AG-14361Potent PARP1 inhibitor CAS# 328543-09-5 |
- MK-4827 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4173
CAS No.:1038915-64-8
- MK-4827 tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC4174
CAS No.:1038915-73-9
- EB 47
Catalog No.:BCC2452
CAS No.:1190332-25-2
- Iniparib (BSI-201)
Catalog No.:BCC2208
CAS No.:160003-66-7
- WIKI4
Catalog No.:BCC2455
CAS No.:838818-26-1
- ABT-888 (Veliparib)
Catalog No.:BCC1267
CAS No.:912444-00-9
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 328543-09-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9840076 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H20N4O | M.Wt | 320.39 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | AG14361,AG 14361 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 25 mg/mL (78.03 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
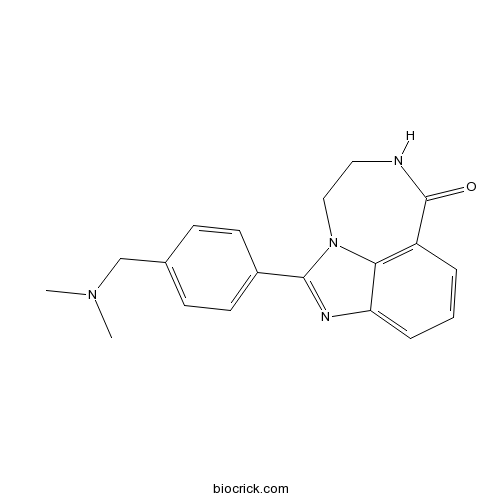
| SMILES | CN(C)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=NC3=CC=CC4=C3N2CCNC4=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SEKJSSBJKFLZIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H20N4O/c1-22(2)12-13-6-8-14(9-7-13)18-21-16-5-3-4-15-17(16)23(18)11-10-20-19(15)24/h3-9H,10-12H2,1-2H3,(H,20,24) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AG14361 is a potent inhibitor of PARP1 with Ki of <5 nM. | |||||
| Targets | PARP1 | |||||
| IC50 | 5 nM (Ki) | |||||

AG-14361 Dilution Calculator

AG-14361 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1212 mL | 15.606 mL | 31.212 mL | 62.4239 mL | 78.0299 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6242 mL | 3.1212 mL | 6.2424 mL | 12.4848 mL | 15.606 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3121 mL | 1.5606 mL | 3.1212 mL | 6.2424 mL | 7.803 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0624 mL | 0.3121 mL | 0.6242 mL | 1.2485 mL | 1.5606 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0312 mL | 0.1561 mL | 0.3121 mL | 0.6242 mL | 0.7803 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AG-14361 is a selective inhibitor of PARP-1 with Ki50 value <5 nM [1].
PARP1 is a member of PRAP family and plays an important role in many cellular processes, such as DNA repair, programmed cell death. It has been revealed that PARP1 is abnormally expressed in a variety of cancers and many PARP inhibitors have been developed as the anti-tumor drugs [1] [2] [3, 4].
AG-14361 is a potent PARP-1 inhibitor. When exposed HR and BRCA2-defective cells and parental cells to AG-14361, HR-defective cells were hypersensitive to the AG-14361 even at non-cytotoxic concentrations and lacking BRCA2 made the cells more sensitive to AG-14361 [5]. In human K562 cells, AG14361 treatment for 16 hours resulted in significant (~2-fold) potentiation of camptothecin-induced growth inhibition (GI50, 16 hours, camptothecin + AG14361 2.4 ± 0.1 nmol/L), cytotoxicity (LC50, camptothecin + AG14361 2.77 ± 0.55 nmol/L) and DNA single-strand breaks via inhibiting PARP-1 [1]. When tested with MMR-proficient (HCT-Ch3, A2780, and CP70-ch3) and MMR-deficient (HCT116, CP70, and CP70-ch2) cells, MMR-proficient cells were more sensitivity to temozolomide compared with MMR-deficient cells after exposed to AG-14361 which inhibited PARP1 activity [2].
In mouse model xenografted with BRCA2-deficient and BRCA-2 proficient tumor cells, BRCA2 deficiency group had more response even completely regressed tumor compared with BRCA-2 proficient group when treated with AG-14361 [5].
References:
[1]. Smith, L.M., et al., The novel poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase inhibitor, AG14361, sensitizes cells to topoisomerase I poisons by increasing the persistence of DNA strand breaks. Clin Cancer Res, 2005. 11(23): p. 8449-57.
[2]. Curtin, N.J., et al., Novel poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor, AG14361, restores sensitivity to temozolomide in mismatch repair-deficient cells. Clin Cancer Res, 2004. 10(3): p. 881-9.
[3]. Calabrese, C.R., et al., Anticancer chemosensitization and radiosensitization by the novel poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor AG14361. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2004. 96(1): p. 56-67.
[4]. Veuger, S.J., et al., Radiosensitization and DNA repair inhibition by the combined use of novel inhibitors of DNA-dependent protein kinase and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Cancer Res, 2003. 63(18): p. 6008-15.
[5]. Kyle, S., et al., Exploiting the Achilles heel of cancer: the therapeutic potential of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors in BRCA2-defective cancer. Br J Radiol, 2008. 81 Spec No 1: p. S6-11.
- GlyH-101
Catalog No.:BCC4104
CAS No.:328541-79-3
- Lannaconitine
Catalog No.:BCN2504
CAS No.:32854-75-4
- (H-Cys-OMe)2.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2916
CAS No.:32854-09-4
- Coniferyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN4651
CAS No.:32811-40-8
- Phortress
Catalog No.:BCC3901
CAS No.:328087-38-3
- Ceranib 1
Catalog No.:BCC6186
CAS No.:328076-61-5
- H-D-Leu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2975
CAS No.:328-38-1
- Nomifensine
Catalog No.:BCC7226
CAS No.:32795-47-4
- Panaxatriol
Catalog No.:BCN1081
CAS No.:32791-84-7
- Labetalol HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5489
CAS No.:32780-64-6
- Protopanaxatriol
Catalog No.:BCC9245
CAS No.:32773-56-1
- Macrocarpal O
Catalog No.:BCN7371
CAS No.:327622-65-1
- Benzylamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN6908
CAS No.:3287-99-8
- Cajanin
Catalog No.:BCN5249
CAS No.:32884-36-9
- Lasiodiplodin
Catalog No.:BCN4770
CAS No.:32885-81-7
- De-O-methyllasiodiplodin
Catalog No.:BCN7187
CAS No.:32885-82-8
- Tildipirosin
Catalog No.:BCC5478
CAS No.:328898-40-4
- pep2-SVKI
Catalog No.:BCC5784
CAS No.:328944-75-8
- C646
Catalog No.:BCC4546
CAS No.:328968-36-1
- 4E1RCat
Catalog No.:BCC5338
CAS No.:328998-25-0
- Norepinephrine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5133
CAS No.:329-56-6
- DL-Adrenaline
Catalog No.:BCC4318
CAS No.:329-65-7
- PMSF
Catalog No.:BCC1229
CAS No.:329-98-6
- Withanolide A
Catalog No.:BCN8010
CAS No.:32911-62-9
Ionizing radiation-induced NF-kappaB activation requires PARP-1 function to confer radioresistance.[Pubmed:19060926]
Oncogene. 2009 Feb 12;28(6):832-42.
Recent reports implicate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) in the activation of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB). We investigated the role of PARP-1 in the NF-kappaB signalling cascade induced by ionizing radiation (IR). AG14361, a potent PARP-1 inhibitor, was used in two breast cancer cell lines expressing different levels of constitutively activated NF-kappaB, as well as mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) proficient or deficient for PARP-1 or NF-kappaB p65. In the breast cancer cell lines, AG14361 had no effect on IR-induced degradation of IkappaBalpha or nuclear translocation of p50 or p65. However, AG14361 inhibited IR-induced NF-kappaB-dependent transcription of a luciferase reporter gene. Similarly, in PARP-1(-/-) MEFs, IR-induced nuclear translocation of p50 and p65 was normal, but kappaB binding and transcriptional activation did not occur. AG14361 sensitized both breast cancer cell lines to IR-induced cell killing, inhibited IR-induced XIAP expression and increased caspase-3 activity. However, AG14361 failed to increase IR-induced caspase activity when p65 was knocked down by siRNA. Consistent with this, AG14361 sensitized p65(+/+) but not p65(-/-) MEFs to IR. We conclude that PARP-1 activity is essential in the upstream regulation of IR-induced NF-kappaB activation. These data indicate that potentiation of IR-induced cytotoxicity by AG14361 is mediated solely by inhibition of NF-kappaB activation.
Effects of novel inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and the DNA-dependent protein kinase on enzyme activities and DNA repair.[Pubmed:15286704]
Oncogene. 2004 Sep 23;23(44):7322-9.
DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) participate in nonhomologous end joining and base excision repair, respectively, and are key determinants of radio- and chemo-resistance. Both PARP-1 and DNA-PK have been identified as therapeutic targets for anticancer drug development. Here we investigate the effects of specific inhibitors on enzyme activities and DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair. The enzyme activities were investigated using purified enzymes and in permeabilized cells. Inhibition, or loss of activity, was compared using potent inhibitors of DNA-PK (NU7026) and PARP-1 (AG14361), and cell lines proficient or deficient for DNA-PK or PARP-1. Inactive DNA-PK suppressed the activity of PARP-1 and vice versa. This was not the consequence of simple substrate competition, since DNA ends were provided in excess. The inhibitory effect of DNA-PK on PARP activity was confirmed in permeabilized cells. Both inhibitors prevented ionizing radiation-induced DSB repair, but only AG14361 prevented single-strand break repair. An increase in DSB levels caused by inhibition of PARP-1 was shown to be caused by a decrease in DSB repair, and not by the formation of additional DSBs. These data point to combined inhibition of PARP-1 and DNA-PK as a powerful strategy for tumor radiosensitization.
Drug repurposing screen identifies lestaurtinib amplifies the ability of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 inhibitor AG14361 to kill breast cancer associated gene-1 mutant and wild type breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:24962108]
Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Jun 24;16(3):R67.
INTRODUCTION: Breast cancer is a devastating disease that results in approximately 40,000 deaths each year in the USA. Current drug screening and chemopreventatitive methods are suboptimal, due in part to the poor specificity of compounds for cancer cells. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) inhibitor (PARPi)-mediated therapy is a promising approach for familial breast cancers caused by mutations of breast cancer-associated gene-1 and -2 (BRCA1/2), yet drug resistance frequently occurs during the treatment. Moreover, PARPis exhibit very little effect on cancers that are proficient for DNA repair and clinical efficacy for PARPis as single-agent therapies has yet to be illustrated. METHODS: Using a quantitative high-throughput screening approach, we screened a library containing 2,816 drugs, most of which are approved for human or animal use by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or other countries, to identify compounds that sensitize breast cancer cells to PARPi. After initial screening, we performed further cellular and molecular analysis on lestaurtinib, which is an orally bioavailable multikinase inhibitor and has been used in clinical trials for myeloproliferative disorders and acute myelogenous leukemia. RESULTS: Our study indicated that lestaurtinib is highly potent against breast cancers as a mono-treatment agent. It also strongly enhanced the activity of the potent PARPi AG14361 on breast cancer cell growth both in vitro and in vivo conditions. The inhibition of cancer growth is measured by increased apoptosis and reduced cell proliferation. Consistent with this, the treatment results in activation of caspase 3/7, and accumulation of cells in the G2 phase of the cell cycle, irrespective of their BRCA1 status. Finally, we demonstrated that AG14361 inhibits NF-kappaB signaling, which is further enhanced by lestaurtinib treatment. CONCLUSIONS: Lestaurtinib amplifies the ability of the PARP1 inhibitor AG14361 to kill BRCA1 mutant and wild-type breast cancer cells, at least in part, by inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling. Each of these drugs has been approved for clinical trials for several different cancers, thus, their combination treatment should be applicable for a breast cancer trial in the future.
Exploiting the Achilles heel of cancer: the therapeutic potential of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors in BRCA2-defective cancer.[Pubmed:18820000]
Br J Radiol. 2008 Oct;81 Spec No 1:S6-11.
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) facilitates DNA single-strand break-base excision repair to maintain genomic stability. Inhibition or loss of PARP activity leads to a recombinogenic phenotype characterized by increased sister chromatid exchange. Deficiency in homologous recombination (HR) owing to loss of BRCA1 or BRCA2 is associated with hereditary cancers of the breast, ovary, pancreas and prostate. We investigated the therapeutic potential of PARP inhibitors in HR and BRCA2-defective cells. We exposed cells defective in the HR component XRCC3 (irs1SF) and BRCA2 (V-C8) and their parental (AA8, V79) or deficiency corrected (CXR3, V-C8+B2) cells to the PARP inhibitors NU1025 and AG14361. Mice bearing BRCA2-deficient and BRCA2-proficient tumours were treated with AG14361. All HR-defective cells were hypersensitive to normally non-cytotoxic concentrations of PARP inhibitors. Cells lacking BRCA2 were 20 times more sensitive to PARP inhibitor-induced cytotoxicity. Three out of five BRCA2-defective xenografts responded to the potent PARP inhibitor, AG14361, and one tumour regressed completely, compared with non-responses in the BRCA2-proficient tumours treated with AG14361 or any mice treated with vehicle control. Untreated PARP-1(-/-) mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) accumulated more DNA double-strand breaks than did PARP-1(+/+) MEFs. We believe the underlying cytotoxic mechanism is due to PARP inhibitor-mediated suppression of repair of DNA single-strand breaks, which are converted to DNA double-strand breaks at replication. These replication-associated double-strand breaks, which are normally repaired by HR, become cytotoxic in cells defective in HR. Using a DNA repair inhibitor alone to selectively kill a tumour represents an exciting new concept in cancer therapy.


