10-DEBC hydrochlorideAkt inhibitor CAS# 925681-41-0 |
- Docetaxel
Catalog No.:BCN5342
CAS No.:114977-28-5
- ABT-751 (E7010)
Catalog No.:BCC1085
CAS No.:141430-65-1
- Epothilone A
Catalog No.:BCC1091
CAS No.:152044-53-6
- Honokiol
Catalog No.:BCN1001
CAS No.:35354-74-6
- Altretamine
Catalog No.:BCC1216
CAS No.:645-05-6
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 925681-41-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16760284 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H26Cl2N2O | M.Wt | 381.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
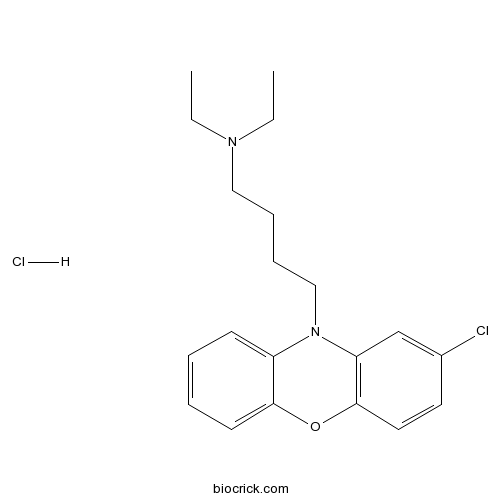
| Chemical Name | 4-(2-chlorophenoxazin-10-yl)-N,N-diethylbutan-1-amine;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CCN(CC)CCCCN1C2=CC=CC=C2OC3=C1C=C(C=C3)Cl.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SVKSJUIYYCQZEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H25ClN2O.ClH/c1-3-22(4-2)13-7-8-14-23-17-9-5-6-10-19(17)24-20-12-11-16(21)15-18(20)23;/h5-6,9-12,15H,3-4,7-8,13-14H2,1-2H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective inhibitor of Akt/PKB. Inhibits IGF-1-stimulated phosphorylation and activation of Akt (complete inhibition at 2.5 μM), suppressing downstream activation of mTOR, p70 S6 kinase and S6 ribosomal protein. Shows no activity at PDK1, SGK1 or PI 3-kinase. Inhibits cell growth (IC50 ~ 2-6 μM) and induces apoptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells. |

10-DEBC hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

10-DEBC hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6223 mL | 13.1117 mL | 26.2233 mL | 52.4466 mL | 65.5583 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5245 mL | 2.6223 mL | 5.2447 mL | 10.4893 mL | 13.1117 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2622 mL | 1.3112 mL | 2.6223 mL | 5.2447 mL | 6.5558 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0524 mL | 0.2622 mL | 0.5245 mL | 1.0489 mL | 1.3112 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0262 mL | 0.1311 mL | 0.2622 mL | 0.5245 mL | 0.6556 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
10-DEBC hydrochloride is a selective inhibitor of Akt (or termed PKB) [1], with an IC50 value of approximate 48 μM [2].
Akt is a type of serine/threonine kinase. It phosphorylates and inactivates components in the apoptotic machinery, including Caspase 9 and BAD. Akt phosphorylates and inhibits a Forkhead transcription factor, and hence promotes cell survival [3].
As demonstrated by LDH and MTT tests, 10-DEBC dihydrochloride at 10 μM did not affect cell viability when it was applied alone. 10-DEBC dihydrochloride at this concentration in cisplatin-treated U251 cells abrogated the cytoprotective effect of metformin. 10-DEBC dihydrochloride showed neutralization effect on the antiapoptotic activity of metformin, increasing the cell membrane phosphatidylserine exposure and DNA fragmentation to the levels observed with cisplatin alone. In U251 cells, 10-DEBC dihydrochloride significantly induced the production of reactive oxygen species. In cisplatin-treated cells, 10-DEBC dihydrochloride consequently reduced the antioxidative effect of metformin [1].
Studies in effects of 10-DEBC hydrochloride on BAT explants incubated with phentolamine were carried out. Without any effect on total Akt protein, 10-DEBC hydrochloride inhibited the phosphorylation of Akt Ser473 by ~40%. In WT explants, the 10-DEBC hydrochloride alone had no effect on the phosphorylation of Ser485/491 of AMPK, and did not affect the phentolamine effect. However, in β-AR KO explants, 10-DEBC hydrochloride blunted the AMPK Ser485/491 phosphorylation increased by phentolamine [4].
References:
[1]. Janjetovic K, Vucicevic L, Misirkic M, et al. Metformin reduces cisplatin-mediated apoptotic death of cancer cells through AMPK-independent activation of Akt. European journal of pharmacology, 2011, 651(1): 41-50.
[2]. De Abreu LA, Calixto C, Waltero CF, et al. The conserved role of the AKT/GSK3 axis in cell survival and glycogen metabolism in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus embryo tick cell line BME26. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2013, 1830(3): 2574-2582.
[3]. Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, et al. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. cell, 1999, 96(6): 857-868.
[4]. Pulinilkunnil T, He H, Kong D, et al. Adrenergic regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase in brown adipose tissue in vivo. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2011, 286(11): 8798-8809.
- Jingzhaotoxin III
Catalog No.:BCC6327
CAS No.:925463-91-8
- Viscidulin I
Catalog No.:BCN4465
CAS No.:92519-95-4
- Viscidulin II
Catalog No.:BCN3187
CAS No.:92519-93-2
- Viscidulin III
Catalog No.:BCN4464
CAS No.:92519-91-0
- 21-Deoxyneridienone B
Catalog No.:BCN4463
CAS No.:924910-83-8
- Rupesin E
Catalog No.:BCN7009
CAS No.:924901-58-6
- 4,5-Epoxyartemisinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4462
CAS No.:92466-31-4
- AZD-5597
Catalog No.:BCC6453
CAS No.:924641-59-8
- T 5601640
Catalog No.:BCC5617
CAS No.:924473-59-6
- AdipoRon
Catalog No.:BCC4756
CAS No.:924416-43-3
- HBX 41108
Catalog No.:BCC6137
CAS No.:924296-39-9
- DUBs-IN-2
Catalog No.:BCC5257
CAS No.:924296-19-5
- KU-60019
Catalog No.:BCC3699
CAS No.:925701-49-1
- Acitretin sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4299
CAS No.:925701-88-8
- 3-Isomangostin hydrate formate
Catalog No.:BCN4466
CAS No.:925705-36-8
- TG100713
Catalog No.:BCC4985
CAS No.:925705-73-3
- Secaubryenol
Catalog No.:BCN4467
CAS No.:925932-08-7
- Secaubrytriol
Catalog No.:BCN4468
CAS No.:925932-10-1
- Dayecrystal A
Catalog No.:BCN4859
CAS No.:926010-24-4
- AMTB hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7834
CAS No.:926023-82-7
- Radotinib(IY-5511)
Catalog No.:BCC6398
CAS No.:926037-48-1
- O-Demethylforbexanthone
Catalog No.:BCN4469
CAS No.:92609-77-3
- Milnacipran
Catalog No.:BCC4194
CAS No.:92623-85-3
- BG45
Catalog No.:BCC6469
CAS No.:926259-99-6
Unusual 4-arsonoanilinium cationic species in the hydrochloride salt of (4-aminophenyl)arsonic acid and formed in the reaction of the acid with copper(II) sulfate, copper(II) chloride and cadmium chloride.[Pubmed:28378716]
Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2017 Apr 1;73(Pt 4):325-330.
Structures having the unusual protonated 4-arsonoanilinium species, namely in the hydrochloride salt, C6H9AsNO3(+).Cl(-), (I), and the complex salts formed from the reaction of (4-aminophenyl)arsonic acid (p-arsanilic acid) with copper(II) sulfate, i.e. hexaaquacopper(II) bis(4-arsonoanilinium) disulfate dihydrate, (C6H9AsNO3)2[Cu(H2O)6](SO4)2.2H2O, (II), with copper(II) chloride, i.e. poly[bis(4-arsonoanilinium) [tetra-mu-chlorido-cuprate(II)]], {(C6H9AsNO3)2[CuCl4]}n, (III), and with cadmium chloride, i.e. poly[bis(4-arsonoanilinium) [tetra-mu-chlorido-cadmate(II)]], {(C6H9AsNO3)2[CdCl4]}n, (IV), have been determined. In (II), the two 4-arsonoanilinium cations are accompanied by [Cu(H2O)6](2+) cations with sulfate anions. In the isotypic complex salts (III) and (IV), they act as counter-cations to the {[CuCl4](2-)}n or {[CdCl4](2-)}n anionic polymer sheets, respectively. In (II), the [Cu(H2O)6](2+) ion sits on a crystallographic centre of symmetry and displays a slightly distorted octahedral coordination geometry. The asymmetric unit for (II) contains, in addition to half the [Cu(H2O)6](2+) ion, one 4-arsonoanilinium cation, a sulfate dianion and a solvent water molecule. Extensive O-H...O and N-H...O hydrogen bonds link all the species, giving an overall three-dimensional structure. In (III), four of the chloride ligands are related by inversion [Cu-Cl = 2.2826 (8) and 2.2990 (9) A], with the other two sites of the tetragonally distorted octahedral CuCl6 unit occupied by symmetry-generated Cl-atom donors [Cu-Cl = 2.9833 (9) A], forming a two-dimensional coordination polymer network substructure lying parallel to (001). In the crystal, the polymer layers are linked across [001] by a number of bridging hydrogen bonds involving N-H...Cl interactions from head-to-head-linked As-O-H...O 4-arsonoanilinium cations. A three-dimensional network structure is formed. Cd(II) compound (IV) is isotypic with Cu(II) complex (III), but with the central CdCl6 complex repeat unit having a more regular M-Cl bond-length range [2.5232 (12)-2.6931 (10) A] compared to that in (III). This series of compounds represents the first reported crystal structures having the protonated 4-arsonoanilinium species.
Lens opacities in children using methylphenidate hydrochloride.[Pubmed:28376677]
Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2017 Dec;36(4):362-365.
PURPOSE: To assess clinical findings of eye examination in children having attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) administered with methylphenidate hydrochloride. METHODS: Fifty-seven consecutive patients diagnosed of ADHD and administered with oral methylphenidate hydrochloride treatment for at least one year were involved in this study (Group 1). Sixty healthy subjects (Group 2) having demographic features similar to group 1 were involved as a control group. All patients underwent detailed ophthalmological examination. RESULTS: One hundred and seventeen consecutive subjects with a mean age of 11.2 +/- 2.4 years (7-18 years) were enrolled. Fifty-seven consecutive patient (32 males, 25 females) under oral methylphenidate hydrochloride treatment (Group 1) and 60 healthy control subjects (30 males, 30 females) (Group 2)) were recruited for this prospective study. The mean methylphenidate hydrochloride dosage was 0.9 +/- 0.1 mg/kg/day and the mean duration of methylphenidate hydrochloride usage was for 2.73 +/- 0.73 years (1-7 years). High intraocular pressure was not observed in any of the patients in our study. We detected lens opacities in five eyes of five patients in group 1 (p = 0.019). The patient with the highest degree of cataract formation had been using MPH for 84 months and this patient's cataract score was P4. CONCLUSION: Long-term use of methylphenidate may cause lens opacities. In particular, patients who have been using methylphenidate for more than two years should go for regular eye examination.
Biophysical Study on the Interaction between Eperisone Hydrochloride and Human Serum Albumin Using Spectroscopic, Calorimetric, and Molecular Docking Analyses.[Pubmed:28380300]
Mol Pharm. 2017 May 1;14(5):1656-1665.
Eperisone hydrochloride (EH) is widely used as a muscle relaxant for patients with muscular contracture, low back pain, or spasticity. Human serum albumin (HSA) is a highly soluble negatively charged, endogenous and abundant plasma protein ascribed with the ligand binding and transport properties. The current study was undertaken to explore the interaction between EH and the serum transport protein, HSA. Study of the interaction between HSA and EH was carried by UV-vis, fluorescence quenching, circular dichroism (CD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, Forster's resonance energy transfer, isothermal titration calorimetry and differential scanning calorimetry. Tryptophan fluorescence intensity of HSA was strongly quenched by EH. The binding constants (Kb) were obtained by fluorescence quenching, and results show that the HSA-EH interaction revealed a static mode of quenching with binding constant Kb approximately 10(4) reflecting high affinity of EH for HSA. The negative DeltaG degrees value for binding indicated that HSA-EH interaction was a spontaneous process. Thermodynamic analysis shows HSA-EH complex formation occurs primarily due to hydrophobic interactions, and hydrogen bonds were facilitated at the binding of EH. EH binding induces alpha-helix of HSA as obtained by far-UV CD and FTIR spectroscopy. In addition, the distance between EH (acceptor) and Trp residue of HSA (donor) was calculated 2.18 nm using Forster's resonance energy transfer theory. Furthermore, molecular docking results revealed EH binds with HSA, and binding site was positioned in Sudlow Site I of HSA (subdomain IIA). This work provides a useful experimental strategy for studying the interaction of myorelaxant with HSA, helping to understand the activity and mechanism of drug binding.
Fabrication yields of serially harvested calf-fed Holstein steers fed zilpaterol hydrochloride.[Pubmed:28380524]
J Anim Sci. 2017 Mar;95(3):1209-1218.
Holstein steers ( = 110) were fed zilpaterol hydrochloride (ZH) for 0 or 20 d before slaughter during a 280-d serial harvest study. Cattle were harvested every 28 d beginning at 254 d on feed (DOF) and concluding at 534 DOF. After slaughter, carcasses were chilled for 48 h and then fabricated into boneless closely trimmed or denuded subprimals, lean trim, trimmable fat, and bone. Inclusion of ZH increased cold side weight (CSW) by 10.3 kg ( < 0.01; 212.7 vs. 202.4 kg [SEM 1.96]) and saleable yield by 10.4 kg ( < 0.01; 131.9 vs. 121.5 kg [SEM 1.16]) in calf-fed Holstein steer carcasses. Additionally, saleable yield as a percentage of CSW increased (
Synthesis and chemical characterization of N-substituted phenoxazines directed toward reversing vinca alkaloid resistance in multidrug-resistant cancer cells.[Pubmed:1527786]
J Med Chem. 1992 Sep 4;35(18):3358-64.
A series of 21 N-substituted phenoxazines has been synthesized in an effort to find more specific and less toxic modulators of multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer chemotherapy. Thus, N-(omega-chloroalkyl)- and N-(chloroacyl)phenoxazines were found to undergo iodide-catalyzed nucleophilic substitution on reaction with various secondary amines, including N,N-diethylamine, N,N-diethanolamine, morpholine, piperidine, pyrrolidine and (beta-hydroxyethyl)piperazine. Products were characterized by UV, IR, 1H-, and 13C-NMR, mass spectral data, and elemental analyses. All of the compounds were examined for cytotoxicity and for their ability to increase the accumulation of the vinca alkaloids, vincristine (VCR) and vinblastine (VLB) in multidrug-resistant GC3/Cl (human colon adenocarcinoma) and KBChR-8-5 (HeLa variant) cell lines. Compounds were compared to the standard modulator verapamil (VRP). Substitutions on the phenoxazine ring at position 10 were associated with an increase in antiproliferative and anti-MDR activities. Modification of the length of the alkyl bridge and the type of amino side chain also influenced the potency of these effects. From among the compounds examined, 10 derivatives were found to increase the accumulation of VCR and VLB in GC3/Cl and KBChR-8-5 cells relative to the effect of VRP, suggesting that with the exception of pyrrolidinyl, the tertiary amine attachments to the phenoxazine nucleus linked through a three- or four-carbon alkyl chain resulted in enhanced anti-MDR activity. On the basis of their 50% growth inhibitory (IC50) values, five of the ten compounds, namely, 10-(3'-chloropropyl)phenoxazine, 10-[3'-[N-bis(hydroxyethyl)- amino]propyl]phenoxazine, 10-(3'-N-morpholinopropyl)phenoxazine, 10-(4'-N-morpholinobutyl)phenoxazine and 10-(N-piperidinoacetyl)phenoxazine were selected as relatively nontoxic chemosensitizers. These modulators, at nontoxic concentrations, potentiated the cytotoxicity of VCR and VLB in GC3/Cl and KBChR-8-5 cells. Further, two compounds 10-(3'-N-morpholinopropyl)phenoxazine, and the butyl derivative, enhanced accumulation of VLB in GC3/Cl, KBChR8-5 and highly resistant KB-V1 cells to a level significantly greater than the maximal level achieved with VRP. Additional experiments to understand the mechanism of action of these agents in modulating MDR are in progress.


