KT 5823Selective protein kinase G inhibitor CAS# 126643-37-6 |
- Elacridar
Catalog No.:BCC1546
CAS No.:143664-11-3
- Elacridar hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1547
CAS No.:143851-98-3
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 126643-37-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 108152 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C29H25N3O5 | M.Wt | 495.53 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in DMSO | ||
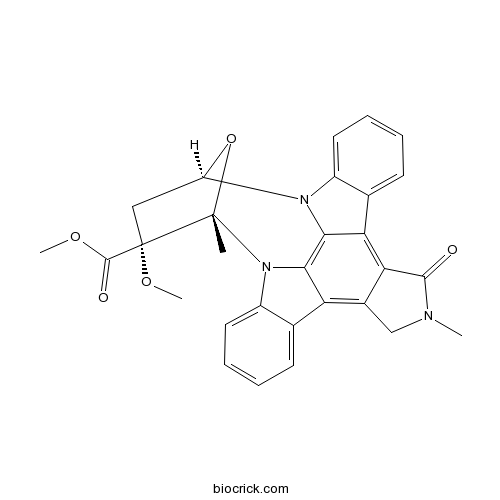
| SMILES | CC12C(CC(O1)N3C4=CC=CC=C4C5=C6C(=C7C8=CC=CC=C8N2C7=C53)CN(C6=O)C)(C(=O)OC)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QTYMDECKVKSGSM-YMUMJAELSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C29H25N3O5/c1-28-29(36-4,27(34)35-3)13-20(37-28)31-18-11-7-5-9-15(18)22-23-17(14-30(2)26(23)33)21-16-10-6-8-12-19(16)32(28)25(21)24(22)31/h5-12,20H,13-14H2,1-4H3/t20-,28+,29+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective inhibitor of protein kinase G (Ki values are 0.23, 4 and > 10 μM for inhibition of PKG, PKC and PKA respectively). Inhibits SNP-stimulated PKG activity with an IC50 of 60 nM in dispersed smooth muscle cells and has little effect on PKA activity at concentrations of up to 10 μM. |

KT 5823 Dilution Calculator

KT 5823 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.018 mL | 10.0902 mL | 20.1804 mL | 40.3608 mL | 50.451 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4036 mL | 2.018 mL | 4.0361 mL | 8.0722 mL | 10.0902 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2018 mL | 1.009 mL | 2.018 mL | 4.0361 mL | 5.0451 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0404 mL | 0.2018 mL | 0.4036 mL | 0.8072 mL | 1.009 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0202 mL | 0.1009 mL | 0.2018 mL | 0.4036 mL | 0.5045 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 16-Epinormacusine B
Catalog No.:BCN4030
CAS No.:126640-98-0
- A 887826
Catalog No.:BCC7898
CAS No.:1266212-81-0
- Trilobinine
Catalog No.:BCN7927
CAS No.:126595-92-4
- Vallesamine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN6144
CAS No.:126594-73-8
- Cyclocerberidol
Catalog No.:BCN6143
CAS No.:126594-66-9
- Cerberidol
Catalog No.:BCN6142
CAS No.:126594-64-7
- S1RA hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4190
CAS No.:1265917-14-3
- 8,14-Epoxyergosta-4,22-diene-3,6-dione
Catalog No.:BCN1591
CAS No.:1265908-20-0
- Ciclesonide
Catalog No.:BCC5234
CAS No.:126544-47-6
- CH5183284 (Debio-1347)
Catalog No.:BCC5649
CAS No.:1265229-25-1
- Mupirocin
Catalog No.:BCC5558
CAS No.:12650-69-0
- Metasequirin D
Catalog No.:BCN4781
CAS No.:1264694-96-3
- UTPγS trisodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7624
CAS No.:1266569-94-1
- Isoaltenuene
Catalog No.:BCN7313
CAS No.:126671-80-5
- Gancaonin G
Catalog No.:BCN6837
CAS No.:126716-34-5
- Gancaonin I
Catalog No.:BCN7144
CAS No.:126716-36-7
- Tilifodiolide
Catalog No.:BCN6145
CAS No.:126724-95-6
- Acetylsventenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4849
CAS No.:126737-42-6
- Sarafotoxin S6a
Catalog No.:BCC5834
CAS No.:126738-34-9
- GR 89696 fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC7083
CAS No.:126766-32-3
- Sventenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3923
CAS No.:126778-79-8
- Ulipristal acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4068
CAS No.:126784-99-4
- 5,7,3'-Trihydroxy-4'-methoxy-8-prenylflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN1590
CAS No.:1268140-15-3
- 13-Acetoxy-3beta-hydroxygermacra-1(10)E,4E,7(11)-trien-12,6alpha-olide
Catalog No.:BCN7314
CAS No.:126829-66-1
Mechanism of resveratrol-induced relaxation of the guinea pig fundus.[Pubmed:29747754]
Phytomedicine. 2018 Apr 1;43:55-59.
BACKGROUND: Resveratrol is a polyphenolic compound that can be isolated from plants and also is a constituent of red wine. Resveratrol induces relaxation of vascular smooth muscle and may prevent cardiovascular diseases. PURPOSE: Impaired gastric accommodation plays an important role in functional dyspepsia and fundic relaxation and is a therapeutic target of functional dyspepsia. Although drugs for fundic relaxation have been developed, these types of drugs are still rare. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relaxant effects of resveratrol in the guinea pig fundus. STUDY DESIGN: We studied the relaxant effects of resveratrol in the guinea pig fundus. In addition, we investigated the mechanism of resveratrol-induced relaxation on the guinea pig fundus by using tetraethylammonium (a non-selective potassium channel blocker), apamine (a selective inhibitor of the small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel), iberiotoxin (an inhibitor of large conductance calcium-activated potassium channels), glibenclamide (an ATP-sensitive potassium channel blocker), KT 5720 (a cAMP-dependent protein kinase A inhibitor), KT 5823 (a cGMP-dependent protein kinase G inhibitor), NG-nitro-L-arginine (a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase), tetrodotoxin (a selective neuronal Na(+) channel blocker), omega-conotoxin GVIA (a selective neuronal Ca(2+) channel blocker) and G-15 (a G-protein coupled estrogen receptor antagonist). RESULTS: The results of this study showed that resveratrol has potent and dose-dependent relaxant effects on the guinea pig fundic muscle. In addition, the results showed that resveratrol-induced relaxation of the guinea pig fundus occurs through nitric oxide and ATP-sensitive potassium channels. CONCLUSION: This study provides the first evidence concerning the relaxant effects of resveratrol in the guinea pig fundic muscle strips. Furthermore, resveratrol may be a potential drug to relieve gastrointestinal dyspepsia.
The anti-diabetic drug dapagliflozin induces vasodilation via activation of PKG and Kv channels.[Pubmed:29409796]
Life Sci. 2018 Mar 15;197:46-55.
AIM: Considering the clinical efficacy of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 DM and the pathophysiological relevance of Kv channels for vascular reactivity. We investigate the vasodilatory effect of dapagliflozin and related mechanisms using phenylephrine (Phe)-induced contracted aortic rings. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Arterial tone measurement was performed in aortic smooth muscle. KEY FINDINGS: Application of dapagliflozin induced vasodilation in a concentration-dependent manner. Pre-treatment with the BKCa channel inhibitor paxilline, the KATP channel inhibitor glibenclamide, and the Kir channel inhibitor Ba(2+) did not change dapagliflozin-induced vasodilation. However, application of the Kv channels inhibitor 4-AP effectively inhibited dapagliflozin-induced vasodilation. Application of the Ca(2+) channel inhibitor nifedipine and the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA) pump inhibitor thapsigargin did not alter the vasodilatory effect of dapagliflozin. Moreover, the adenylyl cyclase inhibitor SQ 22536 and the protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor KT 5720 had no effect on dapagliflozin-induced vasodilation. Although guanylyl cyclase inhibitors, NS 2028 and ODQ, did not reduce the vasodilatory effect of dapagliflozin, the protein kinase G (PKG) inhibitor KT 5823 effectively inhibited dapagliflozin-induced vasodilation. The vasodilatory effect of dapagliflozin was not affected by elimination of the endothelium. Furthermore, pretreatment with the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-NAME or the small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K (SKCa) channel inhibitor apamin did not change the vasodilatory effect of dapagliflozin. SIGNIFICANCE: We concluded that dapagliflozin induced vasodilation via the activation of Kv channels and PKG, and was independent of other K(+) channels, Ca(2+) channels, intracellular Ca(2+), and the endothelium.
Protein kinases G are essential downstream mediators of the antifibrotic effects of sGC stimulators.[Pubmed:29311148]
Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Mar;77(3):459.
OBJECTIVES: Stimulators of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) are currently investigated in clinical trials for the treatment of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis (SSc). In this study, we aim to investigate the role of protein kinases G (PKG) as downstream mediators of sGC-cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in SSc. METHODS: Mice with combined knockout of PKG1 and 2 were challenged with bleomycin and treated with the sGC stimulator BAY 41-2272. Fibroblasts were treated with BAY 41-2272 and with the PKG inhibitor KT 5823. RESULTS: PKG1 and 2 are upregulated in SSc in a transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGFbeta1)-dependent manner, as an attempt to compensate for the decreased signalling through the sGC-cGMP-PKG pathway. Inhibition or knockout of PKG1 and 2 abrogates the inhibitory effects of sGC stimulation on fibroblast activation in a SMAD-independent, but extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-dependent manner. In vivo, sGC stimulation fails to prevent bleomycin-induced fibrosis in PKG1 and 2 knockout mice. CONCLUSIONS: Our data provide evidence that PKGs are essential mediators of the antifibrotic effects of sGC stimulators through interfering with non-canonical TGFbeta signalling. TGFbeta1 promotes its profibrotic effects through inhibition of sGC-cGMP-PKG signalling, sGC stimulation exerts its antifibrotic effects by inhibition of TGFbeta1-induced ERK phosphorylation.
Inhibition of PDE2 reverses beta amyloid induced memory impairment through regulation of PKA/PKG-dependent neuro-inflammatory and apoptotic pathways.[Pubmed:28935920]
Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 21;7(1):12044.
Beta amyloid peptides (Abeta) are known risk factors involved in cognitive impairment, neuroinflammatory and apoptotic processes in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Phosphodiesterase 2 (PDE2) inhibitors increase the intracellular cAMP and/or cGMP activities, which may ameliorate cognitive deficits associated with AD. However, it remains unclear whether PDE2 mediated neuroapoptotic and neuroinflammatory events, as well as cognitive performance in AD are related to cAMP/cGMP-dependent pathways. The present study investigated how the selective PDE2 inhibitor BAY60-7550 (BAY) affected Abeta-induced learning and memory impairment in two classic rodent models. IL-22 and IL-17, Bax and Bcl-2, PKA/PKG and the brain derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) levels in hippocampus and cortex were detected with immunoblotting assay. The results showed that BAY reversed Abeta-induced cognitive impairment as shown in the water maze test and step-down test. Moreover, BAY treatment reversed the Abeta-induced changes in IL-22 and IL-17 and the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2. Changes in cAMP/cGMP levels, PKA/PKG and BDNF expression were also prevented by BAY. These effects of BAY on memory performance and related neurochemical changes were partially blocked by the PKG inhibitor KT 5823. These findings indicated that the protective effects of BAY against Abeta-induced memory deficits might involve the regulation of neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptotic events.
Possible mechanisms involved in the vasorelaxant effect produced by clobenzorex in aortic segments of rats.[Pubmed:28793049]
Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017 Aug 7;50(9):e5765.
Clobenzorex is a metabolic precursor of amphetamine indicated for the treatment of obesity. Amphetamines have been involved with cardiovascular side effects such as hypertension and pulmonary arterial hypertension. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether the direct application of 10-9-10-5 M clobenzorex on isolated phenylephrine-precontracted rat aortic rings produces vascular effects, and if so, what mechanisms may be involved. Clobenzorex produced an immediate concentration-dependent vasorelaxant effect at the higher concentrations (10-7.5-10-5 M). The present outcome was not modified by 10-6 M atropine (an antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors), 3.1x10-7 M glibenclamide (an ATP-sensitive K+ channel blocker), 10-3 M 4-aminopyridine (4-AP; a voltage-activated K+ channel blocker), 10-5 M indomethacin (a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor), 10-5 M clotrimazole (a cytochrome P450 inhibitor) or 10-5 M cycloheximide (a general protein synthesis inhibitor). Contrarily, the clobenzorex-induced vasorelaxation was significantly attenuated (P<0.05) by 10-5 M L-NAME (a direct inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase), 10-7 M ODQ (an inhibitor of nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase), 10-6 M KT 5823 (an inhibitor of protein kinase G), 10-2 M TEA (a Ca2+-activated K+ channel blocker and non-specific voltage-activated K+ channel blocker) and 10-7 M apamin plus 10-7 M charybdotoxin (blockers of small- and large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels, respectively), and was blocked by 8x10-2 M potassium (a high concentration) and removal of the vascular endothelium. These results suggest that the direct vasorelaxant effect by clobenzorex on phenylephrine-precontracted rat aortic rings involved stimulation of the NO/cGMP/PKG/Ca2+-activated K+ channel pathway.
The bradykinin-cGMP-PKG pathway augments insulin sensitivity via upregulation of MAPK phosphatase-5 and inhibition of JNK.[Pubmed:28679626]
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Sep 1;313(3):E321-E334.
Bradykinin (BK) promotes insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake in adipocytes and other cell types. We demonstrated that in rat adipocytes BK enhances insulin-stimulated glucose transport via endothelial nitric oxide synthase, nitric oxide (NO) generation, and decreased activity of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) JNK (c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase). In endothelial cells, NO increases soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) activity, which, in turn, activates protein kinase G (PKG) by increasing cGMP levels. In this study, we investigated whether BK acts via the sGC-cGMP-PKG pathway to inhibit the negative effects of JNK on insulin signaling and glucose uptake in rat adipocytes. BK augmented cGMP concentrations. The BK-induced enhancement of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake was mimicked by the sGC activator YC-1 and a cell-permeable cGMP analog, CPT-cGMP, and inhibited by the sGC inhibitor ODQ and the PKG inhibitor KT 5823. Transfection of dominant-negative PKG reduced the BK augmentation of insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation. The activation of JNK and ERK1/2 by insulin was attenuated by BK, which was mediated by the sGC-cGMP-PKG pathway. Whereas insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of upstream activators of JNK and ERK, i.e., MKK4 and MEK1/2, was unaffected, BK augmented insulin-mediated induction of MKP-5 mRNA and protein levels. Furthermore, zaprinast, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, enhanced cGMP and MKP-5 and prolonged the action of BK. These data indicate that BK enhances insulin action by inhibition of negative feedback by JNK and ERK via upregulation of MKP-5, mediated by the sGC-cGMP-PKG signaling pathway.
Functional analysis of cGMP-dependent protein kinases I and II as mediators of NO/cGMP effects.[Pubmed:9721015]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1998 Jul;358(1):134-9.
NO and cGMP have emerged as important signal transduction mediators of the effects of certain hormones, inter-/intracellular signals, toxins and drugs. However, a major challenge is to define relevant criteria for determining which of the many NO and/or cGMP effects are dependent on cGMP-dependent protein kinases (cGKs). Important criteria include that: (1) the cell types/tissues investigated contain at least one form of cGK which is activated by the cGMP-elevating agent in the intact cell system; (2) specific activators/inhibitors of cGKs mimic/block the effects of cGMP-elevating agents in the intact cell system; and (3) the cGMP effect is absent or blunted in cGK-deficient systems, or can be reconstituted by the introduction of active cGKs. Previously, analysis of cGK activity in intact cells has been very difficult. However, the analysis of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) phosphorylation by polyclonal antibodies and newly developed monoclonal antibodies, each of which specifically recognize different phosphorylation sites, allows the quantitative measurement of cGK activity in intact cells. With the use of these methods, the properties of certain cGK mutants, cGK activators (cGMP, 8-Br-cGMP, 8-pCPT-cGMP) as well as various "specific cGK inhibitors" (KT 5823, Rp-8Br-PET-cGMPS, Rp-8-pCPT-cGMPS, H8 and H89) were investigated. Although these "specific cGK inhibitors" have been widely used to establish or rule out functional roles of cGKs, very few studies have actually addressed the efficiency/specificity of such compounds in intact cells. Our results demonstrate that these inhibitors are useful tools only when used in combination with other experimental approaches and biochemical evidence.
Interaction of cA-kinase and cG-kinase in mediating relaxation of dispersed smooth muscle cells.[Pubmed:7840145]
Am J Physiol. 1995 Jan;268(1 Pt 1):C171-80.
The signaling pathways mediating relaxation by vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), peptide histidine-isoleucine amide (PHI), isoproterenol (ISO), and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) were examined in dispersed rabbit and guinea pig gastric muscle cells. In rabbit muscle cells, SNP stimulated only guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) and cGMP-dependent protein kinase (cG-kinase) activity; VIP stimulated adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) and cGMP, and both cG-kinase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (cA-kinase) activities; PHI and ISO stimulated only cAMP and cA-kinase activity, and at higher concentrations, cross-activated cG-kinase. All four agents elicited concentration-dependent relaxation. N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89; 1 microM) selectively inhibited cA-kinase activity and abolished relaxation when only cA-kinase was elevated. 8R,9S, 11S-(-)-9-methoxy-carbamyl-8-methyl-2,3,9,10-tetrahydro-8,11-epoxy- 1H,8H,11H-2,7b,11a-trizadibenzo-(a,g)-cy-cloocta-(c,d,e)- trinden-1-one (KT-5823; 1 microM) selectively inhibited cG-kinase activity and abolished relaxation when only cG-kinase was elevated. When both kinases were elevated, H-89 and KT-5823 partially inhibited relaxation and abolished relaxation in combination. In permeabilized guinea pig and rabbit muscle cells, all agents elicited relaxation and inhibited inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3)-induced Ca2+ release. Both functions were inhibited in parallel fashion by protein kinase inhibitor PKI(6-22) and by KT-5823. We conclude that cA-kinase and cG-kinase act separately and in concert to inhibit IP3-dependent Ca2+ release and induce relaxation.
Multiple kinase arrest points in the G1 phase of nontransformed mammalian cells are absent in transformed cells.[Pubmed:1528872]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8626-30.
We have shown that nontransformed mammalian cells arrest early in the G1 phase of the cell cycle when treated with exceedingly low concentrations of the nonspecific kinase inhibitor staurosporine, whereas transformed cells continue to progress through the cell cycle. We have now treated normal or transformed human skin fibroblasts with four other kinase inhibitors. Three of these inhibitors are highly specific: KT5720 inhibits cAMP-dependent protein kinase, KT5823 inhibits cGMP-dependent protein kinase, and KT5926 inhibits myosin light-chain kinase. The fourth inhibitor K252b has a moderate specificity for protein kinase C but also inhibits the three kinases just mentioned. We have found that these inhibitors reversibly arrest normal human skin fibroblasts at different times in the G1 phase but do not affect the cell cycle progression of transformed cells. The times of arrest within the G1 phase can be divided into two categories. Two of the inhibitors, KT5926 and K252b, act at an early time that is approximately 4 h after the transition from G0 to G1. The cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitors KT5720 and KT5823 arrest cells at a later time that is approximately 6 h after the G0/G1 boundary. These data indicate that there are multiple kinase-mediated phosphorylations of different substrates that are essential for the progression of normal cells, but not transformed cells, through the G1 phase. These inhibitors provide us with a set of biochemical probes that should be invaluable in the study of the function of kinases during G1 phase progression of normal cells.


