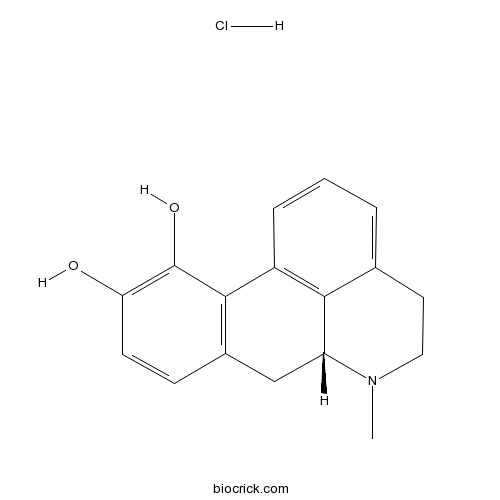
(R)-(-)-Apomorphine hydrochlorideDopamine agonist; non-subtype-selective CAS# 314-19-2 |
- Anguizole
Catalog No.:BCC1365
CAS No.:442666-98-0
- Asunaprevir (BMS-650032)
Catalog No.:BCC1374
CAS No.:630420-16-5
- Balapiravir
Catalog No.:BCC1396
CAS No.:690270-29-2
Quality Control & MSDS
Number of papers citing our products

Chemical structure

3D structure
| Cas No. | 314-19-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9410 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H18ClNO2 | M.Wt | 303.79 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in water and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | (6aR)-6-methyl-5,6,6a,7-tetrahydro-4H-dibenzo[de,g]quinoline-10,11-diol;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CN1CCC2=CC=CC3=C2C1CC4=C3C(=C(C=C4)O)O.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SKYZYDSNJIOXRL-BTQNPOSSSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H17NO2.ClH/c1-18-8-7-10-3-2-4-12-15(10)13(18)9-11-5-6-14(19)17(20)16(11)12;/h2-6,13,19-20H,7-9H2,1H3;1H/t13-;/m1./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Prototypical dopamine agonist (pKi values are 6.43, 7.08, 7.59, 8.36 and 7.83 for human recombinant D1, D2L, D3, D4 and D5 receptors respectively). Produces biphasic effects on locomotor activity, and displays anti-Parkinsonian and neuroprotective actions following systemic administration in vivo. |

(R)-(-)-Apomorphine hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

(R)-(-)-Apomorphine hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2917 mL | 16.4587 mL | 32.9175 mL | 65.835 mL | 82.2937 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6583 mL | 3.2917 mL | 6.5835 mL | 13.167 mL | 16.4587 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3292 mL | 1.6459 mL | 3.2917 mL | 6.5835 mL | 8.2294 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0658 mL | 0.3292 mL | 0.6583 mL | 1.3167 mL | 1.6459 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0329 mL | 0.1646 mL | 0.3292 mL | 0.6583 mL | 0.8229 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Evans Blue tetrasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6815
CAS No.:314-13-6
- VDM 11
Catalog No.:BCC7044
CAS No.:313998-81-1
- [cPP1-7,NPY19-23,Ala31,Aib32,Gln34] - hPancreatic Polypeptide
Catalog No.:BCC5750
CAS No.:313988-89-5
- PU 02
Catalog No.:BCC6265
CAS No.:313984-77-9
- o-3M3FBS
Catalog No.:BCC7210
CAS No.:313981-55-4
- FLI-06
Catalog No.:BCC5110
CAS No.:313967-18-9
- [Des-octanoyl]-Ghrelin (human)
Catalog No.:BCC7304
CAS No.:313951-59-6
- 13-Oxo-9,11-octadecadienoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8437
CAS No.:31385-09-8
- PD 118057
Catalog No.:BCC7499
CAS No.:313674-97-4
- Bombesin
Catalog No.:BCC5708
CAS No.:31362-50-2
- INH1
Catalog No.:BCC6040
CAS No.:313553-47-8
- T0070907
Catalog No.:BCC2261
CAS No.:313516-66-4
- BPTES
Catalog No.:BCC6506
CAS No.:314045-39-1
- IU1
Catalog No.:BCC2086
CAS No.:314245-33-5
- Isotachioside
Catalog No.:BCN5230
CAS No.:31427-08-4
- Nocodazole
Catalog No.:BCC3826
CAS No.:31430-18-9
- 4-Amino-3-nitrobenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8682
CAS No.:31431-19-3
- Mebendazole
Catalog No.:BCC9016
CAS No.:31431-39-7
- 6-Methoxysalicylic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC8288
CAS No.:3147-64-6
- Sunifiram
Catalog No.:BCC4167
CAS No.:314728-85-3
- Crotaline
Catalog No.:BCN4983
CAS No.:315-22-0
- Allopurinol
Catalog No.:BCC3720
CAS No.:315-30-0
- Testosterone enanthate
Catalog No.:BCC9169
CAS No.:315-37-7
- Acetylheliosupine
Catalog No.:BCN1981
CAS No.:31514-30-4
Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes.[Pubmed:12388666]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Nov;303(2):791-804.
Because little comparative information is available concerning receptor profiles of antiparkinson drugs, affinities of 14 agents were determined at diverse receptors implicated in the etiology and/or treatment of Parkinson's disease: human (h)D(1), hD(2S), hD(2L), hD(3), hD(4), and hD(5) receptors; human 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)(1A), h5-HT(1B), h5-HT(1D), h5-HT(2A), h5-HT(2B), and h5-HT(2C) receptors; halpha(1A)-, halpha(1B)-, halpha(1D)-, halpha(2A)-, halpha(2B)-, halpha(2C)-, rat alpha(2D)-, hbeta(1)-, and hbeta(2)-adrenoceptors (ARs); and native histamine(1) receptors. A correlation matrix (294 pK(i) values) demonstrated substantial "covariance". Correspondingly, principal components analysis revealed that axis 1, which accounted for 76% variance, was associated with the majority of receptor types: drugs displaying overall high versus modest affinities migrated at opposite extremities. Axis 2 (7% of variance) differentiated drugs with high affinity for hD(4) and H(1) receptors versus halpha(1)-AR subtypes. Five percent of variance was attributable to axis 3, which distinguished drugs with marked affinity for hbeta(1)- and hbeta(2)-ARs versus hD(5) and 5-HT(2A) receptors. Hierarchical (cluster) analysis of global homology generated a dendrogram differentiating two major groups possessing low versus high affinity, respectively, for multiple serotonergic and hD(5) receptors. Within the first group, quinpirole, quinerolane, ropinirole, and pramipexole interacted principally with hD(2), hD(3), and hD(4) receptors, whereas piribedil and talipexole recognized dopaminergic receptors and halpha(2)-ARs. Within the second group, lisuride and terguride manifested high affinities for all sites, with roxindole/bromocriptine, cabergoline/pergolide, and 6,7-dihydroxy-N,N-dimethyl-2-ammotetralin (TL99)/apomorphine comprising three additional subclusters of closely related ligands. In conclusion, an innovative multivariate analysis revealed marked heterogeneity in binding profiles of antiparkinson agents. Actions at sites other than hD(2) receptors likely participate in their (contrasting) functional profiles.
Apomorphine protects against MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in mice.[Pubmed:10435498]
Mov Disord. 1999 Jul;14(4):612-8.
R-apomorphine is a potent radical scavenger and iron chelator. The neuroprotective property of R-apomorphine, a dopamine D1-D2 receptor agonist, has been studied in the MPTP (N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) model of Parkinson's disease. Pretreatment with 5-10 mg/kg R-apomorphine administered subcutaneously in C57BL mice protects against MPTP (24 mg/kg administered intraperitoneally) induced loss of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons as indicated by striatal dopamine content, tyrosine hydroxylase content, and tyrosine hydroxylase activity. In vitro, R-apomorphine inhibited mice striatal MAO-A and MAO-B activities with IC50 values of 93 microM and 241 microM. It is suggested that the neuroprotective effect of R-apomorphine against MPTP neurotoxicity derives from its radical scavenging and MAO inhibitory actions and not from its agonistic activity because the mechanism of MPTP dopaminergic neurotoxicity involves the generation of oxygen radical species-induced oxidative stress.
Low doses of apomorphine suppress operant motor performance in rats.[Pubmed:8808141]
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1996 Feb;53(2):335-40.
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of low doses of apomorphine on motor performance. Six rats were rewarded with sugar water on a partial reinforcement schedule for pressing force-sensitive beams with a minimum force of 1 g. The kinetics of individual responses and the temporal characteristics of response sequences were measured; open field locomotor activity was also measured in a separate apparatus. Apomorphine (APO), amphetamine (AMP), and haloperidol (HAL) were administered systemically. It was found that low doses of APO (0.03 and 0.1 mg/kg, SC) produced weaker and longer beam presses. These decreases in response peak force resulted from decreases in the rate of rise of force. APO also caused disproportionate lengthening of beam release time. In addition, the low doses of APO increased the time intervals between consecutive components of response sequences. These low doses of APO are known to decrease dopaminergic tone. Hence, the observed pattern of motor dysfunctions produced by APO is similar to the bradykinesia seen in human Parkinson's disease.


