Echistatin, α1 isoformαVβ3 and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (integrin αIIbβ3) inhibitor CAS# 154303-05-6 |
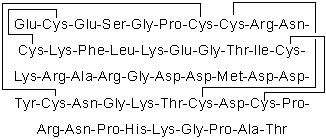
- Ruscogenin
Catalog No.:BCN6287
CAS No.:472-11-7
- Pectolinarigenin
Catalog No.:BCN5813
CAS No.:520-12-7
- Dauricine
Catalog No.:BCN4977
CAS No.:524-17-4
- Oroxin A
Catalog No.:BCN1202
CAS No.:57396-78-8
- Triptophenolide
Catalog No.:BCN2546
CAS No.:74285-86-2
- Wilforlide A
Catalog No.:BCN4383
CAS No.:84104-71-2
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure
3D structure
| Cas No. | 154303-05-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 159296 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C217H341N71O74S9 | M.Wt | 5417.1 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in water | ||
| Sequence | ECESGPCCRNCKFLKEGTICKRARGDDMDD (Modifications: Disulfide bridge between 2 - 11, 7 - 32, 8 - 37, 20 - 39) | ||
| Chemical Name | [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-2-(phosphonooxymethyl)oxolan-3-yl] dihydrogen phosphate | ||
| SMILES | C1=NC2=C(C(=N1)N)N=CN2C3C(C(C(O3)COP(=O)(O)O)OP(=O)(O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WHTCPDAXWFLDIH-KQYNXXCUSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H15N5O10P2/c11-8-5-9(13-2-12-8)15(3-14-5)10-6(16)7(25-27(20,21)22)4(24-10)1-23-26(17,18)19/h2-4,6-7,10,16H,1H2,(H2,11,12,13)(H2,17,18,19)(H2,20,21,22)/t4-,6-,7-,10-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent irreversible αVβ3 integrin antagonist (Ki = 0.27 nM). Disrupts attachment of osteoclasts to bone and inhibits bone reabsorption (IC50 = 0.1 nM). Prevents ADP-induced platelet aggregation via inhibition of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GpIIb/IIIa, αIIbβ3) receptors (IC50 = 30 nM) in vitro. |

Echistatin, α1 isoform Dilution Calculator

Echistatin, α1 isoform Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- CB-5083
Catalog No.:BCC6528
CAS No.:1542705-92-9
- Ampalex
Catalog No.:BCC1359
CAS No.:154235-83-3
- Abiraterone
Catalog No.:BCC2259
CAS No.:154229-19-3
- Abiraterone Acotate
Catalog No.:BCN2184
CAS No.:154229-18-2
- Clasto-Lactacystin β-lactone
Catalog No.:BCC1224
CAS No.:154226-60-5
- N-[2-Isopropylthiazol-4-ylmethyl(methyl)carbamoyl]-L-valine
Catalog No.:BCC9067
CAS No.:154212-61-0
- YM 90K hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7455
CAS No.:154164-30-4
- DMAB-anabaseine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7301
CAS No.:154149-38-9
- PD 144418 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7429
CAS No.:154130-99-1
- 4-Hydroxy-2-(3-methoxypropyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-thieno[3,2-e][1,2]thiazine-6-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
Catalog No.:BCC8707
CAS No.:154127-42-1
- 2-(3-Methoxypropyl)-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-thieno[3,2-e][1,2]thiazine-6-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
Catalog No.:BCC8480
CAS No.:154127-41-0
- ((2-cyclopropyl-4-(4-fluorophenyl)quinolin-3-yl)methyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide
Catalog No.:BCC8373
CAS No.:154057-58-6
- Capecitabine
Catalog No.:BCN2168
CAS No.:154361-50-9
- Methyl 3-O-feruloylquinate
Catalog No.:BCN3403
CAS No.:154418-15-2
- 5,5'-Dimethoxylariciresinol 4-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1556
CAS No.:154418-16-3
- Zinc protoporphyrin IX
Catalog No.:BCC6775
CAS No.:15442-64-5
- Lysicamine
Catalog No.:BCN6523
CAS No.:15444-20-9
- Pramanicin
Catalog No.:BCN1853
CAS No.:154445-05-3
- Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3040
CAS No.:154445-77-9
- NU 7026
Catalog No.:BCC3933
CAS No.:154447-35-5
- LY 294002
Catalog No.:BCC3659
CAS No.:154447-36-6
- LY 303511
Catalog No.:BCC1715
CAS No.:154447-38-8
- Methyl 5-O-feruloylquinate
Catalog No.:BCN3402
CAS No.:154461-64-0
- Sinapaldehyde glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1689
CAS No.:154461-65-1
Biochemical characterization of the binding of echistatin to integrin alphavbeta3 receptor.[Pubmed:9353406]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Nov;283(2):843-53.
Echistatin is a 49-amino-acid peptide belonging to the family of disintegrins that are derived from snake venoms and are potent inhibitors of platelet aggregation and cell adhesion. Integrin alphavbeta3 receptor plays a critical role in several physiological processes such as tumor-induced angiogenesis, tumor cell metastasis, osteoporosis and wound repair. In this study, we have characterized the binding of echistatin to purified integrin alphavbeta3 receptor and the form expressed on human embryonic kidney 293 cells. We show that both purified and membrane-bound integrin alphavbeta3 binds to echistatin with a high affinity, which can be competed efficiently by linear and cyclic peptides containing the RGD sequence. Previous studies have shown that alphavbeta3 binds to vitronectin in a nondissociable manner, whereas an RGD-containing peptide derived from vitronectin binds in a dissociable manner with a Kd of 9.4 x 10(-7) M. Our studies indicate that radiolabeled echistatin binds to alphavbeta3 in a nondissociable manner, similar to native echistatin. However, echistatin does not support the adhesion of 293 cells expressing alphavbeta3 receptor because of poor binding to plastic dishes and is a potent antagonist of the adhesion of these cells to vitronectin. These studies demonstrate that echistatin binding to alphavbeta3 is of high affinity and irreversible similar to vitronectin and provides an alternate ligand for high-throughput screening for alphavbeta3 antagonists.
Inhibition of platelet adhesion to surfaces of extracorporeal circuits by disintegrins. RGD-containing peptides from viper venoms.[Pubmed:2364514]
Circulation. 1990 Jul;82(1):261-73.
Previous studies indicate that exposure of fibrinogen receptors associated with glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex contributes to platelet loss during cardiopulmonary bypass. Recently, we isolated a number of RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp)-containing, low molecular weight, cysteine-rich peptides from viper venoms. These peptides, which we propose to call "disintegrins," block platelet-fibrinogen interaction and platelet aggregation. We compared the effect of RGDS (Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser) and four disintegrins (echistatin, flavoridin, albolabrin, and bitistatin) on platelet behavior in a membrane oxygenator. During simulated extracorporeal circulation for 2 hours, platelet count decreased to about 30% of initial values. Addition of echistatin (60-200 nM), albolabrin (60-200 nM), bitistatin (60 nM), and flavoridin (45 nM) significantly inhibited platelet loss in the circuit. RGDS (33 microM) did not show any significant inhibitory effect. ADP-induced platelet aggregation was inhibited in samples of platelet-rich plasma taken from the circuits containing disintegrins. However, echistatin appeared to be a more potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation, whereas albolabrin and flavoridin interfered more selectively with platelet loss from the circuit. Echistatin prevented the accumulation of glycoprotein IIIa on the surface of the circuit. Echistatin (60-200 nM), flavoridin (45 nM), bitistatin (60 nM), and albolabrin (200 nM) significantly inhibited the loss of beta-thromboglobulin from platelets into circulating plasma. Electron microscopy studies demonstrated shape change but not degranulation in platelets circulating in the presence of 200 nM echistatin. On the other hand, this peptide (up to 1,000 nM) did not prevent loss of alpha granules and beta-thromboglobulin from thrombin-stimulated platelets, although it prevented their aggregation. In conclusion, disintegrins protect platelets in the circuit by preventing their adhesion to surfaces and, therefore, preventing fragmentation of adhered platelets under the shear stress of flowing blood. This study indicates that disintegrins may be potential candidates for platelet protection during cardiopulmonary bypass.
Echistatin is a potent inhibitor of bone resorption in culture.[Pubmed:2211834]
J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1713-23.
The venom protein, s-echistatin, originally derived from the saw-scaled viper Echis carinatus, was found to be a potent inhibitor of bone resorption by isolated osteoclasts. This Arg24-Gly25-Asp26-(RGD)-containing protein inhibited the excavation of bone slices by rat osteoclasts (IC50 = 0.1 nM). It also inhibited the release of [3H]proline from labeled bone particles by chicken osteoclasts (IC50 = 100 nM). By comparison, the tetrapeptide Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (RGDS) inhibited resorption by rat or chicken osteoclasts with an IC50 of 0.1 mM while ala24-echistatin was inactive. Video microscopy showed that rat osteoclast attachment to substrate was more sensitive to s-echistatin than was the attachment of mononuclear cells or chicken osteoclasts. The difference in sensitivity of rat and chicken osteoclasts to s-echistatin may be due to differences between receptors on rat and chicken osteoclasts for s-echistatin. Antibody localization of echistatin on these cells showed much greater echistatin binding to rat osteoclasts than to chicken osteoclasts. Laser scanning confocal microscopy after immunohistochemical staining showed that s-echistatin binds to osteoclasts, that s-echistatin receptors are most abundant at the osteoclast/glass interface, and that s-echistatin colocalizes with vinculin. Confocal interference reflection microscopy of osteoclasts incubated with s-echistatin, demonstrated colocalization of s-echistatin with the outer edges of clusters of grey contacts at the tips of some lamellipodia. Identification of the echistatin receptor as an integrin was confirmed by colocalization of echistatin fluorescence with staining for an alpha-like subunit. Attachment of bone particles labeled with [3H]proline to chicken osteoclasts confirmed that the mechanism of action of echistatin was to inhibit osteoclast binding to bone presumably by disrupting adhesion structures. These data demonstrate that osteoclasts bind to bone via an RGD-sequence as an obligatory step in bone resorption, that this RGD-binding integrin is at adhesion structures, and that it colocalizes with vinculin and has an alpha-like subunit.


