BKM120Inhibitor of pan-Class I PI3K CAS# 944396-07-0 |
- A66
Catalog No.:BCC3715
CAS No.:1166227-08-2
- PI3k-delta inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC1861
CAS No.:1332075-63-4
- PIK-75
Catalog No.:BCC1163
CAS No.:372196-77-5
- CAL-101 (Idelalisib, GS-1101)
Catalog No.:BCC1270
CAS No.:870281-82-6
- PIK-294
Catalog No.:BCC4995
CAS No.:900185-02-6
- PI-3065
Catalog No.:BCC5379
CAS No.:955977-50-1
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure
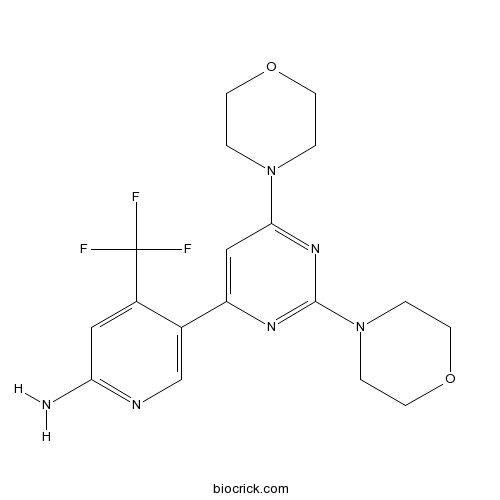
3D structure
| Cas No. | 944396-07-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16654980 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H21F3N6O2 | M.Wt | 410.39 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Buparlisib; BKM120 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (243.67 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 5-(2,6-dimorpholin-4-ylpyrimidin-4-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-amine | ||
| SMILES | C1COCCN1C2=NC(=NC(=C2)C3=CN=C(C=C3C(F)(F)F)N)N4CCOCC4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CWHUFRVAEUJCEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H21F3N6O2/c19-18(20,21)13-9-15(22)23-11-12(13)14-10-16(26-1-5-28-6-2-26)25-17(24-14)27-3-7-29-8-4-27/h9-11H,1-8H2,(H2,22,23) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | BKM120(NVP-BKM120, Buparlisib) is a selective PI3K inhibitor of p110α/β/δ/γ with IC50 of 52 nM/166 nM/116 nM/262 nM, respectively. | ||||||
| Targets | p110α | p110β | p110δ | p110γ | |||
| IC50 | 52-99 nM | 166 nM | 116 nM | 262 nM | |||
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
| Cell lines | MM cell lines (RPMI-8226, OPM1, MM.1S, OPM2 and H929) |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | IC50: 0.5-1μM, 48 hours |
| Applications | The effect of the pan-PI3K inhibition, mediated by increased concentrations of buparlisib on MM cell survival was tested by MTT assay. Buparlisib induced cell toxicity after 48 hr treatment in all MM cell lines tested; with an IC50 between 0.5 and 1 μM. In addition, buparlisib decreased the activation of signaling proteins downstream of PI3K including pAkt, pS6R, pP70S6K, and p-mTOR in MM.1S cells in a dose dependent manner. |
| Animal experiment: [1] | |
| Animal models | Female SCID-Bg mice injected with MM.1S-GFP+/luc+ cells |
| Dosage form | Oral administration, 50 mg/kg, once a day for 5 weeks |
| Application | Treatment of mice with buparlisib significantly decreased the rate of tumor progression compared with the vehicle treated group, as shown in representative images of the BLI and quantification of the BLI. These results were further confirmed by fluorescence microscopy, showing that the number of MM.1S- GFP+/luc+ cells present in the BM of mice treated with buparlisib decreased significantly compared with those present in the BM of mice treated with vehicle, as shown in representative images of immunofluorescence. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1] Sahin I, Azab F, Mishima Y, Moschetta M, Tsang B, Glavey SV, Manier S, Zhang Y, Sacco A, Roccaro AM, Azab AK, Ghobrial IM. Targeting survival and cell trafficking in multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia using pan-class I PI3K inhibitor, buparlisib. Am J Hematol. 2014 Jul 24. | |

BKM120 Dilution Calculator

BKM120 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4367 mL | 12.1835 mL | 24.3671 mL | 48.7341 mL | 60.9177 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4873 mL | 2.4367 mL | 4.8734 mL | 9.7468 mL | 12.1835 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2437 mL | 1.2184 mL | 2.4367 mL | 4.8734 mL | 6.0918 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0487 mL | 0.2437 mL | 0.4873 mL | 0.9747 mL | 1.2184 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0244 mL | 0.1218 mL | 0.2437 mL | 0.4873 mL | 0.6092 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
NVP-BKM120, a class I PI3K inhibitor, concentration-dependently inhibited the growth of H1975 cells, which increased the proportion of H1975 cells in G0-G1 phase at 1 umol/L and promoted apoptosis at 2 umol/L. Moreover, NVP-BKM120 overcame acquired gefitinib resistance in H1975 cells though down-regulation of phosphorylated protein in PI3K/AKT signal pathways, including Akt, S6 and 4E-BP1.
Abstract
NVP-BKM120 is an orally-available inhibitor of class I phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase that promoted mitochondrial apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia primary cells through blocking phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling, decreasing Akt and FoxO3a phosphorylation and inducing Bim expression. NVP-BKM120 disrupts phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia primary cells by inhibiting microenvironment signals, including B-cell receptor- and stroma-dependent Akt pathway activation, B-cell receptor stimulation induced chemokines secretion and CXCL12 triggered cell chemotaxis and actin polymerization upon CXCR4.
Abstract
Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mammalian target of mTOR signaling pathway by NVP-BKM120, a pan-class I PI3K inhibitot, in DLBCL cells results in decreased cell proliferation, increased apoptotic cell death, increased expression of Puma and Bim and down-regulation of Bcl-xL and Mcl-1.
Abstract
BKM120, a PI3 kinase inhibitor, induced apoptosis and enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human lung cancer cells through facilitating Mcl-1 degradation involving a GSK3/FBXW7-dependent mechanism.
Abstract
BKM120, an orally-available pan-PI3K inhibitor, has the potential to treat T-ALL for its abilities to induce G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis T-ALL cells and patient T lymphoblasts, significantly delay tumor growth in a subcutaneous xenotransplant model of human T-ALL and synergize with chemotherapeutic agents for treating T-ALL patients.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
BKM120(NVP-BKM120, Buparlisib) is a selective PI3K inhibitor of p110α/β/δ/γ with IC50 of 52 nM/166 nM/116 nM/262 nM, respectively.
The intracellular phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase(PI3K) pathway regulates cellular functions incuding cell proliferation, growth, survival, apoptosis, protein synthesis, and glucose metabolism. BKM120, a biologic characterization of the 2-morpholino pyrimidine derivative, is a pan-PI3K inhibitor.
In vitro: NVP-BKM120 inhibits all four class I PI3K isoforms in biochemical assays with at least 50-fold selectivity against other protein kinases. NVP-BKM120 is also active against the most common somatic PI3Ka mutations but does not significantly inhibit the related class III (Vps34) and class IV (mTOR, DNA-PK) PI3K kinases. Consistent with its mechanism of action, NVP-BKM120 decreases the cellular p-Akt levels in mechanistic models and relevant tumor cell lines. In a panel of 353 cell lines test, NVP-BKM120 showed preferential inhibition of tumor cells with PIK3CA mutations, rather than either KRAS or PTEN mutant models [1].
In vivo: NVP-BKM120 shows dose-dependent in vivo pharmacodynamic activity as measured by significant inhibition of p-Akt and tumor growth inhibition in mechanistic xenograft models. In addition, NVP-BKM120 behaves synergistically when combined with either targeted agents such as MEK or HER2 inhibitors or with cytotoxic agents such as docetaxel or temozolomide [1].
Clinical trial: A phase I dose-escalation study investigated the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD), safety, preliminary activity, PK, and PD of BKM120. This study demonstrates feasibility and proof-of-concept of class I PI3K inhibition in cancer patients. BKM120 at the MTD of 100 mg d-1 is safe and well tolerated, with a good PK profile, clear evidence of target inhibition, and preliminary antitumor activity [2].
References:
[1] Maira SM, Pecchi S, Huang A, Burger M, Knapp M, Sterker D, Schnell C, Guthy D, Nagel T, Wiesmann M, Brachmann S, Fritsch C, Dorsch M, Chène P, Shoemaker K, De Pover A, Menezes D, Martiny-Baron G, Fabbro D, Wilson CJ, Schlegel R, Hofmann F, García-Echeverría C, Sellers WR, Voliva CF. Identification and characterization of NVP-BKM120, an orally available pan-class I PI3-kinase inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(2):317-28.
[2] Bendell JC, Rodon J, Burris HA, de Jonge M, Verweij J, Birle D, Demanse D, De Buck SS, Ru QC, Peters M, Goldbrunner M, Baselga J. Phase I, dose-escalation study of BKM120, an oral pan-Class I PI3K inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(3):282-90.
- JNJ 28871063 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7662
CAS No.:944342-90-9
- QS 11
Catalog No.:BCC7648
CAS No.:944328-88-5
- A-803467
Catalog No.:BCC5075
CAS No.:944261-79-4
- MJ 15
Catalog No.:BCC7852
CAS No.:944154-76-1
- Peficitinb (ASP015K, JNJ-54781532)
Catalog No.:BCC6503
CAS No.:944118-01-8
- PG 106
Catalog No.:BCC6330
CAS No.:944111-22-2
- Isomartynoside
Catalog No.:BCN4497
CAS No.:94410-22-7
- Tetrachlorohydroquinone dimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN1301
CAS No.:944-78-5
- Dimethylmatairesinol
Catalog No.:BCN4496
CAS No.:943989-68-2
- BMS-303141
Catalog No.:BCC4097
CAS No.:943962-47-8
- Ophiopogoside A
Catalog No.:BCC8346
CAS No.:943914-99-6
- Sebiferenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4495
CAS No.:94390-09-7
- Bacopaside X
Catalog No.:BCC8126
CAS No.:94443-88-6
- Syzalterin
Catalog No.:BCN3969
CAS No.:94451-48-6
- Cromakalim
Catalog No.:BCC7038
CAS No.:94470-67-4
- Lck inhibitor 2
Catalog No.:BCC1690
CAS No.:944795-06-6
- Rhuscholide A
Catalog No.:BCN4498
CAS No.:944804-58-4
- Isodaphnoretin B
Catalog No.:BCN6913
CAS No.:944824-29-7
- Decernotinib(VX-509)
Catalog No.:BCC6456
CAS No.:944842-54-0
- Angelic anhydride
Catalog No.:BCN3411
CAS No.:94487-74-8
- 2'-Acetylacteoside
Catalog No.:BCN3409
CAS No.:94492-24-7
- Tamibarotene
Catalog No.:BCC1983
CAS No.:94497-51-5
- CYM 5541
Catalog No.:BCC6321
CAS No.:945128-26-7
- 7-Prenyljacareubin
Catalog No.:BCN7353
CAS No.:94513-60-7
Phase II study of the PI3K inhibitor BKM120 in patients with advanced or recurrent endometrial carcinoma: a stratified type I-type II study from the GINECO group.[Pubmed:28072765]
Br J Cancer. 2017 Jan;116(3):303-309.
Backround:Patients with metastatic endometrial carcinoma have a poor prognosis and PIK3CA mutations and amplifications are common in these cancers. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of the pure PI3K inhibitor BKM120 in advanced or recurrent endometrial carcinoma. METHODS: This phase II, multicentre, single-arm, double strata (histological low grade (LG) or high grade (HG)) open-label study enrolled patients with histologically confirmed advanced or recurrent endometrial carcinoma who had received not more than one prior chemotherapy regimen. Patients received initially BKM120 100 mg tablets once daily. Primary end points were proportion of patients free of progression at 2 months (HG strata) or at 3 months (LG strata), objective response rate (ORR), and safety. RESULTS: A total of 40 patients were enrolled, of whom 16 patients had received BKM120 at 100 mg. Because of high toxicities (cutaneous rash (54%), depressive events (47%), and anxiety (40%), the IDMC has proposed to stop recruitment at 100 mg and to continue the clinical trial with a lower dose of 60 mg per day. In addition, 24 patients (median age 67 years old) were newly enrolled (14 in the LG strata and 10 in the HG strata). Rate of nonprogression at 2 months in the HG strata was 70% and at 3 months was 60% in the LG strata. Median progression-free survival (PFS) for all patients is 4.5 months (CI 95% 2.8-6.1), and the median PFS for LG strata is 8.3 months compared with 3.8 months for the HG strata. No response was reported. At 60 mg per day, the most commonly reported treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were hyperglycaemia (58%), cognitive (31%), digestive (28%), hepatic liver functions (26%), and rash (23%). The most commonly reported treatment-related grade 3 AEs were HTA (17%), hyperglycaemia (17%), and increased alanine aminotransferase (24%). Five patients (21%) stopped BKM120 for toxicity. CONCLUSIONS: The BKM120 was associated with an unfavourable safety profile and minimal antitumour activity in monotherapy in advanced or recurrent endometrial carcinoma. The clinical trial was stopped before end of recruitment for toxicity.
Phase Ib dose-finding study of abiraterone acetate plus buparlisib (BKM120) or dactolisib (BEZ235) in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer.[Pubmed:28282611]
Eur J Cancer. 2017 May;76:36-44.
BACKGROUND: The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) signalling axis and androgen receptor (AR) pathways exhibit reciprocal feedback regulation in phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN)-deficient metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) in preclinical models. This phase Ib study evaluated the pan-PI3K inhibitor buparlisib (BKM120) and the dual pan-PI3K/ mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor dactolisib (BEZ235) in combination with abiraterone acetate (AA) in patients with CRPC. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Patients with CRPC who had progressed on AA therapy received escalating doses of either buparlisib or dactolisib, along with fixed doses of AA (1000 mg once daily (qd)) and prednisone (5 mg twice daily (bid)). The primary objective was to define the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and/or the recommended dose for expansion (RDE) of either buparlisib or dactolisib in combination with AA. Secondary objectives included safety, antitumour activity (Prostate Cancer Working Group 2 (PCWG2) criteria; 30% of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) decline at >/=week 12) and pharmacokinetic (PK) profile. RESULTS: In buparlisib + AA arm, 25 patients received buparlisib + AA (median age, 67 years; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) of 0/1/2 for 7/17/1 patients, respectively). At 100 mg qd; two patients experienced dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) (grade 3 hyperglycaemia; grade 2 asthenia), and this was the maximum buparlisib dose explored. Buparlisib + AA showed a 26% lower median area under the curve from time zero to 24 degrees h (AUC0-24) and 48% lower median maximum serum concentration (Cmax) versus the single-agent buparlisib assessed in first-in-human study. No objective response and few PSA decreases were reported. In dactolisib + AA arm, 18 patients (median age, 71 years; ECOG PS of 0/1 for 6/12 patients, respectively) received dactolisib + AA at the first dose level (200 mg bid). Five patients had 9 DLTs (grades 2&3 stomatitis; grade 3 hyperglycaemia; grades 2& 3 diarrhoea; grades 1& 2 pyrexia, grade 2 vomiting, and grade 2 chills). CONCLUSIONS: Based on the assessment of available pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy data, no further study is planned for either buparlisib or dactolisib in combination with AA in CRPC.
In Vitro and In Vivo Synergistic Antitumor Activity of the Combination of BKM120 and Erlotinib in Head and Neck Cancer: Mechanism of Apoptosis and Resistance.[Pubmed:28119490]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Apr;16(4):729-738.
We previously reported that the EGFR-targeted inhibitor erlotinib induces G1 arrest of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN) cell lines without inducing significant apoptosis. Large-scale genomic studies suggest that >50% of SCCHN cases have activation of PI3K pathways. This study investigated whether cotargeting of EGFR and PI3K has synergistic antitumor effects and apoptosis induction. We examined growth suppression, apoptosis, and signaling pathway modulation resulting from single and combined targeting of EGFR and PI3K with erlotinib and BKM120, respectively, in a panel of SCCHN cell lines and a xenograft model of SCCHN. In a panel of 12 cell lines, single targeting of EGFR with erlotinib or PI3K with BKM120 suppressed cellular growth without inducing significant apoptosis. Cotargeting of EGFR and PI3K synergistically inhibited SCCHN cell line and xenograft tumor growth, but induced variable apoptosis; some lines were highly sensitive, others were resistant. Mechanistic studies revealed that the combination inhibited both axes of the mTORC1 (S6 and 4EBP1) pathway in apoptosis-sensitive cell lines along with translational inhibition of Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1, but failed to inhibit p-4EBP1, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1 in an apoptosis-resistant cell line. siRNA-mediated knockdown of eIF4E inhibited Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 and sensitized this cell line to apoptosis. Our results strongly suggest that cotargeting of EGFR and PI3K is synergistic and induces apoptosis of SCCHN cell lines by inhibiting both axes of the AKT-mTOR pathway and translational regulation of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. These findings may guide the development of clinical trials using this combination of agents. Mol Cancer Ther; 16(4); 729-38. (c)2017 AACR.
A phase 1b dose expansion study of the pan-class I PI3K inhibitor buparlisib (BKM120) plus carboplatin and paclitaxel in PTEN deficient tumors and with dose intensified carboplatin and paclitaxel.[Pubmed:28281183]
Invest New Drugs. 2017 Dec;35(6):742-750.
Purpose We previously reported the phase I dose escalation study of buparlisib, a pan-class 1A PI3K inhibitor, combined with platinum/taxane-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced solid tumors. The combination was well tolerated and promising preliminary efficacy was observed in PTEN deficient tumors. This phase I dose expansion study now evaluates buparlisib plus high dose carboplatin and paclitaxel in unselected patients with advanced solid tumors and buparlisib plus standard dose carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with PTEN deficient tumors (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT01297452). Methods There were two expansion cohorts: Cohort A received continuous buparlisib (100 mg/daily) orally plus high dose carboplatin AUC 6 and paclitaxel 200 mg/m2; Cohort B treated patients with PTEN deficient tumors only and they received the recommended phase II dose (RP2D) of continuous buparlisib (100 mg/daily) orally plus standard dose carboplatin AUC 5 and paclitaxel 175 mg/m2. Both cohorts received chemotherapy intravenously on day 1 of the 21-day cycle with pegfilgrastim support. Primary endpoint in Cohort A was to evaluate the safety and tolerability of chemotherapy dose intensification with buparlisib and in Cohort B was to describe preliminary efficacy of the combination among patients with tumors harboring a PTEN mutation or homozygous deletion. Results 14 subjects were enrolled, 7 in Cohort A and 7 in Cohort B. Dose reductions were required in 5 (71%) and 3 (43%) patients, in cohort A and B respectively. Grade 3 adverse events in Cohort A included lymphopenia (n = 5 [71%]), hyperglycemia (n = 2, [29%]), diarrhea (n = 2, [29%]) and rash (n = 2, [29%]) and in cohort B included lymphopenia (n = 5 [71%]), hyperglycemia (n = 4 [57%]) and neutropenia (n = 2 [29%]. The mean number of cycles on protocol was 6. The overall objective response rate was 14% (2 /14). No objective responses were observed in the PTEN deficient cohort. Four out of 6 patients with stable disease (SD) had SD or better for >/=6 cycles, 2 of which had PTEN deficient tumors. Conclusion The addition of buparlisib to high dose carboplatin and paclitaxel was not tolerable. The combination did not reveal significant clinical activity amongst a small and heterogenous group of PTEN deficient tumors.


