(S)-MCPGCAS# 150145-89-4 |
- Deuterated Atazanivir-D3-3
Catalog No.:BCC2117
CAS No.:1092540-52-7
- Deuterated Atazanivir-D3-1
Catalog No.:BCC2115
CAS No.:1092540-56-1
- Amprenavir (agenerase)
Catalog No.:BCC3619
CAS No.:161814-49-9
- Atazanavir
Catalog No.:BCC3622
CAS No.:198904-31-3
- BMS-538203
Catalog No.:BCC4136
CAS No.:543730-41-2
- BMS-707035
Catalog No.:BCC2133
CAS No.:729607-74-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 150145-89-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 446355 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H11NO4 | M.Wt | 209.2 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (+)-MCPG | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 6.2 mg/mL (29.64 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
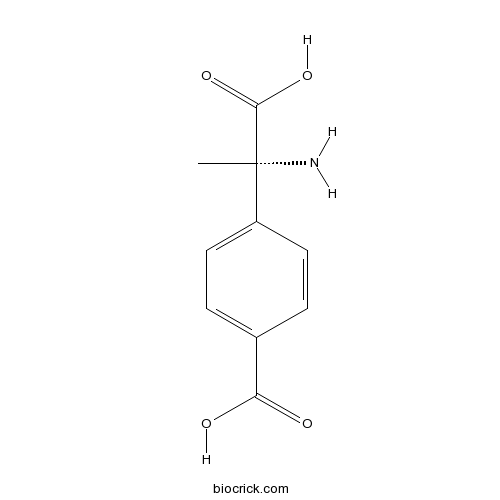
| Chemical Name | (S)-α-Methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine | ||
| SMILES | C[C@@]([NH3+])(C([O-])=O)c1ccc(cc1)C([O-])=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DNCAZYRLRMTVSF-JTQLQIEISA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H11NO4/c1-10(11,9(14)15)7-4-2-6(3-5-7)8(12)13/h2-5H,11H2,1H3,(H,12,13)(H,14,15)/p-1/t10-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Active isomer of (RS)-MCPG. Non-selective group I/group II metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist. Also available as part of the Group I mGlu Receptor, Group II mGlu Receptor and Mixed mGlu Receptor. |

(S)-MCPG Dilution Calculator

(S)-MCPG Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.7801 mL | 23.9006 mL | 47.8011 mL | 95.6023 mL | 119.5029 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.956 mL | 4.7801 mL | 9.5602 mL | 19.1205 mL | 23.9006 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.478 mL | 2.3901 mL | 4.7801 mL | 9.5602 mL | 11.9503 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0956 mL | 0.478 mL | 0.956 mL | 1.912 mL | 2.3901 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0478 mL | 0.239 mL | 0.478 mL | 0.956 mL | 1.195 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
(S)-MCPG is the active isomer of (RS)-MCPG (Cat. No. HY-100371), non-selective group I/group II metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist. In vivo: (S)-MCPG (20.8 μg) injected intraventricularly (i.c.v.) before testing impaired the performance of rats in the spatial version of the Morris water maze, but 1/10 of this dose did not. Memory retention, evaluated 24 hr post-training, is also affected by the high dose of MCPG.
References:
[1]. Bordi F et al. Effects of the metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist MCPG on spatial and context-specific learning. Neuropharmacology. 1996;35(11):1557-65.
[2]. Sekiyama N et al. Structure-activity relationships of new agonists and antagonists of different metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Apr;117(7):1493-503.
[3]. Jane DE et al. Stereospecific antagonism by (+)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) of (1S,3R)-ACPD-induced effects in neonatal rat motoneurones and rat thalamic neurones. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Jul;32(7):725-7.
- Qianhucoumarin A
Catalog No.:BCN3615
CAS No.:150135-35-6
- Decanoyl-RVKR-CMK
Catalog No.:BCC6030
CAS No.:150113-99-8
- Talabostat mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC5357
CAS No.:150080-09-4
- Methyl 2-ethoxybenzimidazole-7-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC9036
CAS No.:150058-27-8
- Cycloshizukaol A
Catalog No.:BCN6567
CAS No.:150033-85-5
- Phytol
Catalog No.:BCN1673
CAS No.:150-86-7
- Mequinol
Catalog No.:BCC4797
CAS No.:150-76-5
- m-Methoxyphenol
Catalog No.:BCN1669
CAS No.:150-19-6
- O-Acetylschisantherin L
Catalog No.:BCN3635
CAS No.:149998-51-6
- Gelomuloside B
Catalog No.:BCN6640
CAS No.:149998-39-0
- Gelomuloside A
Catalog No.:BCN6639
CAS No.:149998-38-9
- 5-O-Methyldalbergiphenol
Catalog No.:BCN8104
CAS No.:1499946-35-8
- Strictosidinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6965
CAS No.:150148-81-5
- 11,13-Dihydroivalin
Catalog No.:BCN4705
CAS No.:150150-61-1
- Crucigasterin 277
Catalog No.:BCN1777
CAS No.:150151-83-0
- Crucigasterin 275
Catalog No.:BCN1776
CAS No.:150151-84-1
- Crucigasterin 225
Catalog No.:BCN1786
CAS No.:150151-85-2
- BIM 23056
Catalog No.:BCC5824
CAS No.:150155-61-6
- Trigothysoid N
Catalog No.:BCN6881
CAS No.:1501943-08-3
- 12-Deoxo-12alpha-acetoxyelliptone
Catalog No.:BCN4803
CAS No.:150226-21-4
- Fmoc-2-Abz-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3204
CAS No.:150256-42-1
- Fmoc-p-amino-benzoic acid,Fmoc-4-Abz-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2622
CAS No.:15026-42-1
- Ledipasvir D-tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4047
CAS No.:1502654-87-6
- H-Aib-Ome.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2671
CAS No.:15028-41-8
(R,S)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) fails to block long-term potentiation under urethane anaesthesia in vivo.[Pubmed:9423922]
Neuropharmacology. 1997 Oct;36(10):1339-54.
The effects of the metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist (R,S)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) on the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) in the dentate gyrus were examined under urethane anaesthesia in vivo. In experiment 1, bilateral intraventricular infusion of either 20 mM or 200 mM (R,S)-MCPG (5 microl each side) failed to block LTP in the perforant path-granule cell projection, relative to vehicle-infused controls; 30 mM D-AP5 (5 microl each side) infused in the same way as MCPG completely blocked LTP. Experiment 2, in which the contralateral perforant path-dentate gyrus pathway was used as a non-tetanized control, revealed that slight baseline changes induced by MCPG infusion were transient; again no block of LTP was obtained. The efficacy of mGluR blockade was confirmed in experiment 3, in which MCPG antagonized an increase in spontaneous activity induced by (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (ACPD). In experiment 4, significant depotentiation was induced by low frequency stimulation (5 Hz for 1 min) given 2 min after high frequency tetanization, but MCPG remained ineffective in blocking LTP after a second tetanus. In experiment 5, increasing the period of low frequency stimulation from 1 to 10 min produced greater depotentiation, but still did not unmask an MCPG-sensitive component of LTP. These experiments fail to support a role for mGluRs in the induction of LTP in the dentate gyrus under urethane anaesthesia in vivo, nor do they support the idea that a metabotropic switch controlling sensitivity to MCPG is reset by depotentiation.
(R,S)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) blocks spatial learning in rats and long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus in vivo.[Pubmed:8177513]
Neurosci Lett. 1994 Feb 14;167(1-2):141-4.
Recently, it was demonstrated by the use of the competitive and selective antagonist (R,S)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) that metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) activation is required to induce long-term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus. Accordingly, we investigated whether MCPG also inhibits spatial learning. Rats were trained on a spatial alternation task in a Y-maze with footshock reinforcement, and MCPG (0.0208 mg) was injected intracerebroventricularly prior to training and/or retention test. Animals injected pre-training are clearly impaired in retention, whereas preretention application was without effect. A state dependency could be excluded. Additionally, MCPG at the same concentration completely blocks a potentiation at perforant path/dentate gyrus synapses in vivo. These results strongly implicate a role of mGluRs in spatial learning and LTP.
Effects of the metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist MCPG on spatial and context-specific learning.[Pubmed:9025103]
Neuropharmacology. 1996;35(11):1557-65.
The effects of the metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist (+)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) on performance in a water maze and in context-specific associative learning were examined in rats previously implanted with cannulae. MCPG (20.8 micrograms) injected intraventricularly (i.c.v.) before testing impaired the performance of rats in the spatial version of the Morris water maze, but 1/10 of this dose did not. Memory retention, evaluated 24 hr post-training, was also affected by the high dose of MCPG. However, performance in a cued version of the water maze was not impaired by the high dose, excluding effects of the drug on perceptual faculties. The effects of the MCPG were further characterized on performance in another hippocampus-dependent spatial learning task, the context-dependent fear conditioning task. MCPG (20.8 micrograms, i.c.v.) did not interfere with conditioned freezing to context in this task. For comparison, a group of rats was injected with the NMDA receptor blocker MK801. MK801 at a dose that disrupted the performance in the spatial version of the Morris water maze (0.08 mg/kg), significantly reduced freezing compared to controls. These experiments indicate that MCPG-sensitive metabotropic receptors may be required for only a restricted subset of spatial learning tasks, while NMDA receptors may play an integral role in all spatial learning.
Structure-activity relationships of new agonists and antagonists of different metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes.[Pubmed:8730745]
Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Apr;117(7):1493-503.
1. We investigated the agonist and antagonist activities of 22 new phenylglycine and phenylalanine derivatives for metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) by examining their effects on the signal transduction of mGluR1, mGluR2 and mGluR6 subtypes expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. This analysis revealed several structural characteristics that govern receptor subtype specificity of the agonist and antagonist activities of phenylglycine derivatives. 2. Hydroxyphenylglycine derivatives possessed either an agonist activity on mGluR1/mGluR6 or an antagonist activity on mGluR1. 3. Carboxyphenylglycine derivatives showed an agonist activity on mGluR2 but an antagonist activity on mGluR1. 4. alpha-Methylation or alpha-ethylation of the carboxyphenylglycine derivatives converts the agonist property for mGluR2 to an antagonist property, thus producing antagonists at both mGluR1 and mGluR2. 5. Structurally-corresponding phenylalanine derivatives showed little or no agonist or antagonist activity on any subtypes of the receptors. 6. This investigation demonstrates that the nature and positions of side chains and ring substituents incorporated into the phenylglycine structure are critical in determining the agonist and antagonist activities of members of this group of compounds on different subtypes of the mGluR family. 7. We also tested two alpha-methyl derivatives of mGluR agonists. (2S, 1'S, 2'S)-2-(2-Carboxycyclopropyl)glycine (L-CCG-I) is a potent agonist for mGluR2 but alpha-methylation of this compound changes its activity to that of an mGluR2-selective antagonist. In contrast, alpha-methylation of L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate (L-AP4) results in retention of an agonist activity on mGluR6. Thus, alpha-methylation produces different effects, depending on the chemical structures of lead compounds and/or on the subtype of mGluR tested.
Phenylglycine derivatives as antagonists of metabotropic glutamate receptors.[Pubmed:7992387]
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Sep;15(9):333-42.
Metabotropic glutamate receptors represent a family of G protein-coupled receptors that can be activated by L-glutamate, the principal excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. Until recently, progress in identifying the physiological and pathological roles of metabotropic glutamate receptors has been hampered by the lack of selective antagonists. In this article, Jeff Watkins and Graham Collingridge describe the pharmacology of, and initial physiological studies using, certain phenylglycine derivatives and related substances--the first definitive antagonists of metabotropic glutamate receptors.
Stereospecific antagonism by (+)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) of (1S,3R)-ACPD-induced effects in neonatal rat motoneurones and rat thalamic neurones.[Pubmed:7689710]
Neuropharmacology. 1993 Jul;32(7):725-7.
The (+)-enantiomer of alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) stereoslectively antagonized the depolarization of neonatal rat motoneurones and the excitation of rat thalamic neurons induced by the specific metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylate (ACPD). (+)-MCPG preferentially reduced (1S,3R)-ACPD-induced responses relative to responses induced by (S)-alpha-amino-3-hydorxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA).


