Losartan Potassium (DuP 753)Angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonist CAS# 124750-99-8 |
- Perindopril Erbumine
Catalog No.:BCC3586
CAS No.:107133-36-8
- Candesartan
Catalog No.:BCC2558
CAS No.:139481-59-7
- Telmisattan
Catalog No.:BCC3863
CAS No.:144701-48-4
- Rosuvastatin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC3853
CAS No.:147098-20-2
- Imidapril HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3792
CAS No.:89396-94-1
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
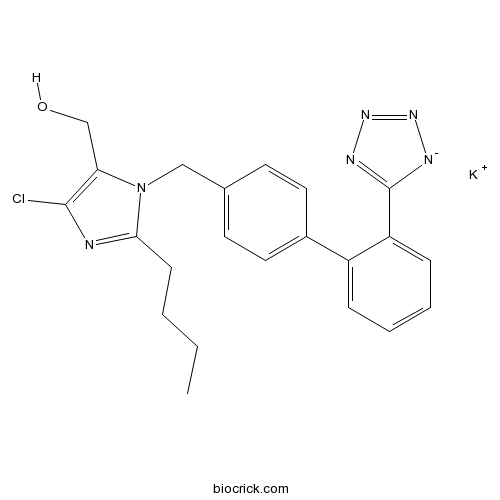
| Cas No. | 124750-99-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11751549 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H23ClKN6O | M.Wt | 462.01 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | DuP-753;DuP753 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 110 mg/mL (238.61 mM) H2O : 33.33 mg/mL (72.30 mM; Need ultrasonic) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-Butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2'-(1H-tetrazol | ||
| SMILES | [K+].CCCCc1nc(Cl)c(CO)n1Cc2ccc(cc2)c3ccccc3c4[n-]nnn4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OXCMYAYHXIHQOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H22ClN6O.K/c1-2-3-8-20-24-21(23)19(14-30)29(20)13-15-9-11-16(12-10-15)17-6-4-5-7-18(17)22-25-27-28-26-22;/h4-7,9-12,30H,2-3,8,13-14H2,1H3;/q-1;+1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective non-peptide angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonist. Inhibits the contractile effects of angiotensin II on rabbit aorta and jugular vein (pA2 = 8.27). Orally active antihypertensive agent. |

Losartan Potassium (DuP 753) Dilution Calculator

Losartan Potassium (DuP 753) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1645 mL | 10.8223 mL | 21.6446 mL | 43.2891 mL | 54.1114 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4329 mL | 2.1645 mL | 4.3289 mL | 8.6578 mL | 10.8223 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2164 mL | 1.0822 mL | 2.1645 mL | 4.3289 mL | 5.4111 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0433 mL | 0.2164 mL | 0.4329 mL | 0.8658 mL | 1.0822 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0216 mL | 0.1082 mL | 0.2164 mL | 0.4329 mL | 0.5411 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Selective non-peptide angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonist. Inhibits the contractile effects of angiotensin II on rabbit aorta and jugular vein (pA2 = 8.27). Orally active antihypertensive agent.
- Quinovic acid 3-O-(6-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranoside) 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1595
CAS No.:124727-10-2
- Meprednisone
Catalog No.:BCC4893
CAS No.:1247-42-3
- Methyl-Dodovisate A
Catalog No.:BCN4719
CAS No.:1246937-33-6
- 5'-Prenylaliarin
Catalog No.:BCN4829
CAS No.:1246926-09-9
- 5,7,4'-Trihydroxy-3,6-dimethoxy-3',5'-diprenylflavone
Catalog No.:BCN1596
CAS No.:1246926-08-8
- VS-5584 (SB2343)
Catalog No.:BCC2047
CAS No.:1246560-33-7
- MPI-0479605
Catalog No.:BCC5347
CAS No.:1246529-32-7
- SR1078
Catalog No.:BCC1963
CAS No.:1246525-60-9
- (-)-Dihydroguaiaretic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8002
CAS No.:124649-78-1
- Officinaruminane B
Catalog No.:BCN3594
CAS No.:1246282-67-6
- C3bot (154-182)
Catalog No.:BCC6117
CAS No.:1246280-79-4
- VU 0364439
Catalog No.:BCC1239
CAS No.:1246086-78-1
- P 22077
Catalog No.:BCC3616
CAS No.:1247819-59-5
- USP7-USP47 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4113
CAS No.:1247825-37-1
- Valaciclovir
Catalog No.:BCC2025
CAS No.:124832-26-4
- Valacyclovir hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4051
CAS No.:124832-27-5
- Nadifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4804
CAS No.:124858-35-1
- 5-Dehydroxyparatocarpin K
Catalog No.:BCN4017
CAS No.:124858-37-3
- Isoaltholactone
Catalog No.:BCN4826
CAS No.:124868-11-7
- Benzoyl leuco methylene blue
Catalog No.:BCC8862
CAS No.:1249-97-4
- (R)-(+)-Tolterodine
Catalog No.:BCC4054
CAS No.:124937-51-5
- Tolterodine tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4586
CAS No.:124937-52-6
- Tectoroside
Catalog No.:BCN6672
CAS No.:124960-89-0
- Raddeanoside R8
Catalog No.:BCN6555
CAS No.:124961-61-1
Human plasma protein binding of the angiotensin II receptor antagonist losartan potassium (DuP 753/MK 954) and its pharmacologically active metabolite EXP3174.[Pubmed:7657853]
J Clin Pharmacol. 1995 May;35(5):515-20.
The in vitro protein binding characteristics of the prototypical angiotensin II receptor antagonist losartan potassium (DuP 753/MK 954) and its pharmacologically active metabolite EXP3174 were determined by ultrafiltration with plasma from naive donors, volunteers dosed with losartan, and purified human plasma proteins. The binding of losartan was high, with a percent unbound (free) of 1.4 +/- 0.2% to 1.2 +/- 0.1% at concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 5.0 micrograms/mL; that is, approximately 98.6 to 98.8% bound. EXP3174 was more highly bound than losartan (P < .05) with 0.2 +/- 0.0% free at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 10.0 micrograms/mL; or, greater than 99.7% bound. The binding in the plasma from volunteers given oral losartan was similar to that determined with plasma from naive donors, with 1.5 +/- 0.3 versus 1.4 +/- 0.1% free for losartan, and 0.5 +/- 0.1 versus 0.4 +/- 0.0% for EXP3174, respectively. This extensive plasma binding of both acidic compounds occurs primarily to albumin, with negligible binding to the alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Although highly bound, neither losartan nor EXP3174 were displaced in vitro by pharmacologically relevant concentrations of non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), warfarin, or diazepam; however, suprapharmacologic concentrations of the NSAIDs increased the free fraction of both compounds. These data show that the angiotensin II receptor antagonists losartan and EXP3174 are highly bound to plasma albumin in humans, although clinically significant drug interactions due to displacement from binding sites are unlikely.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the angiotensin II receptor antagonist losartan potassium (DuP 753/MK 954) in the dog.[Pubmed:8138932]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Mar;268(3):1199-205.
The pharmacokinetics and plasma concentration-effect relationship for the nonpeptide angiotensin II (Ang II) receptor antagonist losartan potassium (losartan) have been determined with conscious and anesthetized dogs. The p.o. bioavailability of single doses of 5 to 20 mg/kg was low, 23 to 33%, and independent of the dose. Absorption was rapid, with peak plasma levels observed within 1 hr, and the Cmax and area under the concentration vs. time curve to infinity were proportional to the dose, P < .05. The elimination half-life, 108 to 153 min, was longer than that observed after a single i.v. dose, 41 min, and may reflect both continuous absorption and enterohepatic recirculation because the major route of excretion was via the bile. Single i.v. doses were eliminated rapidly, with a systemic plasma clearance of 22.2 ml/min/kg. When corrected for the blood:plasma distribution ratio, 0.66 to 0.72, the systemic clearance approximates hepatic blood flow, suggesting that clearance is primarily via hepatic metabolism and biliary excretion. Losartan was not distributed extensively to tissues; apparent volume of distribution at steady-state of 0.30 liters/kg and was highly but not extensively bound to plasma proteins; 2.7 to 2.9% unbound (free). The plasma concentration vs. blockade of exogenous Ang II-induced vasopressor response was also determined after a single 3-mg/kg i.v. dose of losartan with a sigmoidal Emax model. Blockade of the pressor response was rapid, 89% at 5 min, and declined to 11% at 240 min postdose. The relationship between concentration and effect was highly significant (r = 0.922, P < .01), with an IC50 (total) of 96 ng/ml.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Effect of chronic treatment with losartan potassium (DuP 753) on the elevation of blood pressure during chronic exposure of rats to cold.[Pubmed:8483966]
Pharmacology. 1993 Apr;46(4):198-205.
Elevation of diastolic, systolic, and mean blood pressures and cardiac hypertrophy occur in rats exposed to cold (5 degrees C) for 1-3 weeks. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is believed to play a role in the development of cold-induced hypertension since plasma renin activity increases within the first 2 weeks, presumably initiating the hypertensive process, and then returns to control level. The present study was designed to assess the role of angiotension II (Ang II) in the hypertensive process by chronic administration of losartan potassium, an Ang II1 receptor antagonist. Twenty-four rats were divided into four equal groups. After a 1-week control period, one group was kept at 25 degrees C while the remaining three groups were exposed to cold (5 degrees C). One of the cold-treated groups was untreated while the remaining two were given losartan in drinking water at a concentration calculated to provide 56 and 112 mg/kg/day. The untreated cold-exposed group had a significant elevation of systolic blood pressure within 1 week of exposure to cold. Losartan at both doses prevented the elevation of blood pressure and blocked both the dipsogenic and vascular responses to administration of Ang II. Exposure to cold increased food intake, urine output and water intake significantly above that of warm-adapted controls. Treatment with losartan tended to decrease each of these toward the level of controls. At the conclusion of the seventh week of exposure to cold, the rats were sacrificed and heart, kidneys, and brown fat removed and weighed.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
DuP 753 is a specific antagonist for the angiotensin receptor.[Pubmed:1672862]
Hypertension. 1991 Apr;17(4):480-4.
2-n-Butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxy-methyl-1-[(2'-(1H)-tetrazol-5-yl)biph enyl-4- yl)methyl]imidazol potassium salt (DuP 753) is a nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist that inhibits the contractile effects of angiotensin II competitively and shows pA2 values of 8.27 on the rabbit aorta and jugular vein, 8.66 on the rat portal vein and stomach, 8.19 on the rat urinary bladder, and 8.36 on human colon, ileum, and urinary bladder. This agent (more than 10(-5) M) exhibits no agonistic activity and does not affect the contractile effects of norepinephrine, acetylcholine, bradykinin, desArg9-bradykinin, substance P, neurokinin A, neurokinin B, or bombesin in the various tissues. The present results demonstrate that DuP 753 is a potent nonpeptide antagonist with high affinity, specificity, and selectivity for the angiotensin receptor.
Functional studies of nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor subtype-specific ligands: DuP 753 (AII-1) and PD123177 (AII-2).[Pubmed:2243344]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):584-92.
DuP 753 and PD123177 are two nonpeptide angiotensin II (AII)-specific ligands, which show high affinities for two respective and distinct subtypes of AII binding sites, i.e., AII-1 and AII-2 sites, respectively, in the rat adrenal gland, brain and uterus. The objective of this study is to identify the functions of these subtype binding sites in the adrenal, sympathetic ganglia, brain and vascular smooth muscle. In conscious rats, DuP 753 at 1, 3 and 10 mg/kg i.v. but not PD123177 at 30 and 100 mg/kg i.v. inhibited the AII-induced aldosterone increase. In the isolated perfused rat adrenal gland, DuP 753 at 10(-6) and 10(-4) M but not PD123177 at 10(-3) M blocked the AII-induced epinephrine secretion. In control and chemically sympathectomized pithed rats, the pressor and tachycardiac responses to AII were blocked by DuP 753 at 10 mg/kg i.v. but not by PD123177 at 100 mg/kg i.v. In conscious rats, DuP 753 at 10 mg/kg s.c. but not PD123177 at 100 mg/kg s.c. inhibited the AII-induced water drinking. In the rabbit aorta, DuP 753 at 10(-6) M but not PD123177 at 10(-4) M inhibited the contractile effect of AII. In conscious renal artery-ligated hypertensive rats, DuP 753 but not PD123177 at 0.1 to 10 mg/kg i.v. lowered blood pressure. In summary, a function of the PD123177-sensitive AII binding site (AII-2) has not yet been identified. However, the DuP 753-sensitive site (AII-1) appears to mediate the AII-induced responses such as adrenal aldosterone and catecholamine secretion, release of catecholamine from sympathetic ganglia, drinking and vasoconstriction.
Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists. VIII. Characterization of functional antagonism displayed by DuP 753, an orally active antihypertensive agent.[Pubmed:2179531]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Feb;252(2):719-25.
In the spinal pithed rat, DuP 753, 2-n-butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxy-methyl-1-[(2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphe nyl-4-yl) methyl] imidazole potassium salt, inhibited competitively the pressor response to angiotensin II (AII), whereas saralasin showed a noncompetitive pattern of interaction. It did not alter the pressor responses to vasopressin and norepinephrine as well as the heart rate response to isoproterenol. In the anesthetized rat, DuP 753 did not affect the vasodepressor response to bradykinin. Given p.o. or i.v., DuP 753 did not lower blood pressure in conscious normotensive rats, but it inhibited the pressor response to AII but not to vasopressin. It lowered blood pressure in furosemide-treated normotensive rats. Unlike saralasin, DuP 753 did not cause a transient increase in blood pressure even at 100 mg/kg i.v. DuP 753 at 3.5 micrograms i.c.v. inhibited the pressor response to i.c.v. AII, whereas DuP 753 at 10 mg/kg p.o. did not, suggesting that a single p.o. administration of DuP 753 does not affect brain AII receptors which are accessible by i.c.v. injection. Our study indicates that DuP 753 is a p.o. active, nonpeptide, selective, competitive AII receptor antagonist.


