DeferasiroxOral iron chelator CAS# 201530-41-8 |
- LY2835219
Catalog No.:BCC1113
CAS No.:1231930-82-7
- Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202)
Catalog No.:BCC1105
CAS No.:186692-46-6
- Nu 6027
Catalog No.:BCC1154
CAS No.:220036-08-8
- SNS-032 (BMS-387032)
Catalog No.:BCC1152
CAS No.:345627-80-7
- AT7519 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1376
CAS No.:902135-91-5
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure
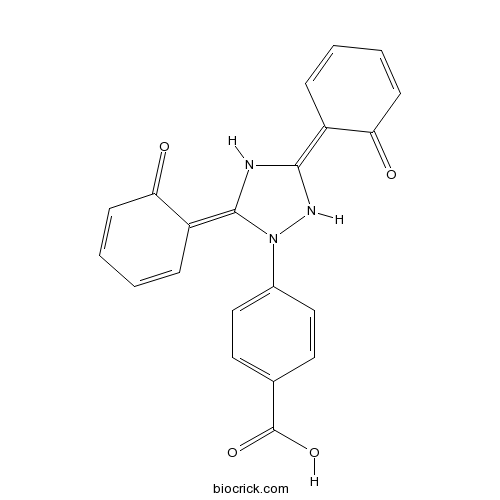
3D structure
| Cas No. | 201530-41-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5493381 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H15N3O4 | M.Wt | 373.36 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (267.84 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-[(3Z,5E)-3,5-bis(6-oxocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-ylidene)-1,2,4-triazolidin-1-yl]benzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C2NC(=C3C=CC=CC3=O)N(N2)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)O)C(=O)C=C1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FMSOAWSKCWYLBB-VBGLAJCLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H15N3O4/c25-17-7-3-1-5-15(17)19-22-20(16-6-2-4-8-18(16)26)24(23-19)14-11-9-13(10-12-14)21(27)28/h1-12,22-23H,(H,27,28)/b19-15-,20-16+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Deferasirox is an orally available iron chelator used for the management of transfusional iron overload.In Vitro:In LX-2 cells treated with 50 μM deferasirox for 12 h, α1(I)procollagen expression is decreased by 25%, with maximal reductions (10-fold) seen following 24-120 h of treatment. Similarly, α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA) expression is significantly lower[1]. Deferasirox had anti-proliferative effects on HL-60 or KG-1 myeloid leukemia cell lines at a concentration as low as 5 μM . The cytotoxicity is both dose and time dependent[2]. The viability of both EL4 cells and L1210 cells incubated with deferasirox decrease in a concentration-dependent manner[3].In Vivo:The tumor is significantly smaller in the SIO mice treated with deferasirox compared with control. Mice treated with DFX showed longer survival than the other groups. Deferasirox has a survival benefit for SIO leukemia murine model in terms of iron chelation and antileukemic therapy[3]. References: | |||||

Deferasirox Dilution Calculator

Deferasirox Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6784 mL | 13.3919 mL | 26.7838 mL | 53.5676 mL | 66.9595 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5357 mL | 2.6784 mL | 5.3568 mL | 10.7135 mL | 13.3919 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2678 mL | 1.3392 mL | 2.6784 mL | 5.3568 mL | 6.696 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0536 mL | 0.2678 mL | 0.5357 mL | 1.0714 mL | 1.3392 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0268 mL | 0.1339 mL | 0.2678 mL | 0.5357 mL | 0.6696 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Deferasirox is an iron chelator [1].
Iron chelate is a soluble complex of iron, sodium and a chelating agent and used to make the iron soluble in water. Iron chelators were initially developed for the treatment of iron overload for clinical use [1].
Deferasirox is an orally iron chelator used for the treatment of iron-overload disease. In DMS-53 lung carcinoma and SK-N-MC neuroepithelioma cell lines, deferasirox inhibited cells proliferation. Deferasirox inhibited iron uptake from human transferrin and mobilized cellular 59Fe [1]. In two oesophageal adenocarcinoma cell lines OE33 and OE19, deferasirox with a standard chemotherapeutic agent inhibited cellular viability and proliferation [2].
In nude mice bearing DMS-53 lung carcinoma xenografts, deferasirox inhibited tumor growth. Also, deferasirox increased cleaved caspase-3, cleaved poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1, the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21CIP1/WAF1 and the expression of the metastasis suppressor protein N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1 while reducing cyclin D1, which suggested deferasirox is an effective antitumor agent [1]. In human xenograft models, deferasirox significantly inhibited tumour growth, which was associated with the decrease in iron levels [2].
References:
[1]. Lui GY, Obeidy P, Ford SJ, et al. The iron chelator, deferasirox, as a novel strategy for cancer treatment: oral activity against human lung tumor xenografts and molecular mechanism of action. Mol Pharmacol, 2013, 83(1): 179-190.
[2]. Ford SJ, Obeidy P, Lovejoy DB, et al. Deferasirox (ICL670A) effectively inhibits oesophageal cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol, 2013, 168(6): 1316-1328.
- Dilazep dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6660
CAS No.:20153-98-4
- Fmoc-Asn-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2586
CAS No.:201484-12-0
- Boc-Dap(Boc)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC2664
CAS No.:201472-68-6
- PKI 14-22 amide, myristoylated
Catalog No.:BCC8087
CAS No.:201422-03-9
- Talarozole
Catalog No.:BCC1980
CAS No.:201410-53-9
- Rutundic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5370
CAS No.:20137-37-5
- Tenofovir disoproxil
Catalog No.:BCN2178
CAS No.:201341-05-1
- Fmoc-D-Tyr(Me)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3269
CAS No.:201335-88-8
- 1-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)propane-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1507
CAS No.:20133-19-1
- H-Thr-OBzl.oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC3103
CAS No.:201274-07-9
- Diosmetin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN5328
CAS No.:20126-59-4
- 3-AQC
Catalog No.:BCC6743
CAS No.:201216-42-4
- Fmoc-Pen(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3306
CAS No.:201531-88-6
- Fmoc-D-Pen(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3309
CAS No.:201532-01-6
- Triptocallic acid D
Catalog No.:BCN4882
CAS No.:201534-09-0
- Triptocalline A
Catalog No.:BCN6783
CAS No.:201534-10-3
- (R)-3,4-DCPG
Catalog No.:BCC7046
CAS No.:201730-10-1
- (S)-3,4-DCPG
Catalog No.:BCC7012
CAS No.:201730-11-2
- Isodiospyrin
Catalog No.:BCN4883
CAS No.:20175-84-2
- Ac-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3005
CAS No.:2018-61-3
- Z-Leu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2766
CAS No.:2018-66-8
- Tenuifolin
Catalog No.:BCN5005
CAS No.:20183-47-5
- Pisatin
Catalog No.:BCN3912
CAS No.:20186-22-5
- Magnolioside
Catalog No.:BCN2832
CAS No.:20186-29-2
Comparison of deferasirox and deferoxamine effects on iron overload and immunological changes in patients with blood transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia.[Pubmed:28316434]
Asian J Transfus Sci. 2017 Jan-Jun;11(1):13-17.
INTRODUCTION: Beta-thalassemias are a cluster of inherited (autosomal recessive) hematological disorders prevalent in the Mediterranean area due to defects in synthesis of beta chains of hemoglobin. The aim of present study was to compare the effects of Deferasirox and deferoxamine on iron overload and immunological changes in patients with blood transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia major and intermedia. PATIENTS AND METHODS: This study involved 64 patients with known cases of beta-thalassemia major or intermedia that has been treated with blood transfusion and iron chelators. Serum ferritin, serum iron, serum total iron binding, unsaturated iron-binding capacity (UIBC), and immunological parameters were assessed in deferoxamine and Deferasirox-treated patients. RESULTS: In deferoxamine-treated patients, serum ferritin levels were high (8160.33 +/- 233.75 ng/dL) compared to Deferasirox-treated patients (3000.62 +/- 188.23 ng/dL; P < 0.0001), also there were significant differences in serum iron, total iron-binding capacity and UIBC (P < 0.0001) in Deferasirox-treated patients compared to deferoxamine-treated patients. Immunological changes between two treated groups showed insignificant differences in levels of complements (C3 and C4) and immunoglobulin levels (IgM, IgG, and IgA) P > 0.05. CONCLUSION: This study indicated that Deferasirox is more effective than deferoxamine regarding the iron overload but not in the immunological profile in patients with blood transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia.
Long-term safety and efficacy of deferasirox in young pediatric patients with transfusional hemosiderosis: Results from a 5-year observational study (ENTRUST).[Pubmed:28296163]
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017 Sep;64(9).
BACKGROUND: Children with red blood cell disorders may receive regular transfusions from an early age and consequently accumulate iron. Adequate iron chelation therapy can prevent organ damage and delayed growth/development. Deferasirox is indicated for treatment of pediatric patients with chronic iron overload due to transfusional hemosiderosis; however, fewer than 10% of patients in the registration studies were aged 2 to less than 6 years. PROCEDURE: Deferasirox, a once-daily oral iron chelator, was evaluated in young pediatric patients with transfusional hemosiderosis during the observational 5-year ENTRUST study. Patients aged 2 to less than 6 years at enrollment received Deferasirox according to local prescribing information, with the primary objective of evaluating safety, specifically renal and hepatic function. Serum ferritin was observed as a surrogate efficacy parameter. RESULTS: In total, 267 patients (mean age 3.2 years) predominantly with beta-thalassemia (n = 176, 65.9%) were enrolled. Mean +/- standard deviation Deferasirox dose was 25.8 +/- 6.5 mg/kg per day over a median of 59.9 months. A total of 145 patients (54.3%) completed 5 years' treatment. The proportion of patients with two or more consecutive postbaseline measurements (>/=7 days apart) of serum creatinine higher than age-adjusted upper limit of normal (ULN) and alanine aminotransferase more than five times the ULN was 4.4% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.1-7.9) and 4.0% (95% CI: 1.8-7.4), respectively. Median serum ferritin decreased from 1,702 ng/ml at baseline to 1,127 ng/ml at 5 years. There were no new safety signals. CONCLUSIONS: Safety and efficacy of Deferasirox in young pediatric patients in this long-term, observational study in everyday clinical practice were consistent with the known Deferasirox profile.
Deferasirox pharmacogenetic influence on pharmacokinetic, efficacy and toxicity in a cohort of pediatric patients.[Pubmed:28346059]
Pharmacogenomics. 2017 Apr;18(6):539-554.
AIM: We aimed to evaluate the influence of genetic polymorphisms involved in Deferasirox metabolism and transport on its pharmacokinetics and treatment toxicity, in a cohort of beta-thalassaemic children. PATIENTS & METHODS: Drug plasma concentrations were measured by a HPLC-UV method. Allelic discrimination for UGT1A1, UGT1A3, CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP2D6, MRP2 and BCRP1 polymorphisms was performed by real-time PCR. RESULTS: CYP1A1 rs2606345AA influenced Ctrough (p = 0.001) and t1/2 (p = 0.042), CYP1A1 rs4646903TC/CC (p = 0.005) and BCRP1 rs2231142GA/AA (p = 0.005) influenced Tmax and CYP2D6 rs1135840CG/GG influenced Cmax (p = 0.044). UGT1A1 rs887829TT (p = 0.002) and CYP1A2 rs762551CC (p = 0.019) resulted as predictive factor of ferritin levels and CYP1A1 rs2606345CA/AA (p = 0.021) and CYP1A2 rs762551AC/CC (p = 0.027) of liver iron concentration. CONCLUSION: Our data suggest the usefulness of Deferasirox pharmacogenetics in pediatric treatment optimization.


