteri preparations and compounds.[Pubmed:24093628]
Pharm Biol. 2014 Jan;52(1):14-20.
CONTEXT: The roots and rhizomes of Ligusticum porteri Coulter & Rose (Apiaceae) are widely used in Mexican folk medicine for several purposes, including painful complaints. OBJECTIVE: The main goal of this work was to demonstrate the analgesic action in mice of some preparations and major compounds from L. porteri. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The extracts, aqueous (AE) and organic (OE), the essential oil (EO) and major compounds (10-316 mg/kg) from L. porteri were evaluated as potential antinociceptive agents using the acetic acid-induced writhing and hot plate tests in ICR mice. RESULTS: All preparations tested exhibited significant antinociceptive effect in the two animal pain models selected. AE and EO were more effective in the writhing test while OE had a better effect in the hot-plate model. On the other hand, Z-ligustilide (1) provoked an increment in the latency period to the thermal stimuli in the hot-plate test at a dose of 31.6 mg/kg, and a decrease in the number of abdominal writhes at 10 mg/kg. Z-3-Butylidenephthalide (2) induced a dose-dependent antinociceptive action in the hot-plate assay; this compound was also effective for controlling the pain provoked by chemical irritation at the doses of 10 and 31.6 mg/kg. Finally, diligustilide (3) inhibited the number of writhing responses at all doses tested but was inactive in the hot-plate model. CONCLUSION: The present investigation provides in vivo evidence supporting the use of L. porteri to treat painful conditions in folk medicine.
(Z)-3-butylidenephthalide from Ligusticum porteri , an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor.[Pubmed:20879744]
J Nat Prod. 2011 Mar 25;74(3):314-20.
An extract from the roots of Ligusticum porteri, orally administered to groups of normal and diabetic mice, showed significant hypoglycemic and antihyperglycemic effects. Experimental type-II DM was achieved by treating mice with streptozotocin 15 min after an injection of beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. (Z)-6,6',7,3'alpha-diligustilide (1), (Z)-ligustilide (2), 3-(Z)-butylidenephthalide (3), myristicin (4), and ferulic acid (5) were isolated from the active extract. When tested In Vivo, compounds 1-3 showed antihyperglycemic activity, with 3 being the most active. Compound 3 (56.2 mg/kg) decreased blood glucose levels in NAD-STZ-diabetic mice after an oral sucrose load, suggesting that its antihyperglycemic effect is due to inhibition of alpha-glucosidase at the intestinal level. Furthermore, 3 inhibited the activity of yeast-alpha-glucosidase (IC(50) 2.35 mM) in a noncompetitive fashion with a K(i) of 4.86 mM. Docking analysis predicted that 3 binds to the enzyme in a pocket close to the catalytic site, but different from that for acarbose, with a K(i) of 11.48 mM. Compounds 1 and 2 did not affect alpha-glucosidase In Vivo, but altered glucose absorption by a mechanism yet to be determined. The stimulatory effect of 5 on insulin secretion, present in high amounts in the extract, has been demonstrated in previous investigations. The present study provides scientific support of the use of L. porteri in Mexican folk medicine for the treatment of diabetes.
Effects of natural phytochemicals in Angelica sinensis (Danggui) on Nrf2-mediated gene expression of phase II drug metabolizing enzymes and anti-inflammation.[Pubmed:23640758]
Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2013 Sep;34(6):303-11.
The root of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (abbreviated as AS) (Danggui) has a long history in Asian herbal medicine. Recently, it was demonstrated that AS possesses anti-cancer and anti-oxidant activities. Because the transcription factor Nrf2 mediates the expression of many cellular anti-oxidative stress genes, including genes that are involved in phase II drug metabolism and anti-oxidative stress, this study sought to investigate whether pure compounds from AS or an AS extract could activate antioxidant response element (ARE)-mediated gene expression and induce anti-inflammatory activities. Z-Ligustilide (Ligu), 3-Butylidenephthalide (Buty) and CO2 supercritical fluid-extracted lipophilic AS extract (SFE) were tested in HepG2-C8 cells stabilized with ARE luciferase reporter gene. Ligu and Buty caused significant toxicity only at 100 mum. All three samples induced ARE-luciferase activity; however, SFE at 8.5 microg/ml induced ARE-luciferase activity 2-3 fold more potently than did either of the pure compounds. SFE also significantly increased the endogenous mRNA of Nrf2 and the Nrf2 target anti-oxidative gene NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1 (NQO1). The protein expression of NQO1 was also significantly induced by SFE. In RAW 264.7 cells, SFE suppressed lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced IL-1beta and TNF-alpha expression about 2 fold stronger than sulforaphane, whereas both pure compounds and SFE suppressed inflammatory nitric oxide (NO) production. In summary, this study demonstrates that AS has anti-inflammatory effects and activates the Nrf2 pathway, which protects against oxidative stress.
Online isolation and purification of four phthalide compounds from Chuanxiong rhizoma using high-speed counter-current chromatography coupled with semi-preparative liquid chromatography.[Pubmed:23484653]
J Chromatogr A. 2013 Apr 5;1284:53-8.
The phthalide compounds of Chuanxiong rhizoma including senkyunolide A, levistolide A, Z-ligustilide and 3-Butylidenephthalide, have been reported as the biologically active compounds because of their therapeutic effects. In this work, online high-speed counter-current chromatography coupled with semi-preparative liquid chromatography instrument was set up, and online separation of the four compounds has been simultaneously achieved using this instrument. In this study, using all the selected solvent system, Z-ligustilide and 3-Butylidenephthalide were eluted in one peak by high-speed counter-current chromatography. Using high-speed counter-current chromatography with a solvent system of n-hexane-ethyl acetate-methanol-water-acetonitrile (8:2:5:5:5, v/v), 3.6 mg of senkyunolide A (94.4%) and 3.0mg of levistolide A (95.3%) were obtained from 100mg of the crude extract. Coeluted Z-ligustilide and 3-Butylidenephthalide peak fraction (8 mL) from high-speed counter-current chromatography was directly transferred and injected to the semi-preparative liquid chromatography for further separation. Finally, 5.6 mg of Z-ligustilide (97.5%) and 4.8 mg of 3-Butylidenephthalide (99.3%) were obtained. The identification of these four compounds was performed by quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer, (1)H and (13)C nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer.


